Shedding new light: A new type of immunosensor for immunoassay tests
2021-05-27
(Press-News.org) Immunosensors are widely used in immunoassays to detect antigens. One such immunosensor is a quenchbody (Q-body), which contains a modified antibody fragment with a quenched fluorescent dye. When an antigen binds to the Q-body, the dye leaves the antibody and the fluorescence intensifies. The change in fluorescence intensity is easy to measure, making Q-body-based antigen detection systems incredibly simple. However, this method requires an external light source to excite the electrons in the fluorescent dye to produce luminescence.
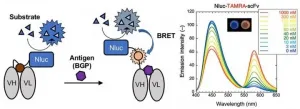
One way to solve this is to induce luminescence by an alternative method. To achieve this, researchers from Tokyo Tech, Japan, have developed a novel immunosensor. They used a modified luciferase enzyme called "NanoLuc" (Nluc) that is originally responsible for bioluminescence in shrimp and fused it to the Q-body. This immunosensor, termed "BRET Q-body", works on the bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) principle. Here, a luminescent substrate is added to the fused Q-body. The substrate reacts with the enzyme and this reaction provides the energy required by the dye to induce fluorescence. This type of luminescence is advantageous, as Professor Hiroshi Ueda, who leads the team of researchers, explains, "The BRET Q-body system can be used to visualize the presence or the absence of an antigen as a change in the emission color without any instrument." Their findings were recently published in the journal Analytical Chemistry.
To prepare the BRET Q-body, the researchers used a single-chain antibody fragment which binds to the antigen BGP, a protein found in the bone. The antibody fragment was then labeled with a fluorescent dye. They then tested the fluorescence intensity of the resulting BRET Q-bodies and observed that the addition of the antigen increased the intensity of the fluorescence.
After these initial results, the researchers tested the antigen dependency of the BRET Q-body. They compared the fluorescence obtained by the new BRET-based method against the conventional irradiation-based method. The fluorescence intensity of the BRET-Q body was initially measured with excitation light and later in the presence of the luminescent substrate. They found that the antigen-binding brought the Nluc enzyme and the dye closer together resulting in higher fluorescence intensity levels when the substrate was used. As luminescence from the BRET Q-body is obtained initially from the enzyme and then from the fluorescent dye upon antigen binding, a simple color change indicates the presence of an antigen.
This study paves the way forward for a new class of bioluminescent sensors that do not require an external excitation light source. The novel BRET Q-bodies are expected to make immunoassay tests much simpler and more accurate. As Prof. Ueda explains the advantages and potential applications of their findings, "The detection of the BRET signal does not need a light source, allows visual observation of the color change, and easier integration to a smartphone-based device. Therefore, we expect that BRET Q-bodies will be a promising tool for diagnosis, food safety, environmental preservation, and biological research."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-27
EUGENE, ORE. -- May 27, 2021 -- Climate skeptics who aren't persuaded by the existing evidence from climate change are unlikely to change their minds for many years, according to a newly published quantitative study by a University of Oregon environmental economist
The central question posed by the study published in the journal Climate Change was "How much evidence would it take to convince skeptics that they are wrong?" The answer depended on the degree of skepticism. The study modeled two types of hypothetical skeptics -- those who were less extreme and believed the change in temperature was slight, as well as ...
2021-05-27
While earlier research has mostly looked into factors such as fear, perceived risk, age and political views to determine what makes individuals and societies more or less willing to drastically change their lifestyle and support government-imposed strict restrictions, in order to mitigate the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, psychologists at the University of Zurich Charlotte Kukowski, Katharina Bernecker and Veronika Brandstätter took a different perspective.
Instead, they chose to find out the impact of people's perception of others' behaviour when it comes to the public good, as well as people's own self-control in sticking to behaviour guidelines. By using data from the United Kingdom and Switzerland, they concluded that, ...
2021-05-27
AUSTIN, Texas -- In the perpetual arms races between bacteria and human-made antibiotics, there is a new tool to give human medicine the edge, in part by revealing bacterial weaknesses and potentially by leading to more targeted or new treatments for bacterial infections.
A research team led by scientists at The University of Texas at Austin has developed chemical probes to help identify an enzyme, produced by some types of E. coli and pneumococcal bacteria, known to break down several common types of antibiotics, making these bacteria dangerously resistant to treatment.
"In response to antibiotic ...
2021-05-27
New York, NY--May 27, 2021--While our facial expressions play a huge role in building trust, most robots still sport the blank and static visage of a professional poker player. With the increasing use of robots in locations where robots and humans need to work closely together, from nursing homes to warehouses and factories, the need for a more responsive, facially realistic robot is growing more urgent.
Long interested in the interactions between robots and humans, researchers in the Creative Machines Lab at Columbia Engineering have been working for five years to create EVA, a new autonomous robot with a soft and expressive ...
2021-05-27
Reanalysis of the prehistoric cemetery Jebel Sahaba (Sudan), one of the earliest sites showing human warfare (13,400 years ago), suggests that hunter-fisher-gatherers engaged in repeated, smaller conflicts. The findings are published in Scientific Reports. Healed trauma on the skeletons found in the cemetery indicates that individuals fought and survived several violent assaults, rather than fighting in one fatal event as previously thought.
Isabelle Crevecoeur and colleagues reanalysed the skeletal remains of 61 individuals, who were originally ...
2021-05-27
Shortly before Jakobshavn Isbræ, a tidewater glacier in Greenland, calves massive chunks of ice into the ocean, there's a sudden change in the slushy collection of icebergs floating along the glacier's terminus, according to a new paper led by the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) at CU Boulder. The work, published in Nature Geoscience, shows that a relaxation in the thick aggregate of icebergs floating at the glacier-ocean boundary occurs up to an hour before calving events. This finding may help scientists better understand future sea-level rise scenarios and could also help ...
2021-05-27
Since its discovery in the 1960s, the Jebel Sahaba cemetery (Nile Valley, Sudan), 13 millennia old, was considered to be one of the oldest testimonies to prehistoric warfare. However, scientists from the CNRS and the University of Toulouse - Jean Jaurès (1) have re-analysed the bones preserved in the British Museum (London) and re-evaluated their archaeological context. The results, published in Scientific Reports on May 27, 2021, show that it was not a single armed conflict but rather a succession of violent episodes, probably exacerbated by climate change.
Many individuals buried at Jebel Sahaba bear injuries, half ot them caused by projectiles, the points of which were found in the bones or the fill where the body was located. The ...
2021-05-27
What The Study Did: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis indicate that enhanced personal protective equipment is associated with low rates of SARS-CoV-2 transmission during tracheostomy.
Authors: Phillip Staibano, M.Sc., M.D., of McMaster University in Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0930)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
2021-05-27
What The Study Did: This survey study of adults living Michigan during the COVID-19 pandemic examines associations between race/ethnicity, medical mistrust within racial/ethnic groups and willingness to participate in COVID-19 vaccine trials or to receive a COVID-19 vaccine.
Authors: Hayley S. Thompson, Ph.D., of the Wayne State University School of Medicine in Detroit, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11629)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-05-27
What The Study Did: In this study of 1,597 Big Ten athletes who had comprehensive cardiac screening, including cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging, after COVID-19 infection, 37 athletes (2.3%) were diagnosed with clinical and subclinical myocarditis. Researchers report CMR screening increased detection of myocarditis, a leading cause of sudden death in competitive athletes.
Authors: Curt J.Daniels, M.D., and Saurabh Rajpal, M.B.B.S., M.D., of Ohio State University in Columbus, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.2065)
Editor's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Shedding new light: A new type of immunosensor for immunoassay tests