Oncotarget: Piperlongumine promotes death of retinoblastoma cancer cells
These Oncotarget findings suggest that PL reduces tumor growth and induces cell death by regulating the cell cycle
2021-05-31
(Press-News.org) Oncotarget published "Piperlongumine promotes death of retinoblastoma cancer cells" which reported that while retinoblastoma initiation is triggered by the inactivation of both alleles of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene in the developing retina, tumor progression requires additional epigenetic changes, retinoblastoma genomes being quite stable.
In this report, the authors analyzed the pro-death effect of piperlongumine, a natural compound isolated from Piper longum L., on two human retinoblastoma cell lines, WERI-Rb and Y79. The effects of PL on cell proliferation, cell death and cell cycle were investigated.
PL effectively inhibited cell growth, impacted the cell cycle by decreasing the level of cyclins and CDK1 and increasing CDKN1A and triggered a caspase-3 independent cell death process in which reactive oxygen species production is a major player.
Indeed, PL toxicity in retinoblastoma cell lines was inhibited by a ROS scavenger N-acetyl-l-cysteine treatment.
These Oncotarget findings suggest that PL reduces tumor growth and induces cell death by regulating the cell cycle.
These Oncotarget findings suggest that PL reduces tumor growth and induces cell death by regulating the cell cycle.
Dr. Nathalie Allaman-Pillet from The Institute for Research in Ophthalmology in Switzerland said, "Retinoblastoma is a malignant tumor derived from photoreceptor precursor cells."
Although the survival rate of patients with retinoblastoma is extremely high in developed countries, left untreated advanced tumors limit eye preservation and expose patients to risks of metastasis and death.
A multi-step model for the progression of normal retina to retinoblastoma has been proposed, the first step being the inactivation of both alleles of the tumor suppressor gene RB1 in the developing retina.
PL was described as an anticancer compound modulating apoptosis, ROS production, cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and showing selective cytotoxic effect on several cancer cell types including pancreatic, renal, prostate, and breast cancers.
In this report, they studied the death potential of PL on two human retinoblastoma cell lines, WERI-Rb and Y79.
The Allaman-Pillet Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output, "Our study reports that PL induces retinoblastoma cells death through the accumulation of ROS resulting in cellular oxidative stress. A potential role of FOXM1 in this cell death process has to be verified using inhibitors or following FOXM1 overexpression. These data provide in vitro evidence that PL could serve as a potential anticancer molecule in retinoblastoma treatment."
INFORMATION:
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27947
Full text - https://www.oncotarget.com/article/27947/text/
Correspondence to - Nathalie Allaman-Pillet - nathalie.allaman@gmail.com
Keywords -
cancer,
retinoblastoma,
piperlongumine,
programmed cell death
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a bi-weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https://www.oncotarget.com or connect with:
SoundCloud - https://soundcloud.com/oncotarget
Facebook - https://www.facebook.com/Oncotarget/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/oncotarget
LinkedIn - https://www.linkedin.com/company/oncotarget
Pinterest - https://www.pinterest.com/oncotarget/
Reddit - https://www.reddit.com/user/Oncotarget/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
18009220957x105
Copyright © 2021 Impact Journals, LLC
Impact Journals is a registered trademark of Impact Journals, LLC
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-31
Gender roles absorbed at an early age seem to have shaped today's youth regarding their involvement in politics, in line with traditional stereotypes, concludes a new study, conducted amongst adolescents and young adults aged between 15 and 30 in Italy, within the Horizon 2020 project: "CATCH-EyoU. Processes in Youth's Construction of Active EU Citizenship".
In their research article, published in the peer-reviewed, open-access scientific journal Social Psychological Bulletin, the research team from the University of Bologna report that it is young males that would more often engage directly with politics, like enrolling in a political party, acting to influence government policy, contacting a politician or taking part in a protest. On ...
2021-05-29
Debates over women's health have long been contentious, but have also resulted in significant improvements in areas like equitable access to health care and survivorship. But the overall picture remains far from perfect. For example, the United States still has the highest rate of maternal death among high-income countries, particularly among African American women.
As the United States Supreme Court prepares to hear a Mississippi abortion case challenging the landmark 1973 Roe v. Wade decision, some experts are questioning whether women's health may be reversing course.
Cynthia A. Stuenkel, MD, clinical professor ...
