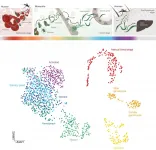
Artificial neurons recognize biosignals in real time
2021-05-27
(Press-News.org) Current neural network algorithms produce impressive results that help solve an incredible number of problems. However, the electronic devices used to run these algorithms still require too much processing power. These artificial intelligence (AI) systems simply cannot compete with an actual brain when it comes to processing sensory information or interactions with the environment in real time.
Neuromorphic chip detects high-frequency oscillations
Neuromorphic engineering is a promising new approach that bridges the gap between artificial and natural intelligence. An interdisciplinary research team at the University of Zurich, the ETH Zurich, and the UniversityHospital Zurich has used this approach to develop a chip based on neuromorphic technology that reliably and accurately recognizes complex biosignals. The scientists were able to use this technology to successfully detect previously recorded high-frequency oscillations (HFOs). These specific waves, measured using an intracranial electroencephalogram (iEEG), have proven to be promising biomarkers for identifying the brain tissue that causes epileptic seizures.
Complex, compact and energy efficient
The researchers first designed an algorithm that detects HFOs by simulating the brain's natural neural network: a tiny so-called spiking neural network (SNN). The second step involved imple-menting the SNN in a fingernail-sized piece of hardware that receives neural signals by means of electrodes and which, unlike conventional computers, is massively energy efficient. This makes calculations with a very high temporal resolution possible, without relying on the internet or cloud computing. "Our design allows us to recognize spatiotemporal patterns in biological signals in real time," says Giacomo Indiveri, professor at the Institute for Neuroinformatics of UZH and ETH Zur-ich.
Measuring HFOs in operating theaters and outside of hospitals
The researchers are now planning to use their findings to create an electronic system that reliably recognizes and monitors HFOs in real time. When used as an additional diagnostic tool in operating theaters, the system could improve the outcome of neurosurgical interventions.
However, this is not the only field where HFO recognition can play an important role. The team's long-term target is to develop a device for monitoring epilepsy that could be used outside of the hospital and that would make it possible to analyze signals from a large number of electrodes over several weeks or months. "We want to integrate low-energy, wireless data communications in the design - to connect it to a cellphone, for example," says Indiveri. Johannes Sarnthein, a neurophysiologist at UniversityHospital Zurich, elaborates: "A portable or implantable chip such as this could identify periods with a higher or lower rate of incidence of seizures, which would enable us to deliver personalized medicine." This research on epilepsy is being conducted at the Zurich Center of Epileptology and Epilepsy Surgery, which is run as part of a partnership between UniversityHospital Zurich, the Swiss Epilepsy Clinic and the University Children's Hospital Zurich.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-27
What keeps consumers hooked on high sugar soft drink? Advertising, of course. But why are some consumers more adept at ignoring these cues than others?
A new study from Flinders University, published in Appetite, found participants with an automatic bias towards soft drinks - or difficulty resisting sweet drinks compared to non-sweetened control beverages (e.g., water) - were more responsive to the ads than those without these tendencies.
The Australian study compared the ability of 127 university-age students (18-25 year olds) to withstand or succumb to the urge to reach for a soft drink when viewing television advertisements.
"Perhaps, then, we can start targeting people who show these ...
2021-05-27
Analysis using a national medical database revealed that the cumulative incidence of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in children born in 2009-2014 was 2.75% by the age of five. A research group led by Associate Professor Daimei Sasayama and Professor Hideo Honda of the Department of Child and Adolescent Development Psychiatry, Shinshu University School of Medicine, used a national medical database to analyze autism spectrum disorders in Japan. It was reported that the cumulative incidence showed an increasing trend for each year of birth, and that there were regional differences.
This cumulative incidence of ASD is the highest in the world based on medical diagnosis, suggesting high diagnostic ...
2021-05-27
Poor sleep impacts the risk of long-term cognitive decline in Hispanic/Latino middle aged and older adults differently than it does in non-Hispanic adults, according to research led by University of Miami Miller School of Medicine neurology faculty and the largest long-term study of U.S. Hispanic/Latinos to date.
