Changes in pregnancy, birth rates during COVID-19
2021-06-03
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: Changes in pregnancy and birth rates before and after COVID-19 lockdown measures were estimated using electronic medical records.
Authors: Molly J. Stout, M.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11621)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11621?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=060321
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-03
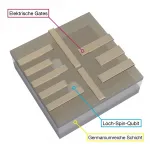
Quantum computers with their promises of creating new materials and solving intractable mathematical problems are a dream of many physicists. Now, they are slowly approaching viable realizations in many laboratories all over the world. But there are still enormous challenges to master. A central one is the construction of stable quantum bits - the fundamental unit of quantum computation called qubit for short - that can be networked together.
In a study published in Nature Materials and led by Daniel Jirovec from the Katsaros group at IST Austria in close collaboration with researchers from the L-NESS Inter-university Centre in Como, Italy, scientists now have created a new and promising candidate system for reliable qubits.
Spinning Absence
The researchers created the qubit using the ...
2021-06-03
Dogs may have earned the title "man's best friend" because of how good they are at interacting with people. Those social skills may be present shortly after birth rather than learned, a new study by University of Arizona researchers suggests.
Published today in the journal Current Biology, the study also finds that genetics may help explain why some dogs perform better than others on social tasks such as following pointing gestures.
"There was evidence that these sorts of social skills were present in adulthood, but here we find evidence that puppies - sort of like humans - are biologically prepared to interact in these social ways," said lead study author Emily Bray, a postdoctoral research associate in the UArizona School of Anthropology in the College of Social and Behavioral ...
2021-06-03
(Toronto, June 3, 2021) -- The impact of deploying Artificial Intelligence (AI) for radiation cancer therapy in a real-world clinical setting has been tested by Princess Margaret researchers in a unique study involving physicians and their patients.
A team of researchers directly compared physician evaluations of radiation treatments generated by an AI machine learning (ML) algorithm to conventional radiation treatments generated by humans.
They found that in the majority of the 100 patients studied, treatments generated using ML were deemed to be clinically acceptable for patient treatments by physicians.
Overall, 89% of ML-generated treatments were considered clinically acceptable for treatments, ...
2021-06-03
For reasons unknown, Earth's solid-iron inner core is growing faster on one side than the other, and it has been ever since it started to freeze out from molten iron more than half a billion years ago, according to a new study by seismologists at the University of California, Berkeley.
The faster growth under Indonesia's Banda Sea hasn't left the core lopsided. Gravity evenly distributes the new growth -- iron crystals that form as the molten iron cools -- to maintain a spherical inner core that grows in radius by an average of 1 millimeter per year.
But the enhanced growth on one side suggests that something in Earth's outer core or mantle under Indonesia is removing heat from the inner core at a faster rate than on the opposite side, under Brazil. Quicker cooling on one side would ...
2021-06-03
Scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), working in partnership with researchers at the Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal (IRCM) in Canada, have identified Meis transcription factors as essential biomolecules for the formation and antero-posterior patterning of the limbs during embryonic development.
In the study, published in Nature Communications, the research team carried out an in-depth characterization of the Meis family of transcription factors. Genetic deletion of all four family members showed that these proteins are essential for the formation of the limbs during embryonic development. "An embryo that develops in the absence of Meis does not ...
2021-06-03
Regular strength and impact-type training may decrease or even prevent age-related bone deterioration in men, new research at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, shows. The tibial bone properties of middle-aged and older male sprint athletes were followed over 10 years. The study presents novel findings on maintaining the adaptability of the aging skeleton and on the importance of regular intensive training for maintaining bone health.
"Part of the age-related bone loss is probably explained by reduced levels of physical activity. Especially intensive, bone-loading exercise ...
2021-06-03
Affecting more than one in a hundred children, autism spectrum disorder is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders. It has a particular impact on social interaction, including difficulties in understanding other people's perspectives, beliefs, desires and emotions, known as 'theory of mind'. Bilingual families with an autistic child often tend - and are sometimes encouraged - to forego the use of one of the home languages, so as not to further complicate the development of their child's communicative skills. A researcher from the University of Geneva (UNIGE, Switzerland), in collaboration with the Universities ...
2021-06-03
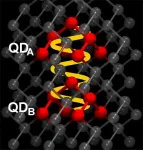
So-called quantum dots are a new class of materials with many applications. Quantum dots are realized by tiny semiconductor crystals with dimensions in the nanometre range. The optical and electrical properties can be controlled through the size of these crystals. As QLEDs, they are already on the market in the latest generations of TV flat screens, where they ensure particularly brilliant and high-resolution colour reproduction. However, quantum dots are not only used as "dyes", they are also used in solar cells or as semiconductor devices, right up to computational building blocks, the qubits, of a quantum computer.
Now, a team led by Dr. Annika Bande at HZB has extended the understanding of the interaction between several quantum dots with an ...
2021-06-03
A biomarker in the blood of patients with bowel cancer may provide valuable insight into the risk of cancer relapse after surgery and the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Research published in PLOS found circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) measured before and after surgery provided a reliable marker for predicting whether the cancer would recur following chemotherapy treatment.
The ctDNA also provided a real-time measure of the effectiveness of chemotherapy, highlighting the potential for this test to provide an early indication of the success of chemotherapy in eradicating microscopic cancer.
At a glance
By measuring levels of ctDNA present in the blood of bowel cancer patients after surgery, researchers were able to predict the likelihood ...
2021-06-03
If insomnia keeps you awake at night, Flinders University researchers recommend a trip to the doctor - not for a sleeping pill prescription but for a short course of intensive behavioural therapy.
Researchers have developed new clinical guidelines for Australian doctors to give family GPs insights into the most effective treatment for insomnia - Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for insomnia (or 'CBTi').
CBTi improves insomnia, mental health and quality of life, and can be more successful than sleeping pills, say Adelaide Institute for Sleep Health (AISH) sleep experts from Flinders University in a new paper in the Australian Journal of General Practice.
Most patients with insomnia managed in general practice are prescribed potentially addictive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Changes in pregnancy, birth rates during COVID-19