2021-05-29
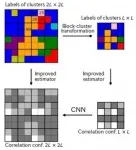
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have enhanced "super-resolution" machine learning techniques to study phase transitions. They identified key features of how large arrays of interacting "particles" behave at different temperatures by simulating tiny arrays before using a convolutional neural network to generate a good estimate of what a larger array would look like using "correlation" configurations. The massive saving in computational cost may realize unique ways of understanding how materials behave.
We are surrounded by different states or "phases" of matter i.e. gases, liquids, and solids. The study of phase transitions, how one phase transforms into another, lies at the heart of our understanding of matter in the universe, and remains a hot topic ...
2021-05-29
Highlight
Among individuals with healthy kidneys, those with more frequent depressive symptoms were more likely to show signs of rapid kidney function decline over a median follow-up of 4 years.
Washington, DC (May 28, 2021) -- In a study of adults with normal kidney function, those who had frequent depressive symptoms were more likely to later experience a rapid decline in kidney function. The study will appear in an upcoming issue of CJASN.
Depression is a common condition in middle-aged and older adults, and it can contribute to a variety of mental and physical problems. Previous research has found a link between depressive symptoms and rapid kidney function decline in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). To look ...
2021-05-28
In 2015, nearly half of Hawai?i's coral reefs were affected by the most severe bleaching event to date. Coral bleaching occurs when warmer-than-normal ocean temperatures prompt corals to expel the algae that normally live inside them and on which the corals rely for food.
Bleaching events are dismaying, but corals can sometimes recover, while others resist bleaching altogether. In a new study in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers led by Katie Barott of the University of Pennsylvania found that these battle-tested, resilient corals could thrive, even when transplanted to a different environment and subjected to additional heat stress. The findings offer hope that hardy corals could ...
2021-05-28
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes
articles online ahead of print. For April, GSA Bulletin topics
include multiple articles about the dynamics of China and Tibet; new
insights into the Chicxulub impact structure; and the dynamic topography of
the Cordilleran foreland basin. You can find these articles at
https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent
.
Tectonic and eustatic control of Mesaverde Group
(Campanian-Maastrichtian) architecture, Wyoming-Utah-Colorado region,
USA
Keith P. Minor; Ronald J. Steel; Cornel Olariu
Abstract:
We describe and analyze the depositional history and stratigraphic
architecture of the Campanian and Maastrichtian ...
2021-05-28
WACO, Texas (May 28, 2021) - About 36 million people have blindness including 1 million children. Additionally, 216 million people experience moderate to severe visual impairment. However, STEM (science, technology, engineering and math) education maintains a reliance on three-dimensional imagery for education. Most of this imagery is inaccessible to students with blindness. A breakthrough study by Bryan Shaw, Ph.D., professor of chemistry and biochemistry at Baylor University, aims to make science more accessible to people who are blind or visually impaired through small, candy-like models.
The ...
2021-05-28
Five researchers shed new light on a key argument to reduce greenhouse gases (GHG): they provided the first economic analysis of conversion factors of other GHG like methane into their CO2 equivalent in overshoot scenarios. Although the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) considers settling for one value of reference (known as "Common Metric") to make this conversion among the Paris Agreement, the models presented here show the economic advantage of flexibility between various factors of conversion. "A key notion in the UNFCCC is to reduce GHG emissions in the least costly way so as to ensure global benefits" highlights Katsumasa Tanaka, primary author of the Science Advances study.
The research provides series of dynamic variations of ...
2021-05-28
A study coordinated by Luís Graça, principal investigator at the Instituto de Medicina Molecular João Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal) and Professor at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Lisbon (FMUL) used lymph nodes, tonsils and blood, to show how the cells that control production of antibodies are formed and act. The results published now in the scientific journal Science Immunology* unveiled key aspects about the regulation of antibody production, with significant importance for diseases where antibody production is dysregulated such as autoimmune diseases or allergies.
In the last few ...
2021-05-28
A new study of dozens of wild fish species commonly consumed in the Peruvian Amazon says that people there could suffer major nutritional shortages if ongoing losses in fish biodiversity continue. Furthermore, the increasing use of aquaculture and other substitutes may not compensate. The research has implications far beyond the Amazon, since the diversity and abundance of wild-harvested foods is declining in rivers and lakes globally, as well as on land. Some 2 billion people globally depend on non-cultivated foods; inland fisheries alone employ some 60 million people, and provide the primary source of protein for some 200 million. The study appears this week in the journal Science Advances.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Oncotarget: Piperlongumine promotes death of retinoblastoma cancer cells
These Oncotarget findings suggest that PL reduces tumor growth and induces cell death by regulating the cell cycle