(Press-News.org) Almost half of the world's population currently lives in cities and that number is projected to rise significantly in the near future. This rapid urbanization is contributing to increased flood risk due to the growing concentration of people and resources in cities and the clustering of cities along coastlines.
These urban shifts also result in more complex and interconnected systems on which people depend, such as transportation networks. Disruptions to urban traffic networks from flooding or other natural disasters can have serious socioeconomic consequences. In fact, what are defined as indirect impacts from these types of events, such as commute-related employee absences, travel time delays and increase in vehicular accident rates, could ultimately outweigh the more direct physical damage to roads and infrastructure caused by severe flooding.
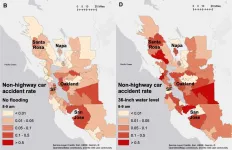
Stanford researchers examined traffic networks in the San Francisco Bay Area (SF Bay Area) as a case study to quantify the indirect impacts of sea-level rise and intensifying coastal flood events on urban systems. Specifically, the researchers sought to identify the effects flooding would have on traffic delays and safety, particularly as road closures rerouted vehicles into adjacent streets and residential neighborhoods not designed to handle heavy vehicle flows. The research was published in the May issue of Urban Climate.
"The goal is to highlight road safety in future climate adaptation planning," said lead study author Indraneel Kasmalkar, an engineering PhD candidate affiliated with the Stanford Institute for Computational and Mathematical Engineering (ICME).
Similar to many other regions across the country, the SF Bay Area has dense urban development concentrated along its coastline and heavily congested traffic grids. Currently, even relatively minor instances of coastal flooding have the potential to inundate major traffic corridors and increase already lengthy commute times and traffic accidents.
"I think one of the key issues about traffic in the Bay is that we're already pretty close to the limit," said senior study author Jenny Suckale, an assistant professor of geophysics at Stanford University's School of Earth, Energy & Environmental Sciences (Stanford Earth). "That's also why some of the relatively minor degrees of water level we're considering here can make quite a difference."
For coastal flooding events, three types of flood impacts were identified: impassable commutes where the origin, destination or critical road connections are flooded and impede driving; travel time delays caused by commuters rerouting to avoid flooded roadways; and increases in car and pedestrian accident rates in communities that experience high inflows of traffic as commuters reroute onto local roads.
The study highlights the challenges of preparing the traffic network in the Bay Area for climate change. Increasing coastal flooding could lead to significant travel time delays across the entire Bay Area, including communities that do not encounter any flooding themselves. However, focusing exclusively on reducing travel time delays may be problematic as some communities will be impacted by coastal flooding primarily through an increase in accident rates.
The research is a followup to the team's recent findings published in Science Advances that revealed commuters living outside the areas of flooding may experience some of the largest commute delays in the Bay Area due to the nature of road networks in the region.
"The two studies provide interesting contrasts on the resilience of communities to flood impacts," Kasmalkar said.
While delays increase sharply at higher water levels, region-wide accident rates increase the most at low water levels, suggesting that accidents may be a greater concern than delays at low-to-moderate water levels. Using only the metric of travel time delay for estimating traffic resilience could impart a bias toward travel efficiency rather than road safety into planning efforts.
When flooding of highways forces commuters onto local roads which pass through residential communities a spike in accident rates occurs. This may especially impact lower income or historically disadvantaged communities that are more likely to be adjacent to highways and may have fewer road-safety provisions.
"Some communities might care a lot more about safety than traffic delays," Suckale said. "The interconnectedness makes governance and decision making harder, and planners are not necessarily accounting for the negative consequences on neighbors."
INFORMATION:
Suckale is also a fellow, by courtesy, of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment, an assistant professor, by courtesy, in Civil and Environmental Engineering and a member of ICME.
The research was supported by the UPS Endowment Fund for Transportation, Logistics, and Urban Issues, Stanford's Bill Lane Center for the American West, the NSF through the Office of Polar Programs and Stanford University. The work is the product of the Stanford Future Bay Initiative, a research-education-practice partnership committed to co-production of actionable intelligence with San Francisco Bay Area communities, to shape a more equitable, resilient, and sustainable urban future.
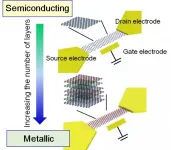
Researchers from Osaka University, Toyo University, and Kyushu Institute of Technology clarified the expression mechanism of semiconducting and metallic properties in graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) by analyzing the carrier transport properties in the field effect transistor (FET) with a multilayer GNR channel (Fig. 1).
The research team fabricated multilayer GNRs with precisely controlled numbers of layers via a chemical vapor deposition method using a solid template. "This enabled us to compare the observed carrier transport properties in the FET using a multilayer ...
