Biopolymer-based electrolyte for the dream of zero-pollution battery
2021-06-01
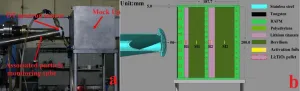
(Press-News.org) In a paper published in NANO, researchers from Guizhou Meiling Power Sources Co., Ltd., China have reviewed the recent progress in biopolymer-based electrolyte. The biopolymer materials with unique characteristics including water solubility, film-forming capability and adhesive property played a key role in the design of zero pollution lithium battery. The biopolymers mentioned in this review were polysaccharide, protein, natural rubber and other polymers.
For polysaccharide, cellulose with good wettability, low cost and good mechanical properties can enhance the mechanical strength of membranes and improve interfacial stability between electrolyte and electrode. However, the porosity control of cellulose-based membranes was still a challenge. Therefore, cellulose derivatives has been studied as electrolyte materials including alkyl cellulose, hydroxyalkyl cellulose, carboxyalkyl cellulose, cellulose esters and bacterial cellulose. In addition, chitin acted as filler of polymeric matrix to increase ionic conductivity. Anionic structure of pectin resulted in the interaction between lithium ions and polymer matrix, which favored the dissolution of lithium salts in electrolyte. Starch can improve the thermal stability of electrolyte. Chitosan contained -NH2 and -OH groups, which favored the formation of complexes with other components and promoted ionic migration. Tamarind seed polysaccharide was a highly branched polymer, which possessed film-forming nature and film transparency.
For protein, soy protein isolate (SPI) and gelatin were emphasized due to their strong interactions with electrodes. Various different functional groups of SPI facilitated the fast transport of lithium ions and effective immobilization of sulfur species. Gelatin possessed electrochemical stability and it can react with the degradation products of the liquid electrolyte to stabilize the interfaces. Epoxidized natural rubber possessed the glass transition temperature of -20 oC, high flexibility and good elasticity for contacting well with electrodes. Some other biopolymers such as agar, iota-carrageenan and eggshell membranes have also been mentioned for the electrolyte fabrication.
In summary, the starting point of choosing biopolymer as battery material is still limited to the physico-chemical consideration such as their functional groups, chain structures and intermolecular interactions. The real biological effects and ideas are still rejected or ignored during the design of lithium battery.
INFORMATION:
This work is supported by S&T Planning Project of Guizhou Province (nos. [2017]1411). Corresponding author for this study is Jiayuan Shi (jiayshi@163.com). Additional co-authors of the NANO paper is Bin Shi (ml3401@126.com).
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
The paper can be found in NANO journal.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-01
Habitat change, for example through urbanisation, is one of the most important causes of biodiversity decline. By 2050, settlements and cities across the globe are predicted to increase by two to three million square kilometres - about half the size of Greenland. Natural and semi-natural habitats will thus gradually be replaced by urban habitats.
How wildlife can adapt to such fundamental changes has mostly been studied for a few species groups, such as mammals and birds.
"In order to make predictions about the development of biodiversity as a whole and to combat current phenomena such as insect declines, robust knowledge is also needed for other species groups," ...
2021-06-01
To realize tritium self-sustaining cycle through tritium breeding blanket has been one of the core technologies of future fusion reactor. Therefore the design and function of blanket must be validated by neutronic experiment under D-T neutron environment. But due to the scarcity of DT neutron source, and highly radioactivity during neutronic experiments, it is very difficult to validate the nuclear response of the blanket, the data of tritium production rate mainly rely on Monte Carlo simulation.
Recently, a research group led by ZHU Qingjun from Institute of Plasma Physics, ...
2021-06-01
As anyone who has ever procrastinated knows, remembering that you need to do something and acting on that knowledge are two different things. To understand how learning changes nerve cells and leads to different behaviors, researchers studied the much simpler nervous system of worms.
"In this study, we can now translate neuronal activity to behavioral response," said Project Researcher Hirofumi Sato, a neuroscientist at the University of Tokyo and first author of the research paper recently published in Cell Reports.
