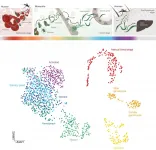
Autism Spectrum Disorder - National database reveals a cumulative incidence of 2.75%
2021-05-27
(Press-News.org) Analysis using a national medical database revealed that the cumulative incidence of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in children born in 2009-2014 was 2.75% by the age of five. A research group led by Associate Professor Daimei Sasayama and Professor Hideo Honda of the Department of Child and Adolescent Development Psychiatry, Shinshu University School of Medicine, used a national medical database to analyze autism spectrum disorders in Japan. It was reported that the cumulative incidence showed an increasing trend for each year of birth, and that there were regional differences.
This cumulative incidence of ASD is the highest in the world based on medical diagnosis, suggesting high diagnostic sensitivity in Japan. The proportion of people diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders has increased globally over the last 20 years, with a 2014 US survey reporting a prevalence of 1.68% in 8-year-olds. In addition, a regional cohort study of children's mental development and psychiatry at Shinshu University School of Medicine reported that 3.1% of children had been diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders by school age. Improving screening accuracy is one of the main reasons why more and more people are being diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders. In order to investigate the actual condition of diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in Japan, the group investigated the cumulative incidence of autism spectrum disorder nationwide and the cumulative incidence by prefecture using National Database (NDB), which aggregates medical data from all over the country.
For children born in 2009-2016 and diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder in 2009-2019, information on gender, year and age at the time of diagnosis, and the prefecture where the diagnosis was made were extracted from NDB. Cumulative incidence was calculated by dividing the number of diagnoses by the number of births each year.
Of the children born in 2009-2016, 313,353 (236,386 boys, 76,967 girls) were diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder in 2009-2019. The lifetime cumulative incidence of autism spectrum disorders at age 5 in children born between 2009 and 2014 was 2.75%. The cumulative incidence tended to increase with each year of birth. By prefecture, the cumulative lifetime incidence of autism spectrum disorders at age 5 ranged from 0.9-7.9% (median 2.4%).
This study published in the journal JAMA Network Open reported that the cumulative incidence of autism spectrum disorders in Japan is high worldwide. It is thought that the nationwide increasing trend is influenced by the recent increase in awareness of autism spectrum disorders. On the other hand, since there are large regional differences in the incidence rate, it is possible that factors such as differences in access to medical care and support also affect the incidence rate. The results of this study show that there is an increasing need to build a support system for autism spectrum disorders. Accurately capturing changes in the frequency of autism spectrum disorders is important both for the realization of an effective support system and for studying the risk factors and etiology of autism spectrum disorders. The research group will continue to investigate trends in the incidence of autism spectrum disorders in Japan and around the world.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by grant-in-aid for scientific research H30-shintai/chiteki-ippan-002 from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare.
Trends in Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnoses in Japan, 2009 to 2019
Daimei Sasayama· Rie Kuge · Yuki Toibana· Hideo Honda
JAMA Network Open
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2779443
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-27
Poor sleep impacts the risk of long-term cognitive decline in Hispanic/Latino middle aged and older adults differently than it does in non-Hispanic adults, according to research led by University of Miami Miller School of Medicine neurology faculty and the largest long-term study of U.S. Hispanic/Latinos to date.
During seven years of follow-up, Hispanics/Latinos were more likely to develop cognitive declines in processing speed, mental flexibility, and verbal memory, if they had sleep disordered breathing, such as obstructive sleep apnea, and long sleep duration of nine or more hours. The risk was especially high in middle-aged adults without metabolic syndrome and women without obesity or metabolic syndrome ...
2021-05-27
Oysters' exposure to plastics is concerning, particularly because these materials can accumulate and release metals which are then absorbed by the molluscs. According to a recent study published in the journal Chemosphere, the combined presence of nanoplastics and arsenic affects the biological functions of oysters. This study was conducted by the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) in Québec City and the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) at the University of Bordeaux in France.
The international research team chose to study arsenic, since it is one of the most common metals absorbed ...
