Trying not to overeat? How you eat matters
Study finds people who eat more tend to take larger bites or eat faster
2021-06-07
(Press-News.org) Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- According to a new study, people who eat faster or take larger bites are more likely to eat more at a meal. The research, which is being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE, provides new insight into the factors that might contribute to overeating.
The study also adds more evidence that people eat more when given larger portions. The researchers found that study participants ate, on average, 43% more when the portion size of a meal was increased by 75%.
"Although studies have consistently found that people eat more when they are served larger portions, less is known about why this happens or why some people are more responsive to the effects of large portions than others," said first author Paige Cunningham, a doctoral student at The Pennsylvania State University. "This is one of the first studies to explore whether the characteristics of eating speed and bite size have an effect on people's food consumption in response to larger portions."
For the new study, the researchers served 44 men and women lunch once a week for four weeks. For each meal, the study participants received, in random order, a different portion of macaroni and cheese with water to drink. The researchers videotaped each meal to assess the speed at which participants ate and the size of their bites.
The fact that participants ate meals that were all four sizes, meant that they could each serve as their own comparison. The researchers expect the results to be generalizable to other groups since the study participants were diverse in terms of age, sex, body weight, income and education.
"Based on our findings, being aware of portion size, slowing down when you eat and taking smaller bites of food could help avoid overconsumption," said Cunningham. "Also, since people eat more when served more, overconsumption of calories from large portions can be reduced by choosing foods that have less calories per bite. This lets you eat the same filling portions of foods while consuming fewer calories."
The researchers plan to perform more studies to see if their findings apply to a longer, more complex meal that includes a variety of foods, textures and flavors.
Cunningham will present this research on-demand during NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE from noon on Monday, June 7 through 5:30 p.m. on Friday, June 10 (abstract; presentation details).
Images available.
Please note that abstracts presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE were evaluated and selected by a committee of experts but have not generally undergone the same peer review process required for publication in a scientific journal. As such, the findings presented should be considered preliminary until a peer-reviewed publication is available.
INFORMATION:
About NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE
NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE, held June 7-10, 2021 is a dynamic virtual event showcasing new research findings and timely discussions on food and nutrition. Scientific symposia explore hot topics including clinical and translational nutrition, food science and systems, global and public health, population science and cellular and physiological nutrition and metabolism. https://meeting.nutrition.org #NutritionLiveOnline
About the American Society for Nutrition (ASN)
ASN is the preeminent professional organization for nutrition research scientists and clinicians around the world. Founded in 1928, the society brings together the top nutrition researchers, medical practitioners, policy makers and industry leaders to advance our knowledge and application of nutrition. ASN publishes four peer-reviewed journals and provides education and professional development opportunities to advance nutrition research, practice and education. http://www.nutrition.org
Find more news briefs and tipsheets at: END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-07
Rockville, Md. (June 7, 2021) - Superfoods like turmeric and honey have long been recognized for their ability to promote health and wellness. New studies being presented at END ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- What we eat during childhood can affect the health of individuals--and populations--for years to come. As rates of childhood obesity continue to rise, five studies being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE bring new insights into the diets of children and teens around the world.
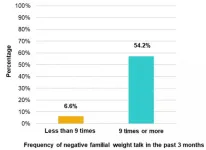
Families report substantial child weight gain during COVID-19
Researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University surveyed over 400 parents about their children's weight and eating habits before the COVID-19 pandemic and at two points during ...
2021-06-07
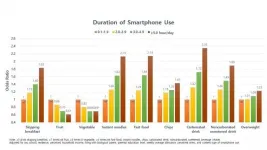
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Even moderate smartphone use may influence teens' diet and weight, according to a new study of more than 53,000 Korean adolescents. Teens who used a smartphone for more than 2 hours per day were significantly more likely to eat more junk food and fewer fruits and vegetables than those spending less time on their phone. Teens spending more than 3 hours per day on a smartphone were significantly more likely to be overweight or obese.
"While earlier studies have shown that TV watching is an important factor that increases the risk of obesity in children and adolescents, little is known about the effects of modern screen time such as smartphone use on diet and obesity," said Hannah Oh, ScD, assistant professor at ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- Studies being presented at END ...
2021-06-07
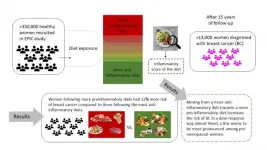
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- A new study of more than 350,000 women found that women with diets incorporating more foods that increase inflammation in the body had a 12% increase in their risk of breast cancer compared to women who consume more anti-inflammatory diets. The new findings are being presented at NUTRITION 2021 LIVE ONLINE.
The study authors found that moving from a more anti-inflammatory diet toward one that increases inflammation upped breast cancer risk in an almost linear manner. Foods that increase inflammation include red and processed meat; high-fat foods such as butter, margarines and frying fats; and ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- What did Americans eat during the Great Recession? A new study suggests dietary quality plummeted along with the economy.
According to the study, adults overall ate more refined grains and solid fats and children increased their intake of added sugar during the recession. The impacts of the downturn were especially pronounced in food-insecure households, where individuals significantly reduced their intake of protein and dark green vegetables while increasing total sugars.
"Overall, we found that the Great Recession had a negative impact on dietary ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- There has been a long-standing debate as to whether a low-fat or a plant-centered diet is better at lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. A new study that followed more than 4,700 people over 30 years, found that a plant-centered diet was associated with a lower long-term risk for cardiovascular disease. However, both diets were linked with lower LDL, or bad cholesterol, levels.
"Since 1980, dietary guidelines in the United States and in Europe have recommended eating low amounts of saturated fat because of the high rates of heart disease in these regions," said research team leader David Jacobs, PhD, from the University of Minnesota. "This is not necessarily wrong, but our study shows that plant-centered ...
2021-06-07
Rockville, Maryland (June 7, 2021) -- As COVID-19 spread throughout the world, our daily routines and behaviors changed drastically. A new study of more than 2,000 people in the U.S. found that the pandemic has also affected how we eat. The authors found a decrease in the consumption of many food groups, particularly healthy foods such as vegetables and whole grains, compared to before the pandemic.
"When the pandemic began, we saw panic buying, problems in the food supply chain, increases in food prices and rising unemployment rates," said Caroline Um, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at ...
2021-06-07
Concerned youths worldwide today delivered a policy vision for policy-makers to address the declining state of the world's ocean.
A carbon neutral economy, preserving biodiversity, achieving sustainable seafood production, and reforming ocean governance are the four fundamental pillars supporting policy recommendations debuted in the Global Blue New Deal, an ocean policy framework built around crowd-sourced youth priorities.
"Healthy oceans are essential to human survival and well-being, and environmental health must be a global priority as we recover from the pandemic and build a sustainable blue economy," says Mark Haver, Chair of the Sustainable Ocean Alliance's Youth Policy Advisory Council.
He and 14 fellow Young Ocean Leaders ...
2021-06-07
During his time at EPFL under the Erasmus program, Romain van Wassenhove came up with an idea for a connector that could be used to make modular structures out of sustainable bamboo rather than wood, plastic or metal. "I wanted to focus my Master's on a topic that had meaning to me and that would lead to a concrete application," he says. "Working with bamboo was something I already had in mind while I was studying in Brussels." His connectors can be 3D-printed in biosourced plastic and are customizable to the type of material used for the structure.
Van Wassenhove got the idea for his connector during a class at EPFL on composite materials and developed the concept further through his Master's project, co-directed at EPFL by Senior Scientist Anastasios Vassilopoulos and by associate ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Trying not to overeat? How you eat matters
Study finds people who eat more tend to take larger bites or eat faster