(Press-News.org) Millions of surgical procedures performed each year would not be possible without the aid of general anesthesia, the miraculous medical ability to turn off consciousness in a reversible and controllable way.
Researchers are using this powerful tool to better understand how the brain reconstitutes consciousness and cognition after disruptions caused by sleep, medical procedures requiring anesthesia, and neurological dysfunctions such as coma.
In a new study published in the journal eLife, a team led by anesthesiologists George Mashour, M.D., Ph.D. of University of Michigan Medical School, Michigan Medicine, Max Kelz, M.D., Ph.D. of the University of Pennsylvania Medical School, and Michael Avidan, MBBCh of the Washington University School of Medicine used the anesthetics propofol and isoflurane in humans to study the patterns of reemerging consciousness and cognitive function after anesthesia.
In the study, 30 healthy adults were anesthetized for three hours. Their brain activity was measured with EEG and their sleep-wake activity was measured before and after the experiment. Each participant was given cognitive tests--designed to measure reaction speed, memory, and other functions--before receiving anesthesia, right after the return of consciousness, and then every 30 minutes thereafter.
The study team sought to answer several fundamental questions: Just how does the brain wake up after profound unconsciousness--all at once or do some areas and functions come back online first? If so, which?
"How the brain recovers from states of unconsciousness is important clinically but also gives us insight into the neural basis of consciousness itself," says Mashour.
After the anesthetic was discontinued and participants regained consciousness, cognitive testing began. A second control group of study participants, who did not receive general anesthesia and stayed awake, also completed tests over the same time period.
Analyzing EEG and test performance, the researchers found that recovery of consciousness and cognition is a process that unfolds over time, not all at once. To the investigators' surprise, one of the brain functions that came online first was abstract problem solving, controlled by the prefrontal cortex, whereas other functions such as reaction time and attention took longer to recover.
"Although initially surprising, it makes sense in evolutionary terms that higher cognition needs to recover early. If, for example, someone was waking up to a threat, structures like the prefrontal cortex would be important for categorizing the situation and generating an action plan," says Kelz.
The EEG readings revealed that the frontal regions of the brain were especially active around the time of recovery. Importantly, within three hours of being deeply anesthetized for a prolonged period of time, participants were able to recover cognitive function to approximately the same level as the group that stayed awake during that time. Furthermore, their sleep schedule in the days after the experiment did not appear to be affected.
"This suggests that the healthy human brain is resilient, even with a prolonged exposure to deep anesthesia. Clinically, this implies that some of the disorders of cognition that we often see for days or even weeks during recovery from anesthesia and surgery--such as delirium--might be attributable to factors other than lingering effects of anesthetic drugs on the brain," says Avidan.
INFORMATION:
This study was funded by a collaborative grant from the James S. McDonnell Foundation, St. Louis, MO; National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, MD, USA) grant T32GM112596; and the anesthesiology departments of the University of Michigan, University of Pennsylvania and Washington University.
Paper Cited: "Recovery of consciousness and cognition after general anesthesia in humans," eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.59525
This striking image showcases the unusually contorted appearance of NGC 2276, an appearance caused by two different astrophysical interactions -- one with the superheated gas pervading galaxy clusters, and one with a nearby galactic neighbour.
The interaction of NGC 2276 with the intracluster medium -- the superheated gas lying between the galaxies in galaxy clusters -- has ignited a burst of star formation along one edge of the galaxy. This wave of star formation is visible as the bright, blue-tinged glow of newly formed massive stars towards the left side of this image, and gives the galaxy a strangely lopsided appearance. NGC 2276's recent burst of star formation is also related to the appearance of more exotic inhabitants -- black holes and neutron stars ...
What does quark-gluon plasma - the hot soup of elementary particles formed a few microseconds after the Big Bang - have in common with tap water? Scientists say it's the way it flows.
A new study, published today in the journal SciPost Physics, has highlighted the surprising similarities between quark-gluon plasma, the first matter thought to have filled the early Universe, and water that comes from our tap.
The ratio between the viscosity of a fluid, the measure of how runny it is, and its density, decides how it flows. Whilst both the viscosity ...
