Survey shows weak trust in Canadian courts on energy projects, climate policy disputes
The University of Ottawa's Positive Energy program released new survey results showing that a large segment of the Canadian public does not trust the courts to settle disputes over energy projects or climate policy
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) The University of Ottawa's Positive Energy program released new survey results showing that a large segment of the Canadian public does not trust the courts to settle disputes over energy projects or climate policy. The survey was conducted by Positive Energy's official pollster, Nanos Research.
Canadians were asked: On a scale of 0 to 10, where 0 means do not trust at all and 10 means trust completely, how much do you trust the courts to settle disputes over government decisions on energy projects? They were asked the same question for climate policy. The results are very similar. Only one in three Canadians trust the courts to settle disputes over energy projects or climate policy (answering between 7 and 10: 31% for energy, 30% for climate). The majority of Canadians answered between 0 and 6 for both questions: one in four do not trust the courts (answering between 0 and 3: 27% for energy; 26% for climate) and about one in three are neutral (scoring between 4 and 6: 31% for energy, 32% for climate). For energy projects, 26% answered between 0 and 3; 31% answered between 4 and 6; 27% answered between 7 and 10; 11% were unsure. For climate policy, 26% answered between 0 and 3; 31% answered between 4 and 6; 27% answered between 7 and 10; 13% were unsure.
Asked why they do or do not trust the courts, the most common responses related to concerns over political interference or bias (27% of responses for energy; 13% for climate). "Respondents who trust the courts on energy and climate change believe the courts are impartial, non-partisan, and have generally done a good job mediating these issues so far. Respondents who do not trust the courts seem particularly concerned about politicization," said Nik Nanos, CEO of Nanos Research and Chair of Positive Energy's Advisory Council.
The survey also asked Canadians about a range of other energy issues, many of which Positive Energy has tracked since 2015. The results show that public confidence in energy decision making is weak across the board, including on federal-provincial cooperation, developing a long-term national energy vision, balancing local and national interests, and building constructive partnerships with Indigenous peoples. Dissatisfaction on these issues is highest in the Prairies and lowest in Quebec.
"These results show governments have a lot of work to do to build public confidence in energy and climate decision-making," said Professor Monica Gattinger, Chair of Positive Energy and Director, Institute for Science, Society and Policy, University of Ottawa. "We were surprised to see such low levels of trust in the courts. This suggests governments need to put in the work to balance competing interests over energy and climate. Resolving controversies in the courts might not strengthen trust in decisions."
The survey was an RDD dual frame (land- and cell-lines) hybrid telephone and online random survey of 1,025 Canadians, 18 years of age or older, between April 29 and May 3, 2021 as part of a Nanos omnibus survey. The margin of error is 3.1 percentage points plus or minus, 19 times out of 20.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-01
Machine learning, when used in climate science builds an actual understanding of the climate system, according to a study published in the journal Chaos by Manuel Santos Gutiérrez and Valerio Lucarini, University of Reading, UK, Mickäel Chekroun, the Weizmann Institute, Israel and Michael Ghil, Ecole Normale Supérieure, Paris, France. This means we can trust machine learning and further its applications in climate science, say the authors. The study is part of the European Horizon 2020 TiPES project on tipping points in the Earth system. TiPES is administered from the University of Copenhagen, Denmark.
Man or ...
2021-06-01
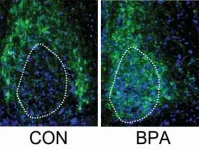
Humans are exposed to a bath of chemicals every day. They are in the beds where we sleep, the cars that we drive and the kitchens we use to feed our families. With thousands of chemicals floating around in our environment, exposure to any number is practically unavoidable. Through the work of researchers like Dr. Deborah Kurrasch, PhD, the implications of many of these chemicals are being thoroughly explored.
"Manufacturers follow standards set by regulatory bodies, it's not up to the manufacturers to prove the chemicals in consumer products are safe," says Kurrasch, a researcher in the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain ...
2021-06-01
Right-wing voices set out powerful but misleading arguments to justify inaction by the Trump administration during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study of the rhetoric used by high-level government officials and influential commentators in the US during the first half of 2020.
In a study published in the DeGruyter journal Open Anthropological Research, Professor Martha Lincoln of San Francisco State University examined how public officials openly pushed for people to accept widespread illness and death from the virus by adopting a tone that suggested premature death was normal and the scale of death acceptable in the grander ...
