Researchers report reference genome for maize B chromosome
2021-05-31
(Press-News.org) Three groups (Dr. James Birchler's group from University of Missouri, Dr. Jan Barto's group from Institute of Experimental Botany of the Czech Academy of Sciences and Dr. HAN Fangpu's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) recently reported a reference sequence for the supernumerary B chromosome in maize in a study published online in PNAS (doi:10.1073/pnas.2104254118).
Supernumerary B chromosomes persist in thousands of plant and animal genomes despite being nonessential. They are maintained in populations by mechanisms of "drive" that make them inherited at higher than typical Mendelian rates. Key properties such as its origin, evolution, and the molecular mechanism for its accumulation in maize have remained unclear even though such chromosomes have been a potent tool for studying maize genetics.
The researchers used a well-established set of sequencing and mapping tools, including chromosome flow-sorting, Illumina sequencing, Bionano optical mapping, and chromatin conformation capture (Hi-C).
The rich availability of deletion derivatives ensured strong scaffolding and vetting of assembly. In addition, 758 protein-coding genes were identified from the 125.9-Mb of chromosome sequence, of which at least 88 are expressed.
The scientists discovered that the current gene content is a result of continuous transfer from the A chromosomal complement over an extended evolutionary period. This process has been accompanied by subsequent degradation even though selection for maintenance of this nonvital chromosome has also continued.
The annotation results demonstrate that transposable elements in the B chromosome are shared with the standard A chromosome set. However, the failure of multiple lines of evidence to reveal a syntenic region in the B chromosome with any A chromosome indicates that this chromosome has been present in the evolutionary lineage for millions of years since any such synteny has disintegrated.
Sequence and deletion analysis reveals that a specific DNA repeat is located in and around the centromere that is involved with its drive mechanism, consisting of nondisjunction at the second pollen mitosis and preferential fertilization of the egg by the B-containing sperm.
This analysis cleverly combines comparisons among a variety of translocation and B-deletion stocks along with many years of genetic analysis. This approach provides a unique view of the sequence of this chromosome, as well as characterization of potentially functional elements within it.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-05-31
While it is widely accepted that climate change drove the evolution of our species in Africa, the exact character of that climate change and its impacts are not well understood. Glacial-interglacial cycles strongly impact patterns of climate change in many parts of the world, and were also assumed to regulate environmental changes in Africa during the critical period of human evolution over the last ~1 million years. The ecosystem changes driven by these glacial cycles are thought to have stimulated the evolution and dispersal of early humans.
A paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) this week challenges this view. Dr. Kaboth-Bahr ...
2021-05-31
The Sahara has not always been covered by only sand and rocks. During the period from 14,500 to 5,000 years ago large areas of North Africa were more heavily populated, and where there is desert today the land was green with vegetation. This is evidenced by various sites with rock paintings showing not only giraffes and crocodiles, but even illustrating people swimming in the "Cave of Swimmers". This period is known as the Green Sahara or African Humid Period. Until now, researchers have assumed that the necessary rain was brought from the tropics through an enhanced summer monsoon. The northward shift of the monsoon was attributed to rotation of the Earth's tilted axis that produces higher levels of ...
2021-05-31
An emotion regulation strategy known as cognitive reappraisal helped reduce the typically heightened and habitual attention to drug-related cues and contexts in cocaine-addicted individuals, a study by Mount Sinai researchers has found. In a paper published in PNAS, the team suggested that this form of habit disruption, mediated by the prefrontal cortex (PFC) of the brain, could play an important role in reducing the compulsive drug-seeking behavior and relapse that are the hallmarks, and long-standing challenges, of addiction.
"Relapse in addiction is often precipitated by heightened attention-bias to drug-related cues, which could consist of sights, smells, ...
2021-05-31
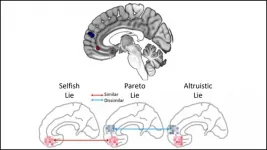
You may think a little white lie about a bad haircut is strictly for your friend's benefit, but your brain activity says otherwise. Distinct activity patterns in the prefrontal cortex reveal when a white lie has selfish motives, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
White lies -- formally called Pareto lies -- can benefit both parties, but their true motives are encoded by the medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC). This brain region computes the value of different social behaviors, with some subregions focusing on internal motivations and others on external ones. Kim and Kim predicted activity patterns in these subregions could elucidate the true motive behind white lies.
The research team deployed a stand in for white lies, having participants tell lies to earn a reward ...
2021-05-31
By including multi-ethnic participants, a largescale genetic study has identified more regions of the genome linked to type 2 diabetes-related traits than if the research had been conducted in Europeans alone.
The international MAGIC collaboration, made up of more than 400 global academics, conducted a genome-wide association meta-analysis led by the University of Exeter. Now published in Nature Genetics, their findings demonstrate that expanding research into different ancestries yields more and better results, as well as ultimately benefitting global patient care.
Up to now, nearly 87 per cent of ...
2021-05-31
Artificial intelligence promises to be a powerful tool for improving the speed and accuracy of medical decision-making to improve patient outcomes. From diagnosing disease, to personalizing treatment, to predicting complications from surgery, AI could become as integral to patient care in the future as imaging and laboratory tests are today.
But as University of Washington researchers discovered, AI models -- like humans -- have a tendency to look for shortcuts. In the case of AI-assisted disease detection, these shortcuts could lead to diagnostic errors if deployed in clinical settings.
In a new paper published May 31 in Nature Machine Intelligence, ...
2021-05-31
The Water Oxidation Reaction (WOR) is one of the most important reactions on the planet since it is the source of nearly all the atmosphere's oxygen. Understanding its intricacies can hold the key to improve the efficiency of the reaction. Unfortunately, the reaction's mechanisms are complex and the intermediates highly unstable, thus making their isolation and characterisation extremely challenging. To overcome this, scientists are using molecular catalysts as models to understand the fundamental aspects of water oxidation - particularly the oxygen-oxygen bond-forming reaction.
For the first time, scientists in ICIQ's ...
2021-05-31
Between 1991 and 2018, more than a third of all deaths in which heat played a role were attributable to human-induced global warming, according to a new article in Nature Climate Change.
The study, the largest of its kind, was led by the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) and the University of Bern within the Multi-Country Multi-City (MCC) Collaborative Research Network. Using data from 732 locations in 43 countries around the world it shows for the first time the actual contribution of man-made climate change in increasing mortality risks due to heat.
Overall, ...
2021-05-31
In a study of 11 medical-mystery patients, an international team of researchers led by scientists at the National Institutes of Health and the Uniformed Services University (USU) discovered a new and unique form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Unlike most cases of ALS, the disease began attacking these patients during childhood, worsened more slowly than usual, and was linked to a gene, called SPTLC1, that is part of the body's fat production system. Preliminary results suggested that genetically silencing SPTLC1 activity would be an effective strategy for combating this type of ALS.
"ALS is a paralyzing ...
2021-05-31
LOS ANGELES (May 31, 2021) -- Today The Lundquist Institute announced that its investigators contributed data from several studies, including data on Hispanics, African-Americans and East Asians, to the international MAGIC collaboration, composed of more than 400 global academics, who conducted a genome-wide association meta-analysis led by the University of Exeter. Now published in Nature Genetics, their findings demonstrate that expanding research into different ancestries yields more and better results, as well as ultimately benefitting global patient care. Up to now nearly 87 percent of genomic research of this type has been conducted in Europeans. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers report reference genome for maize B chromosome