INFORMATION:
Global costs of Plasmodium vivax malaria estimated for the first time
2021-06-01
(Press-News.org) Plasmodium vivax malaria is a mosquito-borne illness that causes significant morbidity. However, the household and healthcare provider costs of the disease are unknown. A new study published in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Dr Angela Devine at Menzies School of Health Research in Australia, and colleagues estimate the global economic burden of P. vivax for the first time using country-level data.
Researchers first estimated household and healthcare provider P. vivax costs, then collated and combined these data with national case estimates for 44 endemic countries in 2017. The resulting global cost estimate was US$359 million.
The authors wanted to explore how these cost estimates might change with widespread access to radical cure. Radical cure refers to a sustained clinical response and prevention of future relapses caused by the dormant liver parasites of P. vivax, requiring complete elimination of both the blood and liver stages of the parasites. New treatments and screening procedures can achieve radical cure, however, the cost benefit of universal access to radical treatment for those who can safely receive it has not been previously estimated.
To analyze the potential cost of a radical cure health policy compared to the costs associated with P. vivax, the authors built a model which simulated two malaria treatment scenarios: 1) complete adherence following daily supervised primaquine therapy; and 2) unsupervised treatment with an assumed 40% effectiveness.
The results suggest that adopting a policy of screening and supervising administration of primaquine to all eligible patients could lower the global cost burden of P. vivax substantially. However, further studies are needed as the model only included costs and benefits over a one-year time horizon (2017) and did not include the benefits in terms of reductions in transmission of P. vivax, which likely underestimated the benefits. Conversely, the costs of scaling up the implementation of the radical cure interventions were not included, likely underestimating the costs.
According to the authors, "Provision of safe and effective radical cure is possible but will require an increased investment that could be a disincentive to national malaria control programs. Our findings suggest that such an investment could ensure high anti-relapse effectiveness with substantial cost savings at the societal level and reductions in vivax malaria case numbers."
"We estimated a global cost of 359 million US dollars due to vivax malaria in 2017. This burden, which largely falls on rural communities with poor access to care, could be reduced through widespread access to safe and effective radical cure, which will be essential to achieving elimination of P. vivax. Future research should focus on low-cost methods of ensuring adherence to treatment regimens and expanding our understanding of how the costs of malaria episodes vary across endemic countries," Dr Angela Devine further explained."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Vitamin D may not provide protection from COVID-19 susceptibility or disease severity
2021-06-01
Observational studies have suggested that increased vitamin D levels may protect against COVID-19. However, these studies were inconclusive and possibly subject to confounding. A study published in PLOS Medicine by Guillaume Butler-Laporte and Tomoko Nakanishi at McGill University in Quebec, Canada, and colleagues suggests that genetic evidence does not support vitamin D as a protective measure against COVID-19.
The ability of vitamin D to protect against severe COVID-19 illness is of great interest to public health experts, but has limited supporting evidence. To assess the relationship between vitamin D levels and COVID-19 susceptibility ...
When should screening start for men with a family history of prostate cancer?
2021-06-01
A nationwide study in Sweden estimates the elevated risk of advanced or fatal prostate cancer among relatives of men with the disease, providing new data that could help refine guidelines for the age at which screening should begin. Mahdi Fallah and Elham Kharazmi of the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Heidelberg, Germany, and colleagues present these new findings in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
Clinical guidelines for the age to start prostate cancer screening aim to ensure that the benefits of identifying the disease early ...
Malaria parasite's partiality for the spleen
2021-06-01
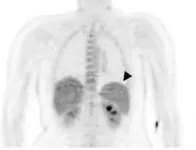
The malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax may accumulate in the spleen soon after infection to a greater extent than its better-known relative P. falciparum, according to new research published by John Woodford of the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia and colleagues in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
Managing and treating P. vivax and P. falciparum infections calls for investigation of their different pathways of infection, and our limited understanding of disease pathology has generally relied on indirect and imprecise approaches. Woodford and colleagues studied 7 healthy participants who were infected under controlled conditions with either P. vivax or P. falciparum. They underwent a Positron Emission Tomography (PET) ...
How best to focus efforts on classifying new species to prevent their extinction?
