(Press-News.org) The discovery of graphene, a 2D layered form of carbon, once caused a paradigm shift in science and technology like no other. As this wonder material drew attention from material scientists around the world, it spurred research on other materials that were structurally similar, such as "van der Waals materials", which comprise strongly-bonded 2D atomic layers that are held together by weak interlayer interactions called "van der Waals forces". These materials quickly caught on because they were highly conducive to structural modifications, such as stacking, twisting, and insertion of foreign molecules between layers, which gave them interesting physical properties with several practical applications.
At about the same time, there emerged another remarkable class of materials called "high-entropy alloys" (HEA). HEA are formed by mixing five or more metals in specific concentrations such that an infinite number of potential combinations are possible simply by tuning their spin (intrinsic angular momentum), charge, and composition! Notable properties of HEAs include their high toughness and corrosion resistance. Thus, just like van der Waals materials, HEAs too have several unique applications.
Now, a team of scientists from Japan and China has attempted to merge these two types of materials to form something that inherits the desirable properties of both. Prof. Hideo Hosono from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan, who is the pioneer of 2D-electride materials, and led the study, outlines their motivation: "The marriage of these two materials would bring us more degrees of freedom and expand the territory of both, opening up newer application possibilities."
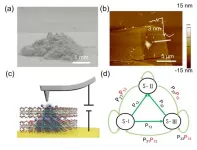
In their study, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the team first synthesized polycrystalline and single crystal samples of the new materials, which they called "high-entropy van der Waals", or HEX, materials. They then characterized the structures and chemical states of these new materials using X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, respectively. Among the physical properties they measured were resistivity, magnetic ordering, and heat capacity. They also measured the materials' corrosion resistance in acid, base, and organic solutions.
The HEX materials came from three categories of van der Waals (vdW) materials, namely, metal dichalcogenides (of formula ME2, M = metal, E = Sulphur, Selenium, Tellurium), halides, and phosphorus trisulfide (PS3), each of which was mixed with a unique combination of transition metals e.g. iron, nickel, cobalt, manganese.
The team found that by introducing multiple components, they could induce several remarkable physical properties such as superconductivity (dichalcogenide HEX), magnetic ordering (PS3 HEX), metal-insulator transition (dichalcogenide HEX), and strong corrosion resistance (dichalcogenide HEX).
With these encouraging findings, the team contemplates practical applications of HEX materials. "The high corrosion resistance could be a promising route for the design of heterogeneous catalysts. The concept of high entropy could also be introduced to other low-dimensional materials, and considering their infinite possibilities, we think these materials deserve the focus of the research community," says an excited Prof. Hosono.
An infinitude of possibilities is hard to ignore!
INFORMATION:
Getting enough sleep can be a real challenge for shift workers affecting their overall health. But what role does being an early bird or night owl play in getting good rest? Researchers from McGill University find a link between chronotype and amount of sleep shift workers can get with their irregular schedules.
"Some people seem to be hardwired to sleep early, while others tend to sleep late. This preference, called chronotype, is modulated by our circadian system - each person's unique internal timekeeper," says lead author Diane B. Boivin, a Professor in the Department of Psychiatry at McGill University.
Their study published in Sleep is the first to examine the relationship between ...
Algorism plays a significant role in predicting future states of a system. Particularly, non-Markov chain algorithm has been widely applied in epidemic spreading processes, social and man-made memory networks, the environment-related quantum entangled states, and artificial algorisms such as face pose tracking. Traditionally, a large number of memories and computing cells are integrated to achieve these goals by software algorisms, showing high complexity. In the paper published in Science Bulletin, a group led by Bilu Liu and Hui-Ming Cheng from Tsinghua-Berkeley Shenzhen Institute (TBSI) of Tsinghua University has realized a non-Markov chain algorithm in a single resistive random access memory (RRAM) based on 2D mineral material ...
Swedish researchers from institutions including Uppsala University have spent four years gathering data from the areas affected by the major forest fire of 2014. In their study of how the ecosystem as a whole has been altered, they could see that water quality in watercourses quickly returned to normal, while forested areas continued to lose carbon for many years after the fire.
The consequences of major forest fires remain poorly studied in Northern Europe. To improve this situation, researchers from Uppsala University, the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU) and the Swedish Meteorological ...
Siberian jays are group living birds within the corvid family that employ a wide repertoire of calls to warn each other of predators. Sporadically, however, birds use one of these calls to trick their neighbouring conspecifics and gain access to their food. Researchers from the universities of Konstanz (Germany), Wageningen (Netherlands), and Zurich (Switzerland) have now examined how Siberian jays avoid being deceived by their neighbours. The study, published in the journal Science Advances, shows that these birds have great trust in the warning calls from members of their own group, but mainly ignore such ...
News media reports about scientific failures that do not recognize the self-correcting nature of science can damage public perceptions of trust and confidence in scientific work, according to findings by researchers at the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania and the University at Buffalo, the State University of New York.
News stories about science follow several specific narratives, the researchers write in a new study in the journal Public Understanding of Science. One is that science is "in crisis" or "broken," a narrative driven in recent years by reports of unsuccessful efforts to replicate findings in ...
A new miniature 3D model of human bone marrow has been described today in the open-access eLife journal.
The model may help clinicians predict which patients will benefit from a new therapy for blood platelet disorders, such as Inherited Thrombocytopenias - a group of familial disorders that inhibit the production of platelets. It could also enable further study of these disorders and give scientists a new tool to test experimental treatments.
Platelets are cells that are necessary for the blood to clot and stop bleeding. Having too few platelets can lead to internal or serious bleeding after surgery or injuries, which is usually treated with therapies that cause clotting. Recent studies have shown that a drug called Eltrombopag increases ...
A college education is estimated to add $1 million to a person's lifetime earning potential, but for some students the path to earning one is riddled with obstacles. That journey is even more difficult for students who have been in the foster care system or experienced homelessness, according to a new study from the University of Georgia.
But the more college administrators and faculty know about these students' problems, the more they can do to ease the burden.
Getting into universities in the first place can frequently be a challenge for students who've had unstable home lives, said David Meyers, co-author of the study.
"Research tells us that every time a student moves from one foster care placement to another, they lose six months of educational ...
In recent months, more than three hundred cases of salmonellosis have occurred in various European countries and Canada, which are linked to each other. In the UK the cases could be partly traced back to frozen breaded poultry meat. The cause was contamination with the bacterium Salmonella Enteritidis, which causes gastrointestinal inflammation. Salmonella is not killed by deep freezing and can remain infectious at temperatures below zero degrees Celsius. The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) and the BfR are monitoring the situation together with the Federal Office of Consumer Protection and Food Safety (BVL). In Germany, the number of reported cases has currently ...
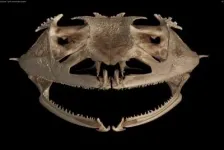
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Scientists have long known that frogs are oddballs when it comes to teeth. Some have tiny teeth on their upper jaws and the roof of their mouths while others sport fanglike structures. Some species are completely toothless. And only one frog, out of the more-than 7,000 species, has true teeth on both upper and lower jaws.
Now, the first comprehensive study of tooth evolution in frogs is bringing the group's dental history into focus. Florida Museum of Natural History researchers analyzed CT scans of nearly every living amphibian genus to reveal that frogs have lost teeth over 20 times during their evolution, more than any ...
DANVILLE, Pa. - Among people who have strokes and COVID-19, there is a higher incidence of severe stroke as well as stroke in younger people, according to new data from a multinational study group on COVID-19 and stroke, led by a team of Geisinger researchers.
The COVID-19 Stroke Study Group's latest report, published in the journal END ...