(Press-News.org) A new physiological measurement of heart function developed at UVA Health could improve survival for people with heart failure by identifying high-risk patients who require tailored treatments, a new study suggests.
The study is the first to show a survival benefit from wireless pressure monitoring sensors implanted in the pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary artery proportional pulse pressure, or PAPP, is a new measure of heart function, developed at UVA, that can identify patients at very high risk of hospitalization or death from systolic heart failure or pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the heart and lungs).
Previous research by the researchers showed that patients with low PAPPs were at far greater risk than those with higher PAPPs, so the UVA researchers tested whether these benefits were maintained in patients undergoing implantation of pressure sensors that continuously monitor pressure in the pulmonary artery.
"We found that PAPP is a very good measure of how stiff or compliant the pulmonary arteries are. The stiffness of the pulmonary arteries determines how much resistance the right side of the heart has overcome to pump blood effectively to the lungs," said Sula Mazimba, MD, MPH, a heart failure expert at UVA Health and the University of Virginia School of Medicine. "The importance of this simple measure is that it can identify patients that are at greatest risk of dying or being hospitalized. This allows us to tailor more aggressive treatments."
Treating Heart Failure
Heart failure is a condition where the heart fails to pump blood adequately through the body. It affects more than 6.5 million Americans and more than 26 million people around the world. It causes more than 1 million hospital admissions each year, and approximately half of patients die within five years of diagnosis.
UVA's new study evaluated the benefits of PAPP monitoring in patients with systolic heart failure, in which the heart's left ventricle is weak, as well as those with pulmonary hypertension - high blood pressure in the arteries in the lungs and right side of the heart.
To test whether PAPP monitoring could predict outcomes in these patients, Mazimba and his colleagues reviewed data from 550 participants in the CHAMPION clinical trial. In the trial, participants were randomized to receive an implantable, wireless heart monitor called the CardioMEMS HF System.
Mazimba and his collaborators found that participants with a below-average PAPP had a significantly higher risk of hospitalization or death than those with higher PAPPs. Further, the monitoring offered significant benefit to those with low PAPPs, reducing the risk of death by 46% annually during two to three years of follow-up.
"The implications of this study are highly significant," said Kenneth Bilchick, MD, MS, a cardiologist at UVA Health and co-investigator on the study. "We now have identified a specific group of patients who appear to have a marked improvement in survival with implantation of these pulmonary artery wireless monitors. As a result, the findings of the study could maximize the impact of this technology for a large number of potential candidate patients. This is an excellent example of how secondary analyses of clinical databases maintained by the National Institutes of Health can result in novel and personalized approaches to patient care."
The UVA researchers say more study is needed to determine the full potential of PAPP monitoring to improve care for patients with heart failure, but they were encouraged by the early results.
"In the past, the function of the right chamber of the heart was often ignored and considered to be inconsequential to the overall performance of the heart, but we are now learning that this is not the case," Mazimba said. "Having tools that signal when the right side of the heart is under strain may aid clinicians to adopt timely tailored treatments for heart-failure patients."
INFORMATION:
Findings Published
The researchers have published their findings in the scientific journal Heart, Lung and Circulation. The research team consisted of Mazimba, Greg Ginn, Hunter Mwansa, Olusola Laja, Christiana Jeukeng, Comfort Elumogo, Brandy Patterson, Jamie L .W. Kennedy, Nishaki Mehta, John A. Hossack, Alex M. Parker, Andrew Mihalek, Jose Tallaj, Nishtha Sodhi, Younghoon Kwon, Salpy V. Pamboukian, Philip B. Adamson and Bilchick.
The CHAMPION Trial was funded CardioMEMS Inc, subsequently acquired by St Jude Medical and then Abbott.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog at http://makingofmedicine.virginia.edu.
Tropical cyclones (TCs) are humbling and powerful forces of nature that can have tremendous impacts on people and human populations. Meteorologists have strived to improve TC forecasting skill, hoping to save lives. In the past few decades, TC track forecasts over the western North Pacific (WNP) have progressed considerably. However, TC intensity forecasts have improved insignificantly, with only a 3-5 day lead time. Therefore, improving TC intensity forecast skill and extending lead forecast time are important and urgent issues.
