(Press-News.org) A cutting-edge digital tool that will make it cheaper, safer and faster for pharmaceutical companies to predict protein stability - a vital step in the development of new medicines - is being rolled out by scientists from the UK's University of Bath through their spin-out company, BLOC Labs.
The tool, launched this week, will help researchers identify the most promising protein molecules for drug development. It has the potential to play an important role in the creation of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The market for these therapeutic antibodies is worth over £70 bn.
Monoclonal antibodies are a type of protein derived from natural antibodies and then refined and mass produced in the lab. They are steadily transforming the way we treat and prevent diseases, from cancer and conditions affecting the immune system to viral infections. The coronavirus pandemic has triggered particular interest in mAbs, as a number of protein candidates are showing great promise as therapies to treat Covid-19, and are currently being trialled in humans.
STABILITY IS KEY
Only mAbs that are known to be stable (that is, they neither break down easily nor clump together to form toxic compounds) are suitable for development, and finding a stable candidate adds massively to the cost and time of finding new drugs.
Until now, the process of determining protein stability has been a big headache for drug companies, with researchers testing vast libraries of molecules in their search for proteins with medicinal properties. However, the tool developed in Bath - called Quantitative Understanding of Bio-molecular Edge-Shift (QUBES) - is able predict the stability of proteins with startling speed and accuracy.
Dr Chris Pudney from the University's Department of Biology & Biochemistry and developer of QUBES, said: "We're really excited by the potential of QUBES because it can be used immediately in the biopharmaceutical industry in quality assurance, formulation and development."
He added: "Proteins are notoriously unstable for a good reason - the body wants to recycle them constantly. But with a therapeutic product, you need stability - if a protein breaks down and aggregates, it becomes toxic. Finding stable proteins is hugely expensive for pharmaceutical companies, but using our tool to find the best molecule possible will cut down on the time and cost of development massively."
QUBES FINGERPRINTING
QUBES works by allowing researchers to accurately 'fingerprint' a protein's structure and predict stability under nearly any condition of concentration or formulation. The technique uses fluorescence to map protein structure and then applies a mathematical algorithm, based on the position and type of the protein's atoms, to calculate stability. Thanks to an online suite of software - also developed in Bath - laboratories can interpret their fluorescent data from anywhere in the world, using equipment found in most biochemistry labs without modifications.
Elaborating on the fingerprinting technique, Dr Pudney said: "Proteins contains tryptophan - an amino acid that emits fluorescent light. Every protein molecule has a unique fluorescent signature, and QUBES leverages this optical phenomenon, applying mathematical techniques to analyse and interpret the fluorescence.
"The software suite takes this academic work and makes it incredibly easy for people to use. You can run it on any machine - even on your mobile phone. It's ultra-rapid and ultra-easy, and it offers an incredibly high level of security - in fact, we have a grade of security that's normally reserved for the financial service industry."
What sets QUBES apart from its competitors is the quality of its readings and its extreme flexibility. Dr Pudney explains: "Not only is our approach faster, more accurate and more sensitive than anything else on the market, but it can also predict stability at any concentration and in any formulation - unlike other tools on the market, which require set conditions."
Dr Pudney's team have recently conducted a validation study of the QUBES technology with the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) under the government backed 'Measurement for Recovery Scheme' scheme, which provides independent validation of technology by the country's leading analytical facility.
Dr Alex Jones, who led the study at NPL, said: "We tested the QUBES approach using a range of analytical methodologies and found that it tracks subtle changes in protein structure and stability with remarkable sensitivity when compared to established methodologies. The approach is fast and simple to implement."
INFORMATION:
The research is published in the Biochemical Journal and the QUBES software is available for commercial trial via BLOC Laboratories Ltd: http://www.bloclaboratories.com.
The research was funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) and the Bath Crescent Fund.
Nearly three years after the Trump administration's "Zero Tolerance" policy went into effect, more than 445 children remain separated from their families, largely due to insufficient identifying paperwork and U.S. immigration officials' failures to plan, track and reunite separated families. In a Policy Forum, Elizabeth Barnert and colleagues - an interdisciplinary group of physicians, scientists and human rights advocates - argue that a well-defined, replicable, scalable, and sustainable framework to collect and manage sensitive DNA data is urgently needed in order to play a part in helping reunite separated migrant families safely and ethically. ...