2021-05-27
PULLMAN, Wash. - For decades, wealthy nations have transported plastic trash, and the environmental problems that go with it, to poorer countries, but researchers have found a potential bright side to this seemingly unequal trade: plastic waste may provide an economic boon for the lower-income countries.
In a study published in the Journal of World Systems Research, Yikang Bai of Washington State University and Jennifer Givens of Utah State University analyzed 11 years of data on the global plastics trade against economic measures for 85 countries. They found that the import of plastic waste was associated with growth in gross domestic product per capita in the lower-income countries.
"Our study offers a nuanced understanding of the global trade in plastic waste," said Bai, ...
2021-05-27
DALLAS, May 27, 2021 -- Adults who have obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) were more than three times as likely to have an ischemic stroke later in life compared to adults who do not have OCD, according to new research published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association.
"The results of our study should encourage people with OCD to maintain a healthy lifestyle, such as quitting or not smoking, getting regular physical activity and managing a healthy weight to avoid stroke-related risk factors," said study senior author Ya-Mei Bai, M.D., Ph.D., a professor in the department of psychiatry at Taipei Veterans General Hospital ...
2021-05-27
Researchers have mapped in fine detail the genetic changes malaria parasites go through as they prepare to infect people.
The atlas maps the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in unprecedented cellular detail as it develops inside a mosquito and prepares to infect humans through a bite. This detailed investigation could lead to new ways to block key stages in the parasite's development and prevent transmission through future drugs or vaccines.
Mosquitoes are increasingly resistant to pesticides, and the parasite that causes malaria is also becoming increasingly ...
2021-05-27
A cutting-edge digital tool that will make it cheaper, safer and faster for pharmaceutical companies to predict protein stability - a vital step in the development of new medicines - is being rolled out by scientists from the UK's University of Bath through their spin-out company, BLOC Labs.
The tool, launched this week, will help researchers identify the most promising protein molecules for drug development. It has the potential to play an important role in the creation of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The market for these therapeutic antibodies is worth over £70 bn.
Monoclonal antibodies are a type of protein derived from natural antibodies and then refined and mass produced in the lab. They are steadily transforming the way we treat and prevent diseases, from ...
2021-05-27
Nearly three years after the Trump administration's "Zero Tolerance" policy went into effect, more than 445 children remain separated from their families, largely due to insufficient identifying paperwork and U.S. immigration officials' failures to plan, track and reunite separated families. In a Policy Forum, Elizabeth Barnert and colleagues - an interdisciplinary group of physicians, scientists and human rights advocates - argue that a well-defined, replicable, scalable, and sustainable framework to collect and manage sensitive DNA data is urgently needed in order to play a part in helping reunite separated migrant families safely and ethically. ...
2021-05-27
Research across a wide range of languages shows that children's home literacy environment can often predict their language and literacy skills. However few studies, especially for English speaking children, examine how children's development affects what parents do and not just how parents affect their children's development. A new longitudinal study examined such bidirectional relationships between home literacy environment and children's progress in learning to read between grades 1 and 3. Results show that parents adjust their reading activities with their children over time, taking into account the level of difficulty the children are having in learning to ...
2021-05-27
Research shows that poor sleep health may disproportionately affect children of color from families of low socioeconomic status and place them at risk for behavior problems and lower academic performance. However, few sleep studies utilize standard measures of both classroom behavior and academic achievement.
A new longitudinal study examined the relation between sleep, classroom behavior, and academic achievement scores among primarily Black children growing up in historically disinvested neighborhoods. Disinvested refers to neighborhoods in which public and private funding, city services, or other necessary resources have been denied or withheld, and which are often segregated ...
2021-05-27
INDIANAPOLIS -- A pilot project using an online survey to gather data on COVID-19 symptoms received more than 87,000 responses from around the world, providing important insight into the spread of disease. Project leaders from Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University and Microsoft believe these questionnaires could be a valuable tool for population health.
The 7-question survey was launched in multiple languages during April 2020, as lockdowns were implemented to slow the spread of COVID-19. A link to the survey was placed in banner ads in Microsoft News articles. Respondents ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Autism Spectrum Disorder - National database reveals a cumulative incidence of 2.75%