Corals tell Arabian Sea story of global warming
2021-06-04
(Press-News.org) Coral insights into 1,000 years of seasonal changes in the Arabian Sea warn of significant impacts caused by global warming.
Every year, the southwesterly winds of the summer monsoon sweep down the Arabian Peninsula, pushing the surface waters of the Arabian Sea away from the coast and driving an upwelling of deep waters to the surface. This rising seawater is colder and less saline than the surface water and is rich in nutrients, providing energy for the various organisms living in the Arabian Sea and Indian Ocean.
Scientists from Japan, Taiwan and Germany, including coral reef scientist Dr. Tsuyoshi Watanabe of Hokkaido University, have uncovered evidence from corals off the coast of Oman suggesting that global warming is causing changes to the Arabian Sea that could impact the climate, ecosystems and socioeconomics of the densely populated areas surrounding the Indian Ocean. The findings were published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Stronger summer monsoon winds lead to a stronger upwelling in the Arabian Sea. Stronger winds form when the air over the Indian subcontinent warms more rapidly than the air over the Indian Ocean. Recently, however, the opposite has been happening. Scientists wanted to know how this change affects the Arabian Sea upwelling, but the phenomenon has not been monitored continuously, so available measurements aren't enough to tell the whole story.
Watanabe and his colleagues analysed fossil and modern corals off an Omani island in the Arabian Sea. They identified the ages of the corals they collected and established a correlation between coral data and seawater temperature changes over a very fine timescale, and used that information to extrapolate salinity changes. The four fossil corals they used dated to approximately 1167 CE, 1624 CE, 1703 CE and 1968 CE, respectively. They took samples from the corals at different depths towards their cores, and then analysed the ratio of strontium to calcium in the samples, as well as the amounts of oxygen and carbon isotopes. The growth rate of the corals is steady over centuries, and the skeletons contain a record of the changes in elements. Generally, as water temperatures rise, the strontium-to-calcium ratio and isotope oxygen-18 in coral decrease.
The results showed that the summer Arabian Sea upwelling was relatively stable through the warmer period of the medieval climate anomaly in the 12th century; the cooler little ice age, which extended between the 14th and 19th centuries AD; and up until the mid-20th century. After this period, however, the scientists observed a clear weakening of the Arabian Sea upwelling. They reason this can most likely be explained by faster warming of the northern Indian Ocean, caused by greenhouse gases, and slowed warming of the Indian subcontinent, caused by the absorption of sunrays by aerosol emissions over South Asia. This then weakens the summer monsoon winds, impacting the strength of the Arabian Sea upwelling.
"The seasonal upwelling is vital for commercial fishing and has significant impacts on the regional climate, ecosystems and socioeconomics," says Tsuyoshi Watanabe. "Our findings imply that weakening of the Arabian Sea upwelling is likely to continue along with global warming, impacting monsoon rainfalls, sea levels, fisheries and even agricultural production."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-04
Delicious to some, but a bitter bane to others' taste buds, vegetables like broccoli rabe, bok choy and turnips are a dinner staple ---and picky eater conflict --- around the world.
It all likely started in the mountains near present-day Afghanistan, where humans first domesticated turnips 3,500 to 6,000 years ago, according to a new study recently published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution. University of Wisconsin-Madison Professor of Botany Eve Emshwiller and her former graduate student Alex McAlvay (now an assistant curator assistant ...
2021-06-04
HOUSTON-(June 3, 2021) - Results were released this week on a new treatment with the potential to improve the outcomes for patients with hereditary BRCA mutations and high-risk, early-stage breast cancer. These results represent the first time a drug that blocks cancer cells from repairing their DNA (called a PARP inhibitor) has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer returning in high-risk patients following completion of standard chemotherapy, surgery and radiation therapy.
Titled "Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 Mutated Breast Cancer," the paper appears in the June 3 issue of the ...
2021-06-04
Could an over-the-counter health "shot" help fight COVID-19? George Mason University researchers think it just might. ...
2021-06-04
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- A study by Mayo Clinic researchers provides some clarity in the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, to treat acute venous thromboembolism (VTE) in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. The findings were published Wednesday, June 2, in Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
Among the study's findings:
Rivaroxaban showed no higher risk of bleeding in luminal gastrointestinal cancer and should not be considered contraindicated in this group of patients.
Apixaban showed a higher risk of bleeding in patients with luminal gastrointestinal cancer, and it should be used with great caution to treat this type of cancer until more studies ...
2021-06-04
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Plastics are everywhere. From cell phones to pens and cars to medical devices, the modern world is full of plastic-- and plastic waste. New research from scientists at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) END ...
2021-06-04
A team led by UC Riverside engineers has developed a catalyst to remove a dangerous chemical from water on Earth that could also make Martian soil safer for agriculture and help produce oxygen for human Mars explorers.
Perchlorate, a negative ion consisting of one chlorine atom bonded to four oxygen atoms, occurs naturally in some soils on Earth, and is especially abundant in Martian soil. As a powerful oxidizer, perchlorate is also manufactured and used in solid rocket fuel, fireworks, munitions, airbag initiators for vehicles, matches and signal flares. It is a byproduct in some disinfectants ...
2021-06-04
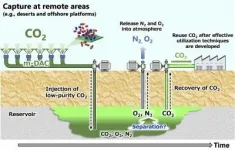
Fukuoka, Japan - The global threat of ongoing climate change has one principal cause: carbon that was buried underground in the form of fossil fuels is being removed and released into the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). One promising approach to addressing this problem is carbon capture and storage: using technology to take CO2 out of the atmosphere to return it underground.
In a new study published in Greenhouse Gases Science and Technology, researchers from Kyushu University and the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan, investigated geological storage of low-purity CO2 mixed with nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), produced by direct air capture (DAC) using membrane-based technology.
Many current ...
2021-06-04
Climate scientists at the Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU, Singapore) have extended the known record of Singapore's sea-level to almost 10,000 years ago, providing a more robust dataset to aid future predictions of sea-level rise.
One of the main challenges in researching climate change is to reconstruct its history over thousands of years. To have a better sense of the potential causes and effects of future changes, scientists need to learn from and understand the past.
Extracting ancient sediments from a depth of up to 40 m underground at a site at Singapore's Marina South, an international team led by NTU researchers put the samples through rigorous laboratory ...
2021-06-04
Bottom Line: The majority of surveyed Americans had an inadequate understanding of palliative care, and frequency of health care utilization was one determinant of knowledge.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Motolani Ogunsanya, PhD, an assistant professor at The University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Background: Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for patients and caretakers by addressing the physical, psychological, and logistical challenges associated with a disease or its treatment. In contrast to hospice, which provides comfort care for patients who have stopped treatment and are near the end of life, palliative care serves as an ...
2021-06-04
Oncotarget published "Characterization of the inflammatory microenvironment and hepatic macrophage subsets in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma models" which reported that HCC typically develops on a background of chronic inflammation and fibrosis with tumor associated macrophages playing an important role in chronic inflammation-induced HCC and progression.
However, the liver harbors unique macrophages, resident liver Kupffer cells and monocyte-derived macrophages, and their contribution to HCC and to the population of TAMs is incompletely known.
Here, the authors characterized the tumor microenvironment and the proportion and transcriptional profile of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Corals tell Arabian Sea story of global warming