Open, expressive family life may reduce social deprivation effects among adopted children
2021-05-28
(Press-News.org) WHAT:
An environment in which family members support one another and express their feelings can reduce the effects of social deprivation on cognitive ability and development among adopted children, suggests a small study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health. In contrast, rule-driven households where family members are in conflict may increase an adopted child's chances for cognitive, behavioral and emotional difficulties.
The study was conducted by Margaret F. Keil, Ph.D., and colleagues in the Section on Endocrinology and Genetics at NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). It appears in Pediatric Research.
Researchers enrolled children who had spent at least eight months in Eastern European orphanages before their adoption by American families. The children ranged from 14 to 40 months of age and were evaluated with physical, psychological and developmental tests twice during the following two years. Families also responded to questionnaires on the children's development and on various aspects of their home lives. The study included 10 adopted children and 19 similar children born to American families.
Overall, the adopted children had significant deficits in growth, cognitive ability and development in comparison to the American-born children. However, differences were smaller among children from families scoring higher in cohesion, where family members provided help and support for each other, and expressiveness--families whose members are encouraged to express their feelings. Children had greater deficits if their families scored higher in conflict--open expression of anger and aggression--and in control--a family life run according to set rules and procedures.
The authors concluded that family cohesion and expressiveness could moderate the effects of pre-adoption adversity, while family conflict and adherence to rules could increase the risk for behavioral problems. The authors added that larger studies are needed to verify their findings.
INFORMATION:
WHO:
Margaret F. Keil, Ph.D., NICHD Section on Endocrinology and Genetics, is available for comment.
ARTICLE:
Keil, MF. Family environment and development in children adopted from institutionalized care. Pediatric Research.2020.
About the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD): NICHD leads research and training to understand human development, improve reproductive health, enhance the lives of children and adolescents, and optimize abilities for all. For more information, visit https://www.nichd.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-28
An analysis led by North Carolina State University researchers found counties with more socially vulnerable populations had a higher density of natural gas pipelines overall.
The findings suggest counties that are more socially vulnerable are also at greater risk of facing water and air pollution, public health and safety issues, and other negative impacts associated with the pipelines.
"We know that the network, as it stands today, is already distributed in such a way that any negative impacts fall disproportionately on vulnerable communities," ...
2021-05-28
Hormonal contraceptives, e.g. the pill, the patch, and the vaginal ring, contain synthetic hormones that prevent pregnancy by either stopping ovulation, changing the cervical mucus to stop sperm from passing through the cervix and finding an egg, or changing the womb's lining to prevent a fertilized egg from being implanted in it.
Despite their widespread use, hormonal contraceptives are known to increase the risk of breast cancer, which is the most common cause of cancer-related death among women worldwide, and also topped the list of most commonly diagnosed cancers in 2020.
The main component of hormonal contraceptives are progestins, ...
2021-05-28
Anesthesia may be an exact science, but it's not yet fully personalized. Anesthesiologists use a variety of methods to calculate the right dose for a given patient: clinical studies, medical databases and laboratory measurements, for example. However, every individual responds to anesthetics in a different way, and there's no way of knowing what that response will be until the anesthetic is administered.
Personalizing dosage
Today patients often receive supplemental doses of an anesthetic during their operation based on their reaction. The role of anesthesiologists is to make sure that a patient doesn't wake up too soon and has no memory of the procedure, but they must use ...
2021-05-28
Scientists from the Wellcome Sanger Institute and the University of Cambridge found that in children with neuroblastoma - a cancer of immature nerve cells - treatment with platinum chemotherapy caused changes to the genome that could then cause leukaemia in some children later on.
The findings, published 27th May 2021 in Blood could lead to an ability to identify which children are more likely to develop the secondary cancer. This in turn could lead to changes in their treatment plan to either avoid these risks or take measures to prepare.
Secondary blood cancer is a challenging complication of childhood neuroblastoma cancer treatment. Every year around 100 children in the UK are diagnosed with neuroblastoma*, ...
2021-05-28
The group of experts includes Professor and Academician of Tallinn University of Technology Jarek Kurnitski, who said that improving ventilation can be regarded more broadly as a paradigm shift equal in scale to the transformation in the standards of drinking water supplies and food hygiene. "There has long been no doubt that you can get infection when you drink water or eat food that has been contaminated. Now we must work towards providing clean air so we can breathe safely," Kurnitski said.
He added, "Researchers see updating of ventilation standards, ventilation requirements based on the probability of infection and more efficient and flexible ventilation systems as a solution. High air change rates are required only in the event of an epidemic, at any ...
2021-05-28
Varying immune response to vaccinations could be countered with microbiota-targeted interventions helping infants, older people and others to take full advantage of the benefits of effective vaccines, Australian and US experts say.
A comprehensive review in Nature Reviews Immunology concludes that evidence is mounting in clinical trials and other studies that the composition and function of individuals' gut microbiota are "crucial factors" in affecting immune responses to vaccinations.
"Never before has the need been greater for robust and long-lasting immunity from our vaccination programs, particularly in low and middle-income countries, and for populations at increased ...
2021-05-28
Researchers at the University of Adelaide are concerned video sharing platforms such as YouTube could be contributing to the normalisation of exotic pets and encouraging the exotic pet trade.
In a study, published in PLOS ONE, researchers analysed the reactions of people to videos on YouTube involving human interactions with exotic animals and found those reactions to be overwhelmingly positive.
The researchers analysed the reactions - via text and emoji usage - in comments posted on 346 popular videos starring exotic wild cats and primates in 'free handling situations'.
These situations involved exotic animals interacting with humans or other animals, such as domestic cats and dogs. The videos examined received ...
2021-05-28
Public use of parks and reserves increased only slightly during last year's COVID-19 national lockdown despite gyms and sports facilities shutting down, a University of Queensland study found.
UQ School of Biological Sciences PhD candidate Violeta Berdejo-Espinola surveyed 1000 people in Brisbane, measuring their use of urban green space and the benefits people associated with visiting the areas during lockdown.
"People all around Brisbane, myself included, noticed a boom in park use in 2020, but while more people ventured into local parks, many folks were left indoors," Ms Berdejo-Espinola said.
"Thirty-six ...
2021-05-28
Professor YAO Huajian's research group from the School of Earth and Space Sciences of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), in cooperation with Dr. Piero Poli from Grenoble-Alpes University of France, combined the unique resolution reflected body waves (P410P and P660P) retrieved from ambient noise interferometry with mineral physics modeling, to shed new light on transition zone physics. Relevant work was published in Nature Communications.
The subduction of oceanic slabs is an important process of the earth's internal material circulation. Studying the ...
2021-05-28
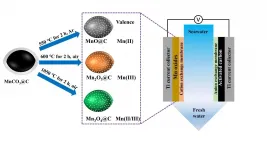
Recently, the researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, by using valence engineering, developed three manganese oxides as electrodes with different Mn valences for high-performance capacitive desalination.
Reverse osmosis and thermal distillation are widely used to treat salt water with high salt concentration, but they have disadvantages including high energy consumption and high cost.
As an alternative method, capacitive deionization (CDI) technology can remove charged ions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Open, expressive family life may reduce social deprivation effects among adopted children