(Press-News.org) Washington, DC-- The cause of Earth's deepest earthquakes has been a mystery to science for more than a century, but a team of Carnegie scientists may have cracked the case.
New research published in AGU Advances provides evidence that fluids play a key role in deep-focus earthquakes--which occur between 300 and 700 kilometers below the planet's surface. The research team includes Carnegie scientists Steven Shirey, Lara Wagner, Peter van Keken, and Michael Walter, as well as the University of Alberta's Graham Pearson.
Most earthquakes occur close to the Earth's surface, down to about 70 kilometers. They happen when stress builds up at a fracture between two blocks of rock--known as a fault--causing them to suddenly slide past each other.
However, deeper into the Earth, the intense pressures create too much friction to allow this kind of sliding to occur and the high temperatures enhance the ability of rocks to deform to accommodate changing stresses. Though theoretically unexpected, scientists have been able to identify earthquakes that originate more than 300 kilometers below the surface since the 1920s.
"The big problem that seismologists have faced is how it's possible that we have these deep-focus earthquakes at all," said Wagner. "Once you get a few tens of kilometers down, it becomes incredibly difficult to explain how we are getting slip on a fault when the friction is so incredibly high."
Ongoing work over the past several decades has shown us that water plays a role in intermediate-depth earthquakes--those that occur between 70 and 300 kilometers below Earth's surface. In these instances, water is released from minerals, which weakens the rock around the fault and allows the blocks of rock to slip. However, scientists didn't think this phenomenon could explain deep-focus earthquakes, largely because it was believed that water and other fluid-creating compounds couldn't make it far enough down into the Earth's interior to provide a similar effect.
This thinking changed for the first time when Shirey and Wagner compared the depths of rare deep-Earth diamonds to the mysterious deep-focus earthquakes.
"Diamonds form in fluids" explained Shirey, "if diamonds are there, fluids are there."
The diamonds themselves indicated the presence of fluids, however, they also brought samples of the deep-Earth to the surface for the scientists to study. When diamonds form in the Earth's interior, they sometimes capture pieces of mineral from the surrounding rock. These minerals are called inclusions and they may make your jewelry less expensive, but they are invaluable to Earth scientists. They are one of the only ways scientists can study direct samples of our planet's deep interior.
The diamond's inclusions had the distinct chemical signature of similar materials found in oceanic crust. This means that the water and other materials weren't somehow created deep in the Earth's interior. Instead, they were carried down as part of a sinking oceanic plate.
Said Wagner: "The seismology community had moved away from the idea that there could be water that deep. But diamond petrologists like Steve were showing us samples and saying 'No, no, no. There's definitely water down here' So then we all had to get together to figure out how it got down there."
To test the idea, Wagner and van Keken built advanced computational models to simulate the temperatures of sinking slabs at much greater depths than had been attempted before. In addition to the modeling, Walter examined the stabilities of the water-bearing minerals to show that under the intense heat and pressures of the Earth's deep interior, they would, indeed, be capable of holding on to water in certain conditions. The team showed that even though warmer plates didn't hold water, the minerals in the cooler oceanic plates could theoretically carry water to the depths we associate with deep-focus earthquakes.
To solidify the study the team compared the simulations to real-life seismological data. They were able to show that the slabs that could theoretically carry water to these depths were also the ones experiencing the previously unexplained deep earthquakes.
This study is unusual in applying four different disciplines--geochemistry, seismology, geodynamics, and petrology--to the same question, all of which point to the same conclusion: water and other fluids are a key component of deep-focus earthquakes.
"The nature of deep earthquakes is one of the big questions in geoscience," said Shirey. "We needed all four of these different disciplines to come together to make this argument. It turned out we had them all in-house at Carnegie."
INFORMATION:
The authors thank the Carnegie Institution for Science and the University of Alberta for continuing support. Diamond research is supported by the Deep Carbon Observatory and the U.S. National Science Foundation.
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with three research divisions on both coasts. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in the life and environmental sciences, Earth and planetary science, and astronomy and astrophysics.
Abstract 803: Impact of social isolation and quarantine on the course of diabetes mellitus and its complications during Covid 19 pandemic in Adjara Region Country of Georgia
Abstract 1337: Psychological distress in patients with hypocortisolism during mass quarantine for Covid-19 epidemic in Italy
Studies reveal that social isolation and quarantine throughout the COVID-19 pandemic may have a detrimental impact on people living with pre-existing conditions.
Social isolation and quarantine can have a detrimental impact on physical and mental health of people living with pre-existing conditions, according to two studies being presented ...
Tobacco use continues to be a primary contributor to the global burden of disease, causing an estimated 12% of deaths worldwide among people aged 30 and over. Four leading cardiovascular organizations - American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, European Society of Cardiology and World Heart Federation - today released a joint opinion calling for greater action at the global scale to end the tobacco epidemic once and for all.
