Ethnically diverse research identifies more genetic markers linked to diabetes
UMass Amherst epidemiologist serves as a leading researcher in global collaboration
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) By ensuring ethnic diversity in a largescale genetic study, an international team of researchers, including a University of Massachusetts Amherst genetic epidemiologist, has identified more regions of the genome linked to type 2 diabetes-related traits.
The findings, published May 31 in Nature Genetics, broaden the understanding of the biological basis of type 2 diabetes and demonstrate that expanding research into different ancestries yields better results. Ultimately the goal is to improve patient care worldwide by identifying genetic targets to treat the chronic metabolic disorder. Type 2 diabetes affects and sometimes debilitates more than 460 million adults worldwide, according to the International Diabetes Federation. About 1.5 million deaths were directly caused by diabetes in 2019, the World Health Organization reports.
Cassandra Spracklen, assistant professor of biostatistics and epidemiology in the UMass Amherst School of Public Health and Health Sciences, is part of the international MAGIC collaboration. That group of more than 400 global academics conducted the genome-wide association meta-analysis, led by the University of Exeter in the United Kingdom.
"Our findings matter because we're moving toward using genetic scores to weigh up a person's risk of diabetes," says Spracklen, one of the paper's lead authors.
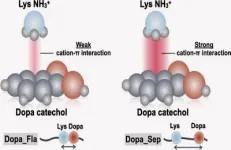
Up to now, some 88% of genomic research of this type has been conducted in white European-ancestry populations. "We know that scores developed exclusively in individuals of one ancestry don't work well in people of a different ancestry," Spracklen adds.
The team analyzed data across a wide range of cohorts, encompassing more than 280,000 people without diabetes. Researchers looked at glycemic traits, which are used to diagnose diabetes and monitor sugar and insulin levels in the blood.
The researchers incorporated 30 percent of the overall cohort with individuals of East Asian, Hispanic, African-American, South Asian and sub-Saharan African origin. By doing so, they discovered 24 more loci - or regions of the genome - linked to glycemic traits than if they had conducted the research in Europeans alone.
"Type 2 diabetes is an increasingly huge global health challenge- with most of the biggest increases occurring outside of Europe," says Inês Barroso, professor of diabetes at the University of Exeter, who led the research. "While there are a lot of shared genetic factors between different countries and cultures, our research tells us that they do differ in ways that we need to understand. It's critical to ensuring we can deliver a precision diabetes medicine approach that optimizes treatment and care for everyone."
First author Ji Chen, a data science expert at the University of Exeter, adds: "Beyond the moral arguments for ensuring research is reflective of global populations, our work demonstrates that this approach generates better results."
Though some loci were not detected in all ancestries, the team found it is useful to capture information about the glycemic trait in individual ancestries.
"This is important as increasingly healthcare is moving toward a more precise approach," Spracklen says. "Failing to account for genetic variation according to ancestry will impact our ability to accurately diagnose diabetes."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-01
The quality of a sewn garment is dependent on the quality of its seams that are the basic structural element. The factors affecting seam quality in garments include sewing thread type and stitch density. Making the right choice of these helps in getting quality seams in garments. However, the choice of suitable sewing threads and stitch densities for particular fabrics can only be determined through testing.
Dr. Patience Danquah Monnie, from the University of Cape Coast, Ghana, with fellow researchers, conducted research aimed to determine sewing thread brand and stitch density suitable for seams for a selected fabric (79% polyester and 21% cotton) for public basic school uniforms in Ghana. For the research, a 2×3 factorial ...
2021-06-01
Nitrates are critical for the growth of plants, so plants have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to ensure sufficient nitrate uptake from their environments. In a new study published in Nature Plants, researchers at Nagoya University, Japan, have identified a plant enzyme that is key to activating a nitrate uptake mechanism in response to nitrogen starvation. This finding explains how plants meet their needs in challenging environments, opening doors to improving agriculture in such environments.
When nitrate levels are plentiful in a plant's environment, a plant can achieve adequate nitrate uptake levels by relying ...
2021-06-01
Oxygen (O2) is an essential gas not only for us and most other lifeforms, but also for many industrial processes, biomedicine, and environmental monitoring applications. Given the importance of O2 and other gases, many researchers have focused on developing and improving gas-sensing technologies. At the frontier of this evolving field lie modern nanogap gas sensors--devices usually comprised of a sensing material and two conducting electrodes that are separated by a minuscule gap in the order of nanometers (nm), or thousand millionths of a meter. When molecules of specific gases get inside this gap, they electronically interact with the sensing layer and the electrodes, altering measurable ...
