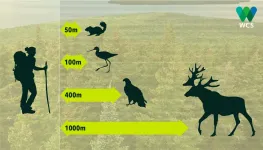
(Press-News.org) Spending time outdoors is good for a person's body and soul, but how good is it for the wildlife around us?
Outdoor recreation has become a popular activity, especially in the midst of a pandemic, where access to indoor activities might be limited. Long known to have negative behavioural and physiological effects on wildlife, outdoor recreation is one of the biggest threats to protected areas. Human disturbance to animal habitats can lower their survival and reproduction rates, and ultimately shrink populations or eradicate them from areas where they would otherwise thrive. Still, park planners and natural resource managers often can't find clear recommendations on how to limit these impacts.
A END
Safe distance: How to make sure our outdoor activities don't harm wildlife
2021-06-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study pinpoints key causes of ocean circulation change
2021-06-01
Researchers have identified the key factors that influence a vital pattern of ocean currents.
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) carries warm water from the tropics northward.
Many scientists think that this heat transport makes areas including north-west Europe and the UK warmer than they would otherwise be.
Climate models suggest the AMOC is likely to weaken over the coming decades, with widespread implications for regional and global climate.
The new study - led by the universities of Exeter and Oxford, and published in Nature Geoscience - pinpoints the causes of monthly and annual AMOC variation and finds a differing picture at two key locations.
Observational data came from large ...
Sick bats also employ 'social distancing' which prevents the outbreak of epidemics
2021-06-01
The Covid-19 pandemic has introduced us to expressions like 'lockdown', 'isolation' and 'social distancing', which became part of social conduct all over the world. Now it appears that bats also maintain social distancing which might help prevent the spread of contagious diseases in their colonies. In a new study published in Annals of the New York Academy of Science, researchers from Tel Aviv University demonstrate that sick bats, just like ill humans, prefer to stay away from their communities, probably as a means for recovery, and possibly also as a measure for protecting others. The study was conducted by postdoctoral researcher Dr. Kelsey Moreno and PhD candidate Maya Weinberg ...
Is the U.S. Understating Climate Emissions from Meat and Dairy Production?
2021-06-01
Methane emissions from North American livestock may be routinely undercounted, a new analysis by researchers at New York University and Johns Hopkins University finds. The work also notes that in developing countries, where animal agriculture is becoming increasingly industrialized, methane emissions could rise more than expected.
These assessments are based on a review, appearing in the journal Environmental Research Letters, of eight existing studies.
Methane is a global warming gas even more powerful than CO2. Its amount and lifetime in the atmosphere are smaller than CO2, but quantities are still increasing. The United Nations has recently ...
Scientists develop new method for ultra-high-throughput RNA sequencing in single cells
2021-06-01
RNA sequencing is a powerful technology for studying cells and diseases. In particular, single-cell RNA sequencing helps uncover the heterogeneity and diversity of our body. This is the central technology of the "Human Cell Atlas" in its quest to map all human cells. However, single-cell RNA sequencing reaches its limits in very large projects, as it is time-consuming and very expensive. To address these challenges, scientists from the research group of Christoph Bock, principal investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and professor at the Medical University of Vienna, developed ...
A mechanism that reduces blood vessels in Alzheimer's patients
2021-06-01
Researchers at the Biomedicine Institute of Seville (IBiS) have discovered a new mechanism of Alzheimer's disease that disorganises the blood vessels around amyloid plaques, one of the characteristic features of the disease. The study, published in the international journal Nature Communications, was led by the laboratory of Dr. Alberto Pascual, from the Neuronal Maintenance Mechanisms Group at IBiS and was chiefly carried out by María Isabel Álvarez Vergara and Alicia E. Rosales-Nieves.
Relevance of the finding
Alzheimer's disease is the leading cause of dementia worldwide. In Spain, its incidence is increasing dramatically as the population ages and yet, unfortunately, the origin of the disease is still unknown.
The mechanism put forward ...
Low levels of omega-3 associated with higher risk of psychosis
2021-06-01
New research has found that adolescents with higher levels of an omega-3 fatty acid in their blood were less likely to develop psychotic disorder in early adulthood, suggesting that it may have a potential preventative effect of reducing the risk of psychosis.
The study, led by researchers from RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, is published in END ...
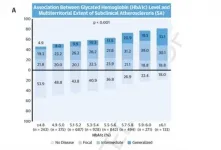
A blood sugar biomarker identifies patients with atherosclerosis and a risk of cardiovascular events
2021-06-01
The routine use of the glycosylated hemoglobin test to track blood sugar levels in the general population can identify individuals with more advanced atherosclerotic disease. Currently used in the diagnosis and management of diabetes, glycosylated hemoglobin can provide a useful estimate of atherosclerotic disease, and therefore of cardiovascular risk, in individuals without diabetes with or without possible prediabetes. This is the main finding of a study carried out by scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC).
The advance heralded by the CNIC study is the use of this blood-sugar measure in apparently healthy middle-aged ...
Zhores supercomputer helps Skoltech researchers model new method of generating gamma-ray combs
2021-06-01
Skoltech researchers used the resources of the university's Zhores supercomputer to study a new method of generating gamma-ray combs for nuclear and X-ray photonics and spectroscopy of new materials. The paper was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
A gamma-ray comb is a series of short bursts that, when plotted as intensity versus frequency, look like sharp and equally spaced teeth of a comb. Generating these combs at high brightness in the gamma-ray domain has been challenging because of something called ponderomotive spectral broadening - an effect that destroys the monochromaticity that allows gamma-ray sources to be used in nuclear spectroscopy, medicine, and other applications.
Sergey ...
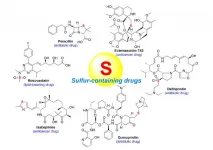
Chemistry and biology of sulfur containing natural products from marine microorganisms
2021-06-01
The intriguing chemistry and biology of sulfur?containing natural products from marine microorganisms (1987-2020)
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-021-00101-2
Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this review article the authors Yang Hai, Mei?Yan Wei, Chang?Yun Wang, Yu?Cheng Gu and Chang?Lun Shao from Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China and Syngenta Jealott's Hill International Research Centre, Berkshire, UK consider the chemistry and biology of sulfur?containing natural products from marine microorganisms.
Natural products derived ...
Academic journal Polar Science features science in the Arctic
2021-06-01
The National Institute of Polar Research (NIPR) publishes Polar Science, a peer-reviewed quarterly journal dealing with polar science in collaboration with the Elsevier B. V.. The most recent issue (Vol. 27 published in March 2021) was a special issue entitled "Arctic Challenge for Sustainability Project (ArCS)," which featured the former national (nation-wide) Arctic research project in Japan. The full text of this issue is freely accessible worldwide for a limited time until 10 September 2021.
The Arctic Research Project "Arctic Challenge for Sustainability (ArCS)" was carried out from September 2015 to March 2020 as a national flagship project funded by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, ...