A recent study by a team of researchers led by Dr Vinod Kumar Saranathan from the Division of Science at Yale-NUS College has discovered a complex, three-dimensional crystal called the single gyroid within feathers of the blue-winged leafbird. Dr Saranathan and his team's breakthrough came from their investigation of the feather colours of leafbirds, an enigmatic group of perching birds endemic to South and Southeast Asia (including Singapore), one species of which has evolved the unique crystals in its plumage.
By comparing the colour-producing nanostructures present in close relatives, the team reported that this species is able to directly synthesise single gyroid ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - College students who engaged in four or more high-impact practices such as study abroad or internships have a 70% chance of either enrolling in graduate school or finding a full-time job after graduating with a bachelor's degree, finds a new University at Buffalo study.
Each additional high-impact practice increased a student's chance of attaining a bachelor's degree and a full-time job by 17% or enrolling in graduate school by 30%, according to the study. These practices - such as study abroad, internships, undergraduate research, community service, first-year ...
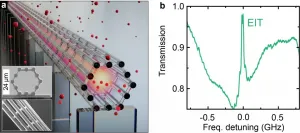
In the rapidly growing field of hybrid quantum photonics, the realization of miniaturized, integrated quantum-optical systems with intense light-matter interaction is of great importance for both fundamental and applied research. In particular, the development of methods for reliably generating, controlling, storing and retrieving quantum states with high fidelity through coherent interaction of light and matter opened up a wide field of applications for quantum information and quantum networks. These include, for example, optical switching, quantum memories, and quantum repeaters.
One promising approach for efficient light-matter interaction is the integration of light-guiding platforms in a near-room-temperature alkali vapor. Several research groups have aimed to ...
Lithium is a vital element in the batteries that power electric vehicles, but soaring lithium demand is expected to exhaust land-based reserves by 2080. KAUST researchers have now developed an economically viable system that can extract high-purity lithium from seawater.
The oceans contain about 5,000 times more lithium than the land but at extremely low concentrations of about 0.2 parts per million (ppm). Larger ions, including sodium, magnesium and potassium, are all present in seawater at much higher concentrations; however, previous research efforts to tease ...
Quantum computing and quantum communication are believed to be the future of information technology. In order to achieve the challenging and long-standing goal to make secure, wide-spread quantum communication networks a reality, high-brightness single-photon sources are indispensable. Single-photon emission from semiconductor quantum dots (QDs) has been shown to be a pure and efficient non-classical light source with a high degree of indistinguishability. However, the total internal reflection (TIR) as a result of the high semiconductor-to-air refractive index contrast severely limits the single-photon extraction efficiency. Another crucial step in the development ...
For decades, researchers have debated whether the buildup of certain electrical activities in the brain indicates that human beings are unable to act out of free will.
Experiments spanning the 1960s and 1980s measured brain signals noninvasively and led many neuroscientists to believe that our brains make decisions before we do--that human actions were initiated by electrical waves that did not reflect free, conscious thought.
However, a new article in Trends in Cognitive Science argues that recent research undermines this case against free will.
"This new perspective on the data turns on its head the way well-known findings have been interpreted," said Adina Roskies, the Helman Family Distinguished Professor and professor of philosophy at ...
Durham, NC -- Type 2 diabetes patients who are not overweight and who have had the disorder for less than a decade can benefit from stromal stem cells transplanted from their own bone marrow, according to a study published today in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine.
In a randomized clinical trial at Vinmec Research Institute of Stem Cell and Gene Technology in Hanoi, Vietnam, researchers investigated the safety and potential therapeutic value of administering bone marrow stromal stem cells to patients with Type 2 diabetes. In each case, the cells were autologous, ...
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (June 3, 2021) -- Since arriving to the northern Atlantic Ocean less than 30 years ago, lionfish have quickly become one of the most widespread and voracious invasive species, negatively impacting marine ecosystems--particularly coral reefs--from the northeast coast of the United States to the Caribbean Islands. In a new study, an international research team including the California Academy of Sciences presents four new records of lionfish off the coast of Brazil, confirming the invasion of the predatory fish into the South Atlantic for the first time. Their findings, published today in Biological Invasions, discuss how the lionfish may have arrived in the ...
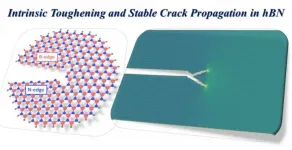
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Rice University in the US, has uncovered the key to the outstanding toughness of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN). h-BN can withstand ten times the amount of force that graphene can, which is known as one of the toughest materials on Earth.
A two-dimensional (2D) material, h-BN has a thickness of just one atom. First used in cosmetics in the 1940s, it was soon abandoned due to its high price, making a resurgence in the late 1990s after technology made its production cheaper.
Today, it is used by nearly all leading producers of cosmetic products because of its ability to absorb excess facial sebum and disperse pigment evenly, ...