Woods Hole, Mass. (May 27, 2021) - With the expansion of oxygen-depleted waters in the oceans due to climate change, some species of foraminifera (forams, a type of protist or single-celled eukaryote) that thrive in those conditions could be big winners, biologically speaking.
A new paper that examines two foram species found that they demonstrated great metabolic versatility to flourish in hypoxic and anoxic sediments where there is little or no dissolved oxygen, inferring that the forams' contribution to the marine ecosystem will increase with the expansion of oxygen-depleted habitats.
In addition, the paper ...
Twenty scientists from 14 countries warn of a hidden "pandemic within the pandemic" in two current publications. On the one hand, physical activity levels have gone down significantly, on the other hand, psychological well-being has suffered. "Governments and those responsible for health systems should take our findings seriously," emphasizes the author team, headed by Dr Jan Wilke from the Institute for Sport Sciences at Goethe University Frankfurt.
About 15,000 people in participating countries answered standardised questionaires as part of an international survey. In April/May 2020, they reported physical activity levels (13,500 participants) as well as their mental and physical well-being (15,000 participants) ...
With global warming decreasing the size of New Zealand's alpine zone, a University of Otago study found out what this means for our altitude-loving kea.
The study, published in Molecular Ecology, analysed whole genome DNA data of the kea and, for the first time, its forest-adapted sister species, the kākā, to identify genomic differences which cause their habitat specialisations.
The researchers found the kea is not an alpine specialist, but rather one that adapted to using such an open habitat because it was least disturbed by human activity.
Co-author Associate Professor Michael Knapp, of the Department of Anatomy, says that is not likely to surprise people ...
Different from small molecules, polymer will fold into lamellar crystals during crystallization and further assemble into lamellar stacks.
Synchrotron Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS) is an important tool to characterize such nanoscale structure and understand polymer crystallization. However, its scattering mechanism in semi-crystalline polymers is not completely elucidated yet.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. TIAN Xingyou from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), proposed a complete set of new methods to characterize polymer lamellar crystals ...
Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the most common lethal gynaecological cancer. Ovarian cancer is usually treated with platinum-based chemotherapy; however, a significant number of patients are resistant to such treatments and relapse soon afterwards. To improve their survival, there is a need to first identify which patients may be platinum-resistant, so that newer treatments may be administered early.
Now, researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS), have discovered a way to predict which patients are resistant to platinum chemotherapy. The study, co-led by CSI Singapore Principal ...
Current best practices for encouraging more female students to pursue degrees in economics may actually have the opposite effect and worsen gender disparities in the field, a recent study from Oregon State University found.
The study examined whether mass emails telling introductory economic students about promising career and earning opportunities helped increase female participation in higher-level economics courses. But instead, these emails appealed more to male students, increasing male enrollment and widening the existing gender gap. There was no change in the probability of female students majoring in economics.
Researchers say this demonstrates a need for more personalized, deliberate interventions.
"There ...
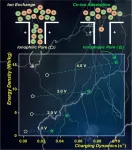
Using renewable energy to replace fossil energy is now considered the best solution for greenhouse gas emission and air pollution problems. As a result, the demand for new and better energy storage technology is strong.
As part of the effort to improve this technology, a group led by Prof. ZHANG Suojiang from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently found that ionophobic electrodes can boost energy storage performance.
Their study was published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A on May 8.
Electric Double-Layer Capacitors (EDLCs) with ionic liquids (ILs)--as a new type of energy storage device--can fill the gap between the power density of batteries and the ...
Human-driven global change is challenging the scientific community to understand how marine species might adapt to predicted environmental conditions in the near-future (e.g. hypoxia, ocean warming, and ocean acidification). The effects of the uptake of anthropogenic atmospheric CO2 by oceans affects (i.e. ocean acidification) propagate across the biological hierarchy, from changes in the building blocks of life at nano-scales to organism, physiology and behaviour through ecosystem processes and their properties.
To survive in a reduced pH environment, marine organisms have to adjust their physiology which, at the molecular level, is achieved by modifying the expression ...