2021-06-01
Many organisms in need of conservation are still unknown or lumped in with similar species, which potentially interferes with conservation efforts. In a new study published June 1 in the Open Access journal PLOS Biology, Jane Melville of Museums Victoria, and her colleagues present a new "return-on-investment" approach to best direct efforts to identify new species before they are lost.
Humans have had a profoundly destructive impact on global biodiversity. However, this loss of biodiversity may be even greater than scientists have realized, due to the unknown number of undocumented species. Before a species and its habitat can be preserved, though, it must first ...
Canadian prescription opioids users experience gaps in access to care
2021-06-01
Stigma and high care needs can present barriers to the provision of high-quality primary care for people with opioid use disorder (OUD) and those prescribed opioids for chronic pain. A study published in PLOS Medicine by Tara Gomes at the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St. Michael's Hospital, Toronto, Canada and colleagues suggests that people treated for an opioid use disorder were less likely to find a new primary care provider (PCP) within one year of termination of enrolment with the previous physician.
People with substance use disorders often have complex medical needs, requiring ...
Healthy lifestyle linked to better cognition for oldest adults -- regardless of genetic risk
2021-06-01
A new analysis of adults aged 80 years and older shows that a healthier lifestyle is associated with a lower risk of cognitive impairment, and that this link does not depend on whether a person carries a particular form of the gene APOE. Xurui Jin of Duke Kunshan University in Jiangsu, China, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine.
The APOE gene comes in several different forms, and people with a form known as APOE ε4 have an increased risk of cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Previous research has also linked cognitive function to lifestyle factors, such as smoking, ...
Parasites may accumulate in spleens of asymptomatic individuals infected with malaria
2021-06-01
Malaria, a disease caused mainly by the parasites Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, (P. vivax) is associated with over 400,000 deaths each year. Previously, the spleen was assumed to mostly play a role in parasite destruction, as it eliminates malaria parasites after antimalarial treatment. A study published in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Steven Kho and Nicholas Anstey at Menzies School of Health Research, Australia, and international colleagues, suggests that in chronic P. vivax infections, malaria parasites survive and replicate via a previously undetected lifecycle within the spleen.
A large biomass of intact asexual-stage ...
Improved detection of atrial fibrillation could prevent disabling strokes
2021-06-01
A clinical trial examining the efficacy of two devices to monitor and detect atrial fibrillation (AF), or an irregular heartbeat, in ischemic stroke patients--one an implantable device that monitors over 12 months, the other an external device that monitors over a 30-day period--found the implantable device is more than three times more effective in detecting AF, and both are a significant improvement over the current standard of care in Alberta, Canada.
The Post-Embolic Rhythm Detection With Implantable Versus External Monitoring (PER DIEM) study, led jointly by University of Alberta ...
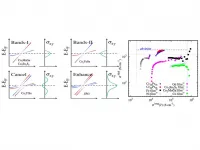
Harmonious electronic structure leads to enhanced quantum materials
2021-06-01
The electronic structure of metallic materials determines the behavior of electron transport. Magnetic Weyl semimetals have a unique topological electronic structure - the electron's motion is dynamically linked to its spin. These Weyl semimetals have come to be the most exciting quantum materials that allow for dissipationless transport, low power operation, and exotic topological fields that can accelerate the motion of the electrons in new directions. The compounds Co3Sn2S2 and Co2MnGa [1-4], recently discovered by the Felser group, have shown some of the most prominent effects due to a set of two topological bands.
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute ...
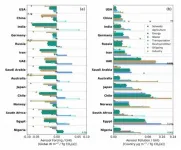
If countries implement Paris pledges with cuts to aerosols, millions of lives can be saved
2021-06-01
Aerosol reductions that would take place as countries meet climate goals could contribute to global cooling and prevent more than one million annual premature deaths over a decade, according to a new study from the University of California San Diego.
The landmark Paris Agreement of 2016 does not address emissions of aerosols--fine particulates like soot that cause pollution. Nonetheless, findings from the recent study authored by researchers at UC San Diego's Scripps Institution of Oceanography and the School of Global Policy and Strategy suggests that aerosol accounting should be explicitly incorporated into international climate policy.
It is crucial because as countries implement their greenhouse gas reduction targets under the Paris climate agreement, ...