(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. - A Cornell University-developed technology provides beekeepers, consumers and farmers with an antidote for deadly pesticides, which kill wild bees and cause beekeepers to lose around a third of their hives every year on average.
An early version of the technology ¬- which detoxified a widely-used group of insecticides called organophosphates - is described in a new study, "Pollen-Inspired Enzymatic Microparticles to Reduce Organophosphate Toxicity in Managed Pollinators," published in Nature Food. The antidote delivery method has now been adapted to effectively protect bees from all insecticides, and has inspired a new company, Beemmunity, based in New York state.
Studies show that wax and pollen in 98% of hives in the U.S. are contaminated with an average of six pesticides, which also lower a bee's immunity to devastating varroa mites and pathogens. At the same time, pollinators provide vital services by helping to fertilize crops that lead to production of a third of the food we consume, according to the paper.
"We have a solution whereby beekeepers can feed their bees our microparticle products in pollen patties or in a sugar syrup, and it allows them to detoxify the hive of any pesticides that they might find," said James Webb, a co-author of the paper and CEO of Beemmunity.
First author Jing Chen is a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of senior author Minglin Ma, associate professor in the Department of Biological and Environmental Engineering in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences (CALS). Scott McArt, assistant professor of entomology in CALS, is also a co-author.
The paper focuses on organophosphate-based insecticides, which account for about a third of the insecticides on the market. A recent worldwide meta-analysis of in-hive pesticide residue studies found that, under current use patterns, five insecticides posed substantial risks to bees, two of which were organophosphates, McArt said.
The researchers developed a uniform pollen-sized microparticle filled with enzymes that detoxify organophosphate insecticides before they are absorbed and harm the bee. The particle's protective casing allows the enzymes to move past the bee's crop (stomach), which is acidic and breaks down enzymes.
Microparticles can be mixed with pollen patties or sugar water, and once ingested, the safe-guarded enzymes pass through the acidic crop to the midgut, where digestion occurs and where toxins and nutrients are absorbed. There, the enzymes can act to break down and detoxify the organophosphates.
After a series of in vitro experiments, the researchers tested the system on live bees in the lab. They fed a pod of bees malathion, an organophosphate pesticide, in contaminated pollen and also fed them the microparticles with enzyme. A control group was simultaneously fed the toxic pollen, without the enzyme-filled microparticles.
Bees that were fed the microparticles with a high dose of the enzyme had a 100% survival rate after exposure to malathion. Meanwhile, unprotected control bees died in a matter of days.
Beemmunity takes the concept a step further, where instead of filling the microparticles with enzymes that break down an insecticide, the particles have a shell made with insect proteins and are filled with a special absorptive oil, creating a kind of micro-sponge. Many insecticides, including widely-used neonicotinoids, are designed to target insect proteins, so the microparticle shell draws in the insecticide where it is sequestered inert within the casing. Eventually, the bees simply defecate the sequestered toxin.
The company is running colony-scale trials this summer on 240 hives in New Jersey and plans to publicly launch its products starting in February 2022. Products include microparticle sponges in a dry sugar medium that can be added to pollen patties or sugar water, and consumer bee feeders in development.
"This is a low-cost, scalable solution which we hope will be a first step to address the insecticide toxicity issue and contribute to the protection of managed pollinators," Ma said.
INFORMATION:
Jin-Kim Montclare, a researcher at New York University's Tandon School of Engineering, is a co-author.
The technology is licensed through Cornell's Center for Technology Licensing (CTL). Ma and McArt are advisors for Beemmunity.
The study was funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's National Institute of Food and Agriculture, the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation.
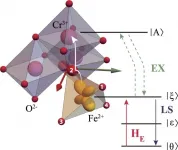
The authors, Kirill Vasin and Mikhail Eremin, contribute to the theory of electronic and structural properties of FeCr2O4 ferrimagnet. Due to the specific quantum state and the symmetry of FeO4 fragment, it has unusual electric and magnetic properties. Below TOO~150K, it lowers the symmetry with the macroscopic deformations due to the cooperative Jahn-Teller effect. The coupling between macroscopic deformation of the crystal FeCr2O4 and its inner ions shifts was revealed. The team enhanced the microscopic crystal field theory for 3D electrons with Kleiner's correction - the effect of penetrating charges density. It allows to have better prediction of electron-deformation ...
