High-capacity electrodes by valence engineering developed for desalination
2021-05-28
(Press-News.org) Recently, the researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, by using valence engineering, developed three manganese oxides as electrodes with different Mn valences for high-performance capacitive desalination.
Reverse osmosis and thermal distillation are widely used to treat salt water with high salt concentration, but they have disadvantages including high energy consumption and high cost.
As an alternative method, capacitive deionization (CDI) technology can remove charged ions from desalt water through electrosorption or pseudocapacitive reaction. However, there are few reports on manganese oxides with lower valence of Mn, compared with the number of reports on MnO2. Hence, whether there is a difference in desalination performance in such different valence states of Mn and the internal reasons are worth exploring.
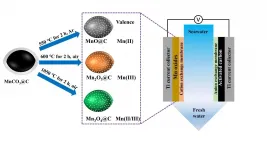
In this study, because of the high-capacity characteristic of the Faradic electrode, the researchers prepared three different manganese oxide carbon compositions with different valence states of Mn by calcining MnCO3@C precursor under different atmospheres and temperatures, and they combined them with commercial activated carbon electrode to assemble an asymmetric CDI unit. All as-prepared manganese oxides maintained the spindle-like morphology of the precursor.
The results showed that manganese oxides with divalent, trivalent and divalent/trivalent all displayed high salt adsorption capacity and corresponding high salt adsorption rates in 500 mg L-1 NaCl solution, surpassing other advanced carbon materials. Among them, MnO@C indicated the best electrosorption performance and Mn3O4@C has the worst.
The density functional theory (DFT) calculation results proved that the valence state of manganese during Na+ absorption could bring distinct discrepancy in the spatial structure and absorption capacity. Therefore, the researchers concluded that in terms of capacity and stability, the manganese oxides with divalent (MnO@C) was more suitable than trivalent (Mn2O3@C) and divalent/trivalent (Mn3O4@C) manganese oxides for CDI desalination.
The valence engineering provides a novel way for preparing high-performance pseudocapacitive materials for capacitive desalination.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-28
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have shed new light on how our brains develop, revealing that the very last step in cell division is crucial for the brain to reach its proper size and function.
The new findings identify a potential contributor to microcephaly, a birth defect in which the head is underdeveloped and abnormally small. That's because the head grows as the brain grows. The federal Centers for Disease Control estimates that microcephaly affects from 1 in 800 children to 1 in 5,000 children in the United States each year. The condition is associated with learning disabilities, developmental delays, ...
2021-05-28
Waking up just one hour earlier could reduce a person's risk of major depression by 23%, suggests a sweeping new genetic study published May 26 in the journal JAMA Psychiatry.
The study of 840,000 people, by researchers at University of Colorado Boulder and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, represents some of the strongest evidence yet that chronotype--a person's propensity to sleep at a certain time --influences depression risk.
It's also among the first studies to quantify just how much, or little, change is required to influence mental health. ...
2021-05-28
Until now, competing types of robotic hand designs offered a trade-off between strength and durability. One commonly used design, employing a rigid pin joint that mimics the mechanism in human finger joints, can lift heavy payloads, but is easily damaged in collisions, particularly if hit from the side. Meanwhile, fully compliant hands, typically made of molded silicone, are more flexible, harder to break, and better at grasping objects of various shapes, but they fall short on lifting power.
The DGIST research team investigated the idea that a partially-compliant ...
2021-05-28
Australian scientists have found what could prove to be a new and effective way to treat a particularly aggressive blood cancer in children.
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, or ALL, is the most common cancer diagnosed in children. Despite dramatic improvements in the survival of children with ALL over past several decades, children who develop 'high risk' ALL - subtypes that grow aggressively and are often resistant to standard treatments - often relapse, and many of these children die from their disease.
One common type of high-risk ALL for which new therapies are urgently needed is 'Philadelphia chromosome-like ALL' (Ph-like ALL), named for its similarity ...
2021-05-28
Scientists from Japan, Europe and the USA have described a pathway leading to the accelerated flowering of plants in low-nitrogen soils. These findings could eventually lead to increases in agricultural production.
Nitrogen is one of the three macronutrients required by plants for growth and development, along with phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen-rich condition induces plant growth, particularly the growth of stems and leaves, while delaying flowering. On the other hand, in some plants, low-nitrogen conditions lead to a change from growth mode to reproductive mode, therefore accelerating flowering. However, the molecular mechanisms that regulate flowering under these conditions are not known.
A team of scientists led by Associate ...
2021-05-28
Corona Virus Disease (COVID -19) patients primarily appear with respiratory issues and viral pneumonia. The patients may also present cardiovascular issues includes early signs of acute myocardial injury. The researchers from Sohag University, Egypt, found that cardiac troponin I (cTnI) can prove to be a gold-standard biomarker for necrosis and myocardial risk assessment in COVID-19 sufferers.
The researchers aimed to assess the prognostic value of cTnI in COVID-19 sufferers. The study included ninety-two COVID-19 patients admitted in the El Helal ...
2021-05-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- The microscopic algae that live inside and provide nutrients to their reef-building coral hosts may be evolving in tandem with the corals they inhabit, so each partner is fine-tuned to meet one another's needs. A new study by Penn State biologists reveals that genetic differences within a species of these microalgal symbionts correspond to the coral species they inhabit, a discovery that could have implications for the conservation of these endangered corals.
"Acroporid corals are some of the primary reef-building species in the Caribbean, providing protection to coastlines and habitat for economically important species," said Iliana Baums, professor of biology at Penn State and leader of the research team. "However, these corals are critically ...
2021-05-28
A study examining Japanese schools' hands-off approach when children fight showed it could create opportunities for autonomy and encourage ownership of solutions, suggesting a new strategy in handling kids squabbles in other countries.
Called mimamoru, the pedagogical strategy is a portmanteau of the Japanese words mi, meaning watch, and mamoru, meaning guard or protect. It is generally understood as "teaching by watching" -- where adults, including early childhood educators, intentionally let kids handle disagreements on their own to promote their learning through voluntary exploration and actions. While not an official part of Japan's early childhood ...
2021-05-28
While DNA is often idealised as the "molecule of life", it is also a highly sophisticated polymer that can be used for next-generation materials. Beyond the fact that it can store information, further fascinating aspects of DNA are its geometric and topological properties, such as knotting and super-coiling. Indeed, very much like a twisted telephone cord, DNA is often found coiled up inside bacteria and other cells and even knotted in viruses. Now, a collaboration of scientists from the Universities of Edinburgh, San Diego and Vienna have started to harness these properties to craft "topologically ...
2021-05-28
MISSOULA - In bear country, it's normal to find bruins munching down on temptations left out by humans - from a backyard apple tree to leftovers in the trash bin - but these encounters can cause trouble for humans and bears alike. One method to reduce human-bear conflicts is to secure attractants like garbage and livestock feed.
While effective when implemented, this approach requires people to change their behavior, and that makes things a little more complicated.
University of Montana researchers recently published a new study in the Journal of Wildlife Management analyzing why landowners do or don't secure attractants in bear country. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High-capacity electrodes by valence engineering developed for desalination