Tuberculosis in Irish prisons: New study recommends increased testing
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) Investigators from Trinity College Dublin, the Irish Mycobacteria Reference Laboratory, St James's Hospital, and the Department of Public Health HSE East believe tuberculosis (TB) care in Irish Prisons should be supported, considering the findings of their study which is published today (Tuesday, 1st June, 2021) in the International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease.
The study describes an investigation into a large outbreak of tuberculosis which occurred in an Irish prison in 2011. This resulted in 34 people contracting active TB from a single infectious case. The use of Whole Genome Sequencing enabled the investigators to track the course of onward transmission, and to link TB cases identified as recently as 2019 to the 2011 outbreak.
The outbreak resulted in litigation costs to the State of more than €5 million euro. The study found that in addition to the active TB cases, 50% of the prison staff tested as close contacts of cases may have developed Latent TB as a result of occupational exposure. This is an asymptomatic, non-infectious form of TB, which may progress to the active form of TB at a future date, in a small number of cases.
Professor Joe Keane, Clinical Medicine, Trinity College Dublin and St James's Hospital Dublin, and co-senior author of the study said:
"This report shows that tuberculosis is an issue in our prisons and will be followed by a 'test and educate' programme- that will mitigate the risk in congregate settings."
Professor Tom Rogers, Clinical Microbiology, Trinity, and formerly Clinical Director, Irish Mycobacteria Reference Laboratory (IMRL) based at St. James's Hospital, said:
" This report demonstrates the power of whole genome sequencing to enhance epidemiological investigations of TB outbreaks over prolonged periods of time. The IMRL has created a national database of TB genomes which will facilitate future public health investigations of TB in Ireland."
Dr Marcus Butler, vice-president, Irish Thoracic Society said:
"This study, along with recommendations from the CDC TB controllers association and a recent review of TB rates in prisons published by The Lancet Public Health, supports the need for improving early TB diagnosis and care in the Irish prison system, through a three-step approach:
1) A TB information and testing service in prisons
2) A Latent TB clinic at St James's Hospital Dublin
3) A National TB lead to oversee this as part of an integrated national TB control service
This integrated national service should comprise a national TB screening programme for high risk groups, investment in contact tracing and TB surveillance activities, and a TB education and awareness programme for healthcare professionals and the public."
Dr Mary O Meara, Specialist in Public Health Medicine , HSE East said:
"This report supports the need for augmenting the public health contact tracing response for infectious diseases such as tuberculosis."
INFORMATION:
More information: A PDF version of the paper 'The largest prison outbreak of TB in Western Europe investigated using whole-genome sequencing' is available upon request to coshea9@tcd.ie
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-01
Researchers working under the leadership of the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have conducted the first precise and comprehensive measurements of sea level rises in the Baltic Sea and the North Sea. A new method now makes it possible to determine sea level changes with millimeter accuracy even in coastal areas and in case of sea ice coverage. This is of vital importance for planning protective measures.
For the billions of people who live in coastal areas, rising sea levels driven by climate change can pose an existential threat. "To protect people and infrastructure - for example by building flood protection structures, securing ports or making ...
2021-06-01
Cells have to constantly adapt to their surroundings in order to survive. A sudden increase in the environmental levels of an osmolyte, such as salt, causes cells to lose water and shrink. In a matter of seconds, they activate a mechanism that allows them to recover their initial water volume and avoid dying.
Finding out which genes are involved in surviving osmotic stress was the subject of a study led by the laboratories of Dr. Posas and Dr. de Nadal at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and Dr. Valverde at Pompeu Fabra University (UPF), in collaboration with a group led by Dr. Moffat from the University of Toronto (Canada). wide-genome genetic screening, the scientists discovered the central role of a gene known as LRRC8A in cellular ...
2021-06-01
In a joint effort, ct.qmat scientists from Dresden, Rostock, and Würzburg have accomplished non-Hermitian topological states of matter in topolectric circuits. The latter acronym refers to topological and electrical, giving a name to the realization of synthetic topological matter in electric circuit networks. The main motif of topological matter is its role in hosting particularly stable and robust features immune to local perturbations, which might be a pivotal ingredient for future quantum technologies. The current ct.qmat results promise a knowledge transfer from electric circuits to alternative optical platforms, and have just been published in Physical Review Letters.
