INFORMATION:
Reducing metabolic cost of walking while generating electricity using an exoskeleton
2021-05-27
(Press-News.org) An exoskeleton can reduce the metabolic cost of walking not by adding energy or by recycling energy from one gait phase to another, as other exoskeletons have done, but by removing the kinetic energy of a striding person's swinging leg so they don't have to tense their muscles so much. Tested in ten healthy males, it also converted the extracted kinetic energy to useable electricity. Although humans are exceptional walkers, walking is metabolically expensive and requires more energy than any other activity of daily living. Exoskeletons and exosuits - wearable devices designed to work along with the body's musculoskeletal system - have been shown to reduce this cost by adding or recycling energy to assist the body's movement. These and other devices have also been designed to "harvest" the body's mechanical energy and convert it into useable electrical energy. However, these biomechanical energy harvesters have not provided their users with a net metabolic benefit. Here, Michael Shepertycky and colleagues present an exoskeleton device that can harvest mechanical energy from walking and convert it to electrical energy while also reducing the overall metabolic energy consumption of the user. Instead of adding energy to supplement the movement, Shepertycky et al.'s device strategically removes kinetic energy during the knee swing phase of the walking gait cycle, effectively saving on the body's costs to operate upper leg muscles as "biological brakes" as they control and slow the leg's outward swing. The removed kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy using an integrated generator. According to the results, in 10 healthy male users, this approach reduced the metabolic cost of walking by as much as 3.3% while also converting the removed energy into roughly .25 watts per gait cycle. In a Perspective, Raziel Reimer and colleagues discuss the study's implications in greater detail.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Seabirds sound alarm: Breeding success corresponds to hemispheric rates of ocean warming
2021-05-27
There is heightened public awareness that the world's oceans are under duress, with over-fishing and plastic pollution as some of the more tangible problems. Now, seabirds are calling attention to another problem and have delivered a warning message.
Serving as translators of the birds' message, an international team of 40 scientists led by William Sydeman at the Farallon Institute in northern California published findings on May 28 in the journal Science that some seabirds are struggling to raise young where the globe is most rapidly warming - in the northern hemisphere.
Using over 50 years of data from 67 seabird species across the globe, the team found ...
Seabirds' success reveals asymmetry in ocean health
2021-05-27
In a study that uniquely evaluates marine ecosystem responses to a changing climate by hemisphere, researchers report that the fish-eating, surface-foraging bird species of the Northern Hemisphere suffered greater breeding productivity stresses over the last half-century than their Southern Hemisphere counterparts. The findings suggest the need for ocean management at hemispheric scales and underscore the importance of long-term seabird monitoring programs - some of which are already under threat - by illustrating the critical role that seabirds play as sentinels of global marine change. To date, global understanding of ocean change has not explicitly considered differences, ...
Managing global climate change--and local conditions--key to coral reefs' survival
2021-05-27
Australian researchers recently reported a sharp decline in the abundance of coral along the Great Barrier Reef. Scientists are seeing similar declines in coral colonies throughout the world, including reefs off of Hawaii, the Florida Keys and in the Indo-Pacific region.
The widespread decline is fueled in part by climate-driven heat waves that are warming the world's oceans and leading to what's known as coral bleaching, the breakdown of the mutually beneficial relationship between corals and resident algae.
But other factors are contributing to the decline ...
Biologists construct a 'periodic table' for cell nuclei
2021-05-27
HOUSTON - (May 27, 2021) - One hundred fifty years ago, Dmitri Mendeleev created the periodic table, a system for classifying atoms based on the properties of their nuclei. This week, a team of biologists studying the tree of life has unveiled a new classification system for cell nuclei and discovered a method for transmuting one type of cell nucleus into another.
The study, which appears this week in the journal Science, emerged from several once-separate efforts. One of these centered on the DNA Zoo, an international consortium spanning dozens of institutions including Baylor College of ...
Seabirds face dire threats from climate change, human activity — especially in Northern Hemisphere
2021-05-27
Many seabirds in the Northern Hemisphere are struggling to breed -- and in the Southern Hemisphere, they may not be far behind. These are the conclusions of a study, published May 28 in Science, analyzing more than 50 years of breeding records for 67 seabird species worldwide.
The international team of scientists -- led by William Sydeman at the Farallon Institute in California -- discovered that reproductive success decreased in the past half century for fish-eating seabirds north of the equator. The Northern Hemisphere has suffered greater impacts from human-caused climate change and other human activities, like overfishing.
Seabirds include albatrosses, puffins, murres, penguins and other birds. Whether they ...
How more inclusive lab meetings lead to better science
2021-05-27
A new paper, published recently in PLOS Computational Biology by a team including UMass Amherst researchers, seeks to help scientists structure their lab-group meetings so that they are more inclusive, more productive and, ultimately, lead to better science.
The word "scientist" might conjure images of lab-coated researchers tending bubbling beakers or building supercomputers, but an enormous amount of scientific work takes place around a conference table during weekly group meetings. "There is plenty of good research showing that diversity and inclusion make the science itself better," says Kadambari Devarajan, one of the paper's co-lead authors and a graduate ...
Changes in how cholesterol breaks down in the body may accelerate progression of dementia
2021-05-27
The blood-brain barrier is impermeable to cholesterol, yet high blood cholesterol is associated with increased risk of Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. However, the underlying mechanisms mediating this relationship are poorly understood. A study published in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Vijay Varma and colleagues at the National Institute on Aging, part of the National Institutes of Health, in Baltimore, Maryland, suggests that disturbances in the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids (called cholesterol catabolism) may play a role in the development of dementia.
Little ...
Astonishing quantum experiment in Science raises questions
2021-05-27
Quantum systems are considered extremely fragile. Even the smallest interactions with the environment can result in the loss of sensitive quantum effects. In the renowned journal Science, however, researchers from TU Delft, RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich now present an experiment in which a quantum system consisting of two coupled atoms behaves surprisingly stable under electron bombardment. The experiment provide an indication that special quantum states might be realised in a quantum computer more easily than previously thought.
The so-called decoherence is one of the greatest enemies of the quantum physicist. Experts understand by this the decay of quantum states. This inevitably occurs when the system interacts with its environment. In ...
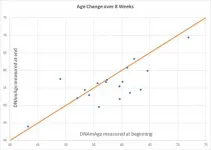
Three years younger in just eight weeks? A new study suggests yes!
2021-05-27
A groundbreaking clinical trial shows we can reduce biological age (as measured by the Horvath 2013 DNAmAge clock) by more than three years in only eight weeks with diet and lifestyle through balancing DNA methylation. A first-of-its-kind, peer-reviewed study provides scientific evidence that lifestyle and diet changes can deliver immediate and rapid reduction of our biological age. Since aging is the primary driver of chronic disease, this reduction has the power to help us live better, longer. The study, released on April 12, utilized a randomized controlled clinical trial conducted among 43 healthy adult males between the ages of 50-72. The 8-week treatment program included diet, sleep, exercise and relaxation ...
The new species of bacteria killing palms in Australia
2021-05-27
The bacterium, which they named Candidatus Phytoplasma dypsidis was found to cause a fatal wilt disease. This new discovery was reported in the International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology.
In 2016, several ornamental palms within a conservatory in the Cairns Botanic Gardens, Queensland, died mysteriously. A sample was taken from one of the diseased plants and investigated by Dr Richard Davis and colleagues from the Australian Government Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment, and state and local government. They compared the characteristics and genome of the bacterium identified as the cause of the disease and found the ...