The organizations are urging governments to take immediate action to implement the World Health Organization's MPOWER framework, which outlines six essential policy approaches proven to reduce tobacco use: Monitor tobacco use and prevention policies; Protect people from tobacco smoke; Offer help to quit tobacco use; Warn about the dangers ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Time not only flies when you're having fun - sometimes anticipating a fun event makes it feel like it will be over as soon as it begins, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that people judge future positive events as being both farther away as well as shorter in duration than negative or neutral events.
Combining those two elements has a strange effect when people look forward to a positive event like a vacation, said Selin Malkoc, co-author of the study and associate professor of marketing at The Ohio State University's Fisher College of Business.
"The seemingly endless wait for the vacation ...
SAN RAMON, Calif., May 26, 2021--A new paper that has been accepted for publication in Ophthalmic & Physiological Optics, the peer-reviewed journal of The College of Optometrists (UK), furthers understanding of myopia control efficacy in the context of normal childhood eye growth. Axial Length Targets for Myopia Control (Chamberlain P, et al.) is now available online via END ...
REYKJAVIK, Iceland 26 May 2021 - Current vaccination programmes alone will have a limited effect in stopping the second wave of COVID infections in the US, according to a study conducted by scientists from Reykjavik University, University of Lyon, University of Southern Denmark and University of Naples Federico II, and published in the Nature Group journal Scientific Reports today. The findings suggest that strict social distancing and other non-pharmaceutical methods are still necessary to end the ongoing second wave in the US and prevent a new one from rising.
The study fed real-world data on human mobility into a mathematical model previously used to predict the second wave of ...
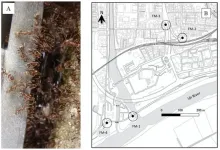
Researchers have successfully detected the environmental DNA (eDNA *1) of the Argentine ant (*2) in surface soil samples from sites on Kobe's Port Island and in Kyoto's Fushimi District, two areas that have a long history of destruction caused by this invasive species. The research group included then graduate student YASASHIMOTO Tetsu and Associate Professor MINAMOTO Toshifumi of Kobe University's Graduate School of Human Development and Environment, Visiting Professor OZAKI Mamiko of the Graduate School of Engineering, and NAKAJIMA Satoko, formally of the Kyoto Prefectural Institute of Public Health and Environment.
This method can be used to enable scientists ...
A newly released scientific paper in Nature Publishing's Scientific Reports Journal has revealed unprecedented amounts of highly toxic mercury are deposited in the deepest trenches of the Pacific Ocean.
The study, a multi-national effort involving scientists from Denmark, Canada, Germany and Japan, reports the first-ever direct measurements of mercury deposition into one of the logistically most challenging environments to sample on Earth, and the deepest at eight to 10 kilometers under the sea.
Lead author Professor Hamed Sanei, Director of the Lithospheric Organic Carbon Laboratory (LOC) at the Department of Geoscience, ...
What information is retained in a memory over time, and which parts get lost? These questions have led to many scientific theories over the years, and now a team of researchers at the Universities of Glasgow and Birmingham have been able to provide some answers.
Their new study, which is published today in Nature Communications, demonstrates that our memories become less vibrant and detailed over time, with only the central gist eventually preserved. Moreover, this 'gistification' of our memories is boosted when we frequently recall our recent experiences.
The work could have implications in a number of areas, including the nature of memories in post-traumatic stress disorder, the repeated questioning ...
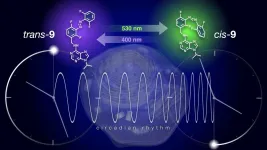
The biological clock is present in almost all cells of an organism. As more and more evidence emerges that clocks in certain organs could be out of sync, there is a need to investigate and reset these clocks locally. Scientists from the Netherlands and Japan introduced a light-controlled on/off switch to a kinase inhibitor, which affects clock function. This gives them control of the biological clock in cultured cells and explanted tissue. They published their results on 26 May in Nature Communications.
Life on Earth has evolved under a 24-hour cycle; of light and dark, hot and cold. 'As a result, our cells are synchronized to these 24-hour oscillations,' says Wiktor Szymanski, Professor of Radiological Chemistry at the University ...
CLEVELAND, Ohio (May 26, 2021)--Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), which causes tingling and numbness in the hand, more commonly affects women than men and tends to peak around the age of menopause. A new study suggests the risk of severe CTS increases in women who underwent bilateral oophorectomy before menopause, and estrogen therapy didn't provide a protective effect. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common nerve disorder in the upper body. Although predominately idiopathic in nature, an association with sex hormones has been suggested because of a higher incidence in women ...