Topological defect tuning in non-Hermitian systems
At the center of the currently reported work is the ...
2021-06-01
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is used to disinfect minor cuts at home and for oxidative reactions in industrial manufacturing. Now, the pandemic has further fueled demand for this chemical and its antiseptic properties. While affordable at the grocery store, H2O2 is actually difficult and expensive to manufacture at scale.
A team led by the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has demonstrated a more efficient and environmentally friendly method to produce H2O2, according to a recent study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
"While the two ingredients--hydrogen and oxygen--are either inexpensive or freely available from the atmosphere, hydrogen peroxide is highly reactive and unstable, which makes it very hard to produce," said first author Tomas ...
2021-06-01
TAMPA, Fla. - Moffitt Cancer Center, a national leader in cancer care and research and the only National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center based in Florida, is presenting new data from dozens of clinical research studies at this year's American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, the world's largest clinical cancer research meeting. Moffitt investigators will lead 25 abstract presentations, five education sessions, two cancer-based panels and two clinical science symposia. The virtual meeting is June 4-8.
Highlights include:
Oral Presentations:
Dr. Bijal Shah will ...
2021-06-01
Physicists at the University of Bath in the UK, in collaboration with researchers from the USA, have uncovered a new mechanism for enabling magnetism and superconductivity to co-exist in the same material. Until now, scientists could only guess how this unusual coexistence might be possible. The discovery could lead to applications in green energy technologies and in the development of superconducting devices, such as next-generation computer hardware.
As a rule, superconductivity (the ability of a material to pass an electrical current with perfect efficiency) and magnetism (seen at work in fridge magnets) make poor bedfellows because the alignment of the tiny electronic magnetic particles in ferromagnets ...
2021-06-01
A catastrophic drop in atmospheric ozone levels around the tropics is likely to have contributed to a bottleneck in the human population around 60 to 100,000 years ago, an international research team has suggested. The ozone loss, triggered by the eruption of the Toba supervolcano located in present-day Indonesia, might solve an evolutionary puzzle that scientists have been debating for decades.
"Toba has long been posited as a cause of the bottleneck, but initial investigations into the climate variables of temperature and precipitation provided no concrete ...
2021-06-01
In interstellar dust clouds, turbulence must first dissipate before a star can form through gravity. A German-French research team has now discovered that the kinetic energy of the turbulence comes to rest in a space that is very small on cosmic scales, ranging from one to several light-years in extent. The group also arrived at new results in the mathematical method: Previously, the turbulent structure of the interstellar medium was described as self-similar - or fractal. The researchers found that it is not enough to describe the structure mathematically as a single fractal, a self-similar structure as known from the Mandelbrot set. Instead, they added several different fractals, so-called multifractals. The new methods can thus be used to resolve ...
2021-06-01
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new state-of-the-art method for controlling how artificial intelligence (AI) systems create images. The work has applications for fields from autonomous robotics to AI training.
At issue is a type of AI task called conditional image generation, in which AI systems create images that meet a specific set of conditions. For example, a system could be trained to create original images of cats or dogs, depending on which animal the user requested. More recent techniques have built on this to incorporate conditions regarding an image layout. This allows users to specify which types of objects they want to appear in particular places on the screen. ...
2021-06-01
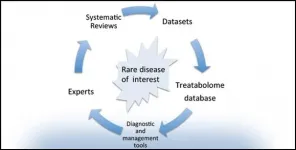
Amsterdam, June 1, 2021 - The Treatabolome project is a research initiative to develop a freely available, interoperable online platform dedicated to disseminating rare disease and gene-specific treatment information to healthcare professionals regardless of their level of specialized expertise. Developed under the Solve-RD European Research Project, it is intended to reduce treatment delays for patients with rare diseases by directly linking diagnosis and treatment information. This initiative is highly relevant to neuromuscular disorders as they are rare diseases by definition. In this special issue of the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases, experts contribute Treatabolome-feeding systematic literature reviews on rare neurological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tuberculosis in Irish prisons: New study recommends increased testing