During seven years of follow-up, Hispanics/Latinos were more likely to develop cognitive declines in processing speed, mental flexibility, and verbal memory, if they had sleep disordered breathing, such as obstructive sleep apnea, and long sleep duration of nine or more hours. The risk was especially high in middle-aged adults without metabolic syndrome and women without obesity or metabolic syndrome ...
2021-05-27
Oysters' exposure to plastics is concerning, particularly because these materials can accumulate and release metals which are then absorbed by the molluscs. According to a recent study published in the journal Chemosphere, the combined presence of nanoplastics and arsenic affects the biological functions of oysters. This study was conducted by the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) in Québec City and the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) at the University of Bordeaux in France.
The international research team chose to study arsenic, since it is one of the most common metals absorbed ...
2021-05-27
PULLMAN, Wash. - For decades, wealthy nations have transported plastic trash, and the environmental problems that go with it, to poorer countries, but researchers have found a potential bright side to this seemingly unequal trade: plastic waste may provide an economic boon for the lower-income countries.
In a study published in the Journal of World Systems Research, Yikang Bai of Washington State University and Jennifer Givens of Utah State University analyzed 11 years of data on the global plastics trade against economic measures for 85 countries. They found that the import of plastic waste was associated with growth in gross domestic product per capita in the lower-income countries.
"Our study offers a nuanced understanding of the global trade in plastic waste," said Bai, ...
2021-05-27
DALLAS, May 27, 2021 -- Adults who have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) were more than three times as likely to have an ischemic stroke later in life compared to adults who do not have OCD, according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
"The results of our study should encourage people with OCD to maintain a healthy lifestyle, such as quitting or not smoking, getting regular physical activity and managing a healthy weight to avoid stroke-related risk factors," said study senior author Ya-Mei Bai, M.D., Ph.D., a professor in the department of psychiatry at Taipei Veterans General Hospital ...
2021-05-27
Researchers have mapped in fine detail the genetic changes malaria parasites go through as they prepare to infect people.
The atlas maps the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in unprecedented cellular detail as it develops inside a mosquito and prepares to infect humans through a bite. This detailed investigation could lead to new ways to block key stages in the parasite's development and prevent transmission through future drugs or vaccines.
Mosquitoes are increasingly resistant to pesticides, and the parasite that causes malaria is also becoming increasingly ...
2021-05-27
A cutting-edge digital tool that will make it cheaper, safer and faster for pharmaceutical companies to predict protein stability - a vital step in the development of new medicines - is being rolled out by scientists from the UK's University of Bath through their spin-out company, BLOC Labs.
The tool, launched this week, will help researchers identify the most promising protein molecules for drug development. It has the potential to play an important role in the creation of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The market for these therapeutic antibodies is worth over £70 bn.
Monoclonal antibodies are a type of protein derived from natural antibodies and then refined and mass produced in the lab. They are steadily transforming the way we treat and prevent diseases, from ...
2021-05-27
Nearly three years after the Trump administration's "Zero Tolerance" policy went into effect, more than 445 children remain separated from their families, largely due to insufficient identifying paperwork and U.S. immigration officials' failures to plan, track and reunite separated families. In a Policy Forum, Elizabeth Barnert and colleagues - an interdisciplinary group of physicians, scientists and human rights advocates - argue that a well-defined, replicable, scalable, and sustainable framework to collect and manage sensitive DNA data is urgently needed in order to play a part in helping reunite separated migrant families safely and ethically. ...
2021-05-27
Research across a wide range of languages shows that children's home literacy environment can often predict their language and literacy skills. However few studies, especially for English speaking children, examine how children's development affects what parents do and not just how parents affect their children's development. A new longitudinal study examined such bidirectional relationships between home literacy environment and children's progress in learning to read between grades 1 and 3. Results show that parents adjust their reading activities with their children over time, taking into account the level of difficulty the children are having in learning to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Artificial neurons recognize biosignals in real time