2021-06-01
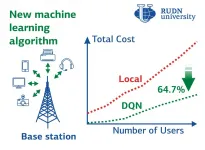
RUDN mathematician and his colleagues from China, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, United Kingdom, and Qatar have developed an algorithm allowing the distribution of computing tasks between the IoT devices and the cloud in an optimal way. As a result, the power and time costs are reduced by about three times. The study was published in the Big Data.
With the development of technologies and devices, Internet of Things (IoT) applications require more and more computing power. The amount of data that the IoT devices need to process can be so large that it is reasonable to migrate computing to the cloud. Cloud computing provides flexible data processing and storage capabilities. But Computation offloading, meaning transferring of the resource-intensive processes ...
2021-06-01
A DTU research team consisting of Malgorzata Gosia Pierchala, Firoz Babu Kadumundi, and Mehdi Mehrali from #TeamBioEngine headed by Alireza Dolatshahi-Pirouz, have developed a new material - CareGum - that among other things has potential for monitoring motor impairment associated with neurological disorders such as Parkinson's.
A green material with many properties
The CareGum property portfolio is incredibly broad with feats such as skin-like softness, it is stretchable up to 30,000 % and has self-healing capacities reminiscent of that of natural tissues. It is printable, moldable, and electrically conductive. Notably, the electrical conductivity enables the material to respond to external stimuli ...
2021-06-01
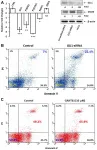
Oncotarget published "STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells" which reported that what induces GLI1 expression in GLI1-unmutated CLL cells is unknown.
Because signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is constitutively activated in CLL cells and sequence analysis detected putative STAT3-binding sites in the GLI1 gene promoter, the authors hypothesized that STAT3 induces the expression of GLI1.
Western immunoblotting detected GLI1 in CLL cells from 7 of 7 patients, flow cytometry analysis confirmed that CD19 /CD5 CLL cells co-express GLI1 and confocal microscopy showed co-localization of GLI1 and phosphorylated STAT3. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed ...
2021-06-01
A series of autopsies performed in an infectious disease hospital in the Brazilian Amazon reveals that infections by the Histoplasma fungus are a major cause of death in people with HIV. The study, led by Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by "la Caixa" Foundation, in collaboration with a team in Manaus, highlights the need of implementing sensitive methods to detect these infections in Histoplasma-endemic regions.
Histoplasmosis is a lung infection caused by inhalation of spores from a fungus (Histoplasma), and is frequent in some areas of the US, Africa, and Latin America.
In the majority of individuals with a functional immune system, the infection causes mild symptoms. However, in people who are immuno-compromised, such ...
2021-06-01
Scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) in Japan have developed a technology that produces high-resolution simulations of one of the basic units of our genomes, called the nucleosome. Their findings were published in the journal Nature Protocols and should help improve understanding of how changes in nucleosome folding influence the inner workings of genes.
Nucleosomes are the basic structural units of DNA packaging inside the nucleus. They are formed of DNA wrapped around a small number of histone proteins. Nucleosomes move around inside the nucleus, folding and unfolding, changing their orientations, and moving closer together or further apart. These movements affect the accessibility of various molecules to DNA, determining ...
2021-06-01
A new discovery in Ewing sarcoma, an aggressive and often fatal childhood cancer, has uncovered the potential to prevent cancer cells from spreading beyond their primary tumour site.
The breakthrough provides new insight into what triggers the process that allows cancer cells to survive while traveling through the body in the bloodstream.
Researchers with the University of British Columbia and BC Cancer have learned that Ewing sarcoma cells--and likely other types of cancer cells--are able to develop a shield that protects them from the harsh environment of the bloodstream and other locations as they search for a new place to settle, or metastasize. The study has just been published in Cancer Discovery.
"You ...
2021-06-01
TROY, N.Y. -- As more dissolved organic matter enters lakes across the northeast United States, darkening the lakes in a phenomena called "browning," new research shows that these waters may be growing less productive and able to sustain less life. In a study published today in Limnology and Oceanography Letters, scientists found that, rather than enriching lakes with nutrients as had previously been assumed, water more heavily laden with dissolved organic matter blocks sunlight and limits plant growth.
"A key question regarding lake browning is what impact it will have on aquatic food webs, including algal growth and fisheries," said Kevin Rose, co-author ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Survey shows weak trust in Canadian courts on energy projects, climate policy disputes
The University of Ottawa's Positive Energy program released new survey results showing that a large segment of the Canadian public does not trust the courts to settle disputes over energy projects or climate policy