The discovery was made possible using technology that researchers describe as a "robot microscope," first developed in 2019 by researchers at Tohoku University in Miyagi Prefecture, northeastern Japan.
The technique involves genetically modifying the worms ...
2021-06-01
A team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology, the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology and the GEOMAR - Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel have been studying biogeochemical processes in the oxygen minimum zone of the eastern South Pacific off Peru, one of the largest low oxygen regions of the world ocean. The researchers focused on so-called marine snow particles of different sizes, which are composed of algal debris and other organic material, aiming to understand how these particles affect the nitrogen cycle in the oxygen minimum zone. Thereby, they solved ...
2021-06-01
Women carrying human papillomavirus (HPV) run an elevated risk of preterm birth, a University of Gothenburg study shows. A connection can thus be seen between the virus itself and the risk for preterm birth that previously has been observed in pregnant women who have undergone treatment for abnormal cell changes due to HPV.
A Swedish study now published in the high-ranking journal PLOS Medicine comprises data on more than a million births. Accordingly, the researchers have compared very large groups. They emphasize that the findings do not support any assessment of risk ...
2021-06-01
In a study that will be published in Nature Communications on May 28, 2021, a research team led by Dr. Yuan Liu from Georgia State University reports that intratumoral SIRPα-deficient macrophages activate tumor antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells to eliminate various syngeneic cancers under radiotherapy.
As a major component of the suppressive tumor microenvironment, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are generally regarded as facilitators of tumor progression. It has been shown that depleting TAMs can enhance the response of tumors to radiotherapy (RT). However, Yuan's ...
2021-06-01
The average IQ of adults born very preterm or very low birth weight was compared to those who were term born in the 1970s to 1990s in 8 longitudinal cohorts from 7 countries around the world
The IQ was significantly lower for very pre-term and very low birth weight adults in comparison to those term born, researchers from the University of Warwick have found
Action needs to be taken to ensure support is available for those born very preterm or very low birth weight
The average IQ of adults who were born very preterm (VP) or at a very low birth weight (VLBW) has been compared to adults born full term by researchers from the Department of Psychology at the University of Warwick. Researchers have found VP/VLBW children may require special ...
2021-06-01
A new extensive genetic resource of rat-infecting malaria parasites may help advance the development of malaria prevention and treatment strategies. This trove of genome and phenome information has been published1 by a team of KAUST researchers, along with colleagues in Japan, and the datasets have been made publicly available for malaria researchers.
Rodent malaria parasites are closely related to human parasites but are easier to study because they can be grown in laboratory mice. "Investigations on rodent malaria parasites have played a key role in revealing many aspects of fascinating biology across ...
2021-06-01
It is time for the management and conservation of the Antarctic to begin focusing on responsibility, rather than rights, through an Indigenous Māori framework, a University of Otago academic argues.
In an article published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, Associate Professor Priscilla Wehi, of the Centre for Sustainability, says now is the time to be thinking of these potential changes.
"New Zealand is currently re-setting its priorities for future Antarctic research, and there may be review of the current international environmental conventions as we approach the 50-year anniversary of the protocols in 2048.
"We argue that Indigenous Māori frameworks offer powerful ways of thinking about how we protect the Antarctic, by focusing on ...
2021-06-01
Invasive species, beware: Your days of hiding may be ending.
Biologists led by the University of Iowa discovered the presence of the invasive New Zealand mud snail by detecting their DNA in waters they were inhabiting incognito. The researchers employed a technique called environmental DNA (eDNA) to reveal the snails' existence, showing the method can be used to detect and control new, unknown incursions by the snail and other invasive species.
"eDNA has been used successfully with other aquatic organisms, but this is the first time it's been applied to detect a new invasive population of these snails, which are a destructive invasive species in fresh waters around the world," says Maurine Neiman, associate professor in the Department ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Biopolymer-based electrolyte for the dream of zero-pollution battery