2021-06-01
The Yakushima sika deer (yakushika: Cervus nippon yakushimae), a subspecies of the Japanese sika deer (Cervus nippon), evolved without natural predators on the island of Yakushima, in Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. It inhabits the forests on the island which were declared a World Heritage Site in 1993. Within the site, the yakushika has not been hunted in the past 50 years; however, since 2014, their population has been decreasing. This phenomenon is especially curious, as Japanese researchers believed that sika deer populations in Japan would not decrease without human intervention.
A group of three scientists, including Hokkaido ...
2021-06-01
Led by the University of Sydney's Charles Perkins Centre, the study looked at medical data from nearly half a million people and found having overweight or obesity considerably amplified the harmful effects of alcohol on liver disease and mortality.
"People in the overweight or obese range who drank were found to be at greater risk of liver diseases compared with participants within a healthy weight range who consumed alcohol at the same level," said senior author and research program director Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis from the Charles Perkins Centre and the Faculty of Medicine and Health.
"Even for people who drank within alcohol guidelines, participants classified as obese were at over 50 percent greater risk of liver disease."
The researchers ...
2021-06-01
Mussels survive by sticking to rocks in the fierce waves or tides underwater. Materials mimicking this underwater adhesion are widely used for skin or bone adhesion, for modifying the surface of a scaffold, or even in drug or cell delivery systems. However, these materials have not entirely imitated the capabilities of mussels.
A joint research team from POSTECH and Kangwon National University (KNU) - led by Professor Hyung Joon Cha and Ph.D. candidate Mincheol Shin of the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH with Professor Young Mee Jeong and Dr. Yeonju Park of the Department ...
2021-06-01
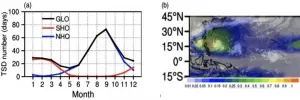
Nearly two billion people live in a region where tropical cyclones (TC) are an annual threat. TCs are deadly and can cause billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide. During peak season in the Northern Hemisphere, typically July through October, about two TCs develop or are ongoing every day. However, this and overall TC frequency vary substantially year-to-year.
To quantify this variability, scientists developed a metric called the tropical storm day (TSD). TSD is a collective measure of how frequently tropical cyclones develop, storm track, and cyclone lifespan, which reflects overall activity. Despite this advancement, researchers have not often studied tropical cyclone variability on a global scale.
Now, ...
2021-06-01
In a paper published in NANO, researchers from Guizhou Meiling Power Sources Co., Ltd., China have reviewed the recent progress in biopolymer-based electrolyte. The biopolymer materials with unique characteristics including water solubility, film-forming capability and adhesive property played a key role in the design of zero pollution lithium battery. The biopolymers mentioned in this review were polysaccharide, protein, natural rubber and other polymers.
For polysaccharide, cellulose with good wettability, low cost and good mechanical properties can enhance the mechanical strength of membranes and improve interfacial stability between electrolyte and electrode. However, the porosity control of cellulose-based membranes was ...
2021-06-01
Habitat change, for example through urbanisation, is one of the most important causes of biodiversity decline. By 2050, settlements and cities across the globe are predicted to increase by two to three million square kilometres - about half the size of Greenland. Natural and semi-natural habitats will thus gradually be replaced by urban habitats.
How wildlife can adapt to such fundamental changes has mostly been studied for a few species groups, such as mammals and birds.
"In order to make predictions about the development of biodiversity as a whole and to combat current phenomena such as insect declines, robust knowledge is also needed for other species groups," ...
2021-06-01
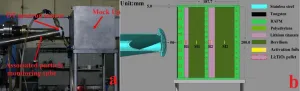
To realize tritium self-sustaining cycle through tritium breeding blanket has been one of the core technologies of future fusion reactor. Therefore the design and function of blanket must be validated by neutronic experiment under D-T neutron environment. But due to the scarcity of DT neutron source, and highly radioactivity during neutronic experiments, it is very difficult to validate the nuclear response of the blanket, the data of tritium production rate mainly rely on Monte Carlo simulation.
Recently, a research group led by ZHU Qingjun from Institute of Plasma Physics, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ethnically diverse research identifies more genetic markers linked to diabetes
UMass Amherst epidemiologist serves as a leading researcher in global collaboration