In a paper published in NANO, the author reviewed many kinds of nanofibrous filters including the component, preparation process, and application performances to provide directional guidance for improvement of the air purification field.
Poor air quality is worldwide recognized as one of five health risks for causing adverse impacts on human health. Nanofibrous membrane is competitive to capture unclean nanoparticles since its lightweight, small diameter, high specific surface area, and easy to combine with functional additives. However, the trade-off between high filtration efficiency and low pressure drop posts challenge.
The removal mechanisms of fibrous filters to nanoparticles follow ...
How to construct the dual emission nitrogen-doped carbon dots (CDs) by a simple method? Professor Lili Ren with her collaborators proposed a new strategy to prepare such materials which were used to the detection of dopamine.
The traditional ratiometric fluorescence (FL) probe usually needs to combine different nanomaterials by chemical or physical methods and the manufacturing process is more complicated. While the dual-emission carbon dots (DECDs) can simplify the detection process. Therefore, it is of great significance to design a simple ratiometric fluorescence probe based on the DECDs for the accurate determination of DA concentration. ...
Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) researchers have uncovered how the environment can impact highly sensitive quantum behaviours like localisation. Their findings, published in Chaos, could lead to future innovations in the design of superconducting materials and quantum devices, including super precise sensors.
Quantum technology, in particular quantum sensing, promises to measure and capture our world at levels of precision never before possible. Such precision has diverse applications, from speedier and more sensitive medical imaging to recording time on high-frequency ...
In the Philippines, in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, there occurred a supply shortage of hydroxychloroquine and methotrexate. Limited access to medication and the life changes caused from the COVID-19 pandemic may prompt patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) to experience disease flares.
The researchers investigated self-reported symptoms of disease flares among patients with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus during the COVID-19 pandemic. They collected information through online surveys from 512 patients with SLE or RA. The data included ...
The Montreal Heart Institute (MHI) announces that the COLCORONA study results are published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine. The article, which is entitled Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, concludes that, given the lack of oral therapies available to prevent COVID-19 complications among non-hospitalized patients and the observed benefit of colchicine in patients with a PCR-confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19, this anti-inflammatory drug could be considered as a treatment for those at risk of ...
Multiple scientific studies show switching completely to vaping with high-quality products has reduced health risks compared to smoking, contrary to many consumer beliefs
Study data indicates that vaping products can provide an alternative for smokers who would not otherwise quit
Review supports the important role for vaping products in Tobacco Harm Reduction
Reinforces the importance of BAT's unique consumer-centric model and how we are reducing the health impact of our business and building A Better Tomorrow™ through our multicategory approach
To mark World Vape Day, BAT has today published a comprehensive review of the scientific evidence ...
In a world first, scientists from the University of Sussex have recorded blood oxygen levels in the hippocampus and provided experimental proof for why the area, commonly referred to as 'the brain's memory centre', is vulnerable to damage and degeneration, a precursor to Alzheimer's disease.
To understand why this region is so sensitive, the University of Sussex researchers, headed up by Dr Catherine Hall from the School of Psychology and Sussex Neuroscience, studied brain activity and blood flow in the hippocampus of mice. The researchers then used simulations to predict that the amount of oxygen supplied to hippocampal neurons furthest from blood vessels is only just enough for the cells to keep working normally.
Dr Catherine ...
The basis for this new take on the classification was laid in 1985, when John Long attributed a fossil tooth plate to a new species, Edaphodon eyrensis. The species was named after Lake Eyre, near which the tooth was found in 1978.
Asscoiate Professor Evgeny Popov had his doubts about the attribution. However, he had to study the fossil personally to advance his theory. The opportunity presented itself during a trip to Australia in 2010. The tooth plate was stored in a museum in Adelaide, South Australia.
"I didn't plan to go there, but I was able to negotiate a temporary ...
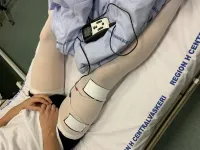
A research group from Aarhus University has developed a special biocompatible electrode for electrical muscle stimulation that the group has integrated and 3D-printed onto medical support stockings.
In the winter 2020/2021, the stockings were tested on hospitalised Covid patients. The studies were completed in March, but apart from a case study (Danish Medical Journal) data have not yet been published. However, the project group reveal that the results are very promising.
The stockings were tested on 16 Covid-19 patients who agreed to try the support stocking during their hospitalisation. The participants were hospitalised for five to seven days and were given a support stocking on each leg, but only ...