Research across a wide range of languages shows that children's home literacy environment can often predict their language and literacy skills. However few studies, especially for English speaking children, examine how children's development affects what parents do and not just how parents affect their children's development. A new longitudinal study examined such bidirectional relationships between home literacy environment and children's progress in learning to read between grades 1 and 3. Results show that parents adjust their reading activities with their children over time, taking into account the level of difficulty the children are having in learning to ...
Research shows that poor sleep health may disproportionately affect children of color from families of low socioeconomic status and place them at risk for behavior problems and lower academic performance. However, few sleep studies utilize standard measures of both classroom behavior and academic achievement.
A new longitudinal study examined the relation between sleep, classroom behavior, and academic achievement scores among primarily Black children growing up in historically disinvested neighborhoods. Disinvested refers to neighborhoods in which public and private funding, city services, or other necessary resources have been denied or withheld, and which are often segregated ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- A pilot project using an online survey to gather data on COVID-19 symptoms received more than 87,000 responses from around the world, providing important insight into the spread of disease. Project leaders from Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University and Microsoft believe these questionnaires could be a valuable tool for population health.
The 7-question survey was launched in multiple languages during April 2020, as lockdowns were implemented to slow the spread of COVID-19. A link to the survey was placed in banner ads in Microsoft News articles. Respondents ...
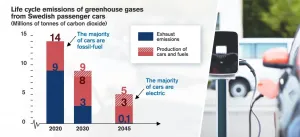
If a ban were introduced on the sale of new petrol and diesel cars, and they were replaced by electric cars, the result would be a great reduction in carbon dioxide emissions. That is the finding of new research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, looking at emissions from the entire life cycle - from manufacture of electric cars and batteries, to electricity used for operation. However, the total effect of a phasing out of fossil-fuelled cars will not be felt until the middle of the century - and how the batteries are manufactured will affect ...
Urgent investment in new tools is needed to address major global losses of wheat crops which cost £22 billion per year.
Leading scientific experts are calling for governments around the world to come together and fund a new international research platform, to reduce the impact of major wheat pathogens and improve global food security.
The John Innes Centre is calling for an internationally coordinated approach to deliver a new 'R-Gene Atlas', which would help identify new genetic solutions conferring disease resistance for crops, which could be bred into commercial wheat varieties.
Globally, we lose one fifth of the projected wheat yield annually to pests and pathogens totaling losses of 209 million tonnes, worth £22 billion ($31 billion). The climate emergency has the ...
Each city has its own unique microbiome, a "fingerprint" of viruses and bacteria that uniquely identify it, according to a new study from an international consortium of researchers that included a team from the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM). The international project, which sequenced and analyzed samples collected from public transit systems and hospitals in 60 cities around the world, was published today in the journal Cell.
The research is considered to be the largest-ever global metagenomic study of urban microbiomes, spanning both the air and the surfaces of multiple cities. It features a comprehensive ...
New research has discovered that monkeys will use the "accent" of another species when they enter its territory to help them better understand one another and potentially avoid conflict.
Published in the journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, the study is the first to show asymmetric call convergence in primates, meaning that one species chooses to adopt another species' call patterns to communicate.
The study, co-authored by Dr Jacob Dunn of Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), investigated the behaviour of 15 groups of pied tamarins (Saguinus bicolor) and red-handed tamarins (Saguinus midas) in the Brazilian Amazon.
Pied tamarins are critically endangered and have one of the smallest ...
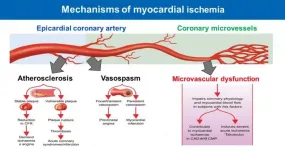
For the first time, a prospective, international study has shown that chest pain caused by problems with the very small vessels supplying blood to the heart is an important health problem that increases the risk of heart attacks, stroke and death due to cardiovascular reasons.
The study, which is published today (Thursday) in the European Heart Journal [1], recruited 686 patients from 14 institutions in seven countries on four continents [2] between July 2015 and December 2018 to investigate microvascular angina (MVA). Until now, MVA was widely thought to be a benign disease that mainly occurs in women. However, the ...
Half a billion tonnes of carbon emissions could be cut from Earth's atmosphere by improved management of peatlands, according to research partly undertaken at the University of Leicester.
A team of scientists, led by the UK Centre for Ecology and Hydrology (UKCEH), estimated the potential reduction of around 500 million tonnes in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by restoring all global agricultural peatlands.
Peatlands - a type of wetland, where dead vegetation is stopped from fully breaking down - cover just 3% of the global land surface, but store around 650 billion tonnes of ...