To address this critical problem, a research group led by Prof. Ruifen ZHAN from the Department of Atmospheric and Ocean Sciences/Institute of Atmospheric Sciences at Fudan University, along with the Shanghai Typhoon Institute of China Meteorological ...
The incidence rate of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is increasing gradually and the mortality is still high. Recent advances in the genomic profile of LUAD have identified a number of driver alterations in specific genes, enabling molecular classification and targeted therapy accordingly. However, only a fraction of LUAD patients with those driver mutations could benefit from targeted therapy, and the remaining large numbers of patients were unclassified. RNA editing events are those nucleotide changes in the RNA. Currently, the role of RNA editing events ...
Glass is one of the most common subjects we see every day, but the detailed structure of this non-metallic and non-liquid material has always been a major mystery in science. A research team co-led by scientists at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has successfully discovered that the amorphous and crystalline metallic glass have the same structural building blocks. And it is the connectivity between these blocks that distinguishes the crystalline and amorphous states of the material. The findings shed light on the understanding of glass structure.
Glass is a non-crystalline amorphous solid which has widespread practical and technological use in daily life. Besides the soda-lime glass used in windows, there are many other ...
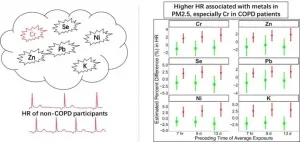
Epidemiological and toxicological studies indicate that the adverse outcomes of PM2.5 exposure associated closely with the chemical composition in PM2.5. Metals in PM2.5 are highly concerned for their induced disruption of iron homeostasis in the lung and following oxidative stress, which is one of the key mechanisms underlying the cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction of PM2.5 exposure. However, there is no clear evidence on whether COPD patients are more susceptible to cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction associated with exposure to metals in ambient PM2.5 than individuals without COPD. Based on a panel study, the researchers directly compared metal-associated cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction between COPD patients and healthy controls.
"We observed higher levels of heart ...
Supermassive black holes (SMBH) occupy the center of galaxies, with masses ranging from one million to 10 billion solar masses. Some SMBHs are in a bright phase called active galactic nuclei (AGN).
AGNs will eventually burn out since there is a maximum mass limit for SMBHs; scientists have long since pondered when that will be.
Tohoku University's Kohei Ichikawa and his research group may have discovered an AGN towards the end of its life span by accident after catching an AGN signal from the Arp 187 galaxy.
Through observing the radio images in the galaxy using two astronomy observatories - the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Very Large Array (VLA) - ...
Globally, the Earth system has thousands of terragrams (Tg) (1 Tg = 10 12 g) of mineral nanoparticles moving around the planet each year. These mineral nanoparticles are ubiquitously distributed throughout the atmosphere, oceans, waters, soils, in and/or on most living organisms, and even within proteins such as ferritin. In natural environments, mineral nanozymes can be produced by two pathways: "top down" and "bottom up" processes. Specifically, the weathering or human-promoted breakdown of bulk materials can result in nanomaterials directly (a top-down process), or nanomaterials ...
A team of researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Ngee Ann Polytechnic, Singapore (NP), and the National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS) have invented a tool that could speed up the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
Powered by artificial intelligence (AI), their innovation uses electrocardiograms (ECGs) to diagnose coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure to an accuracy of more than 98.5 per cent.
The joint development of the diagnostic tool is timely, as the number of deaths caused by cardiovascular disease in Singapore has increased over the past three years. According to the Singapore Heart Foundation, 29.3 per cent of all deaths in Singapore in 2019, or almost 1 out of 3 deaths in Singapore, was due to heart ...
Osteoporosis is a condition that does not exhibit symptoms until there is a bone fracture, so it is said that there is a high percentage of people who remain unaware of their condition. When people are unaware their bones have weakened, the condition is left untreated, and the recent rise of the elderly population has caused an increase in bone fractures. This has a large societal impact, such as overwhelming medical costs and long-term care. Simple screenings at resident health exams are one way for an increase in osteoporosis detecting without having to go to the hospital. When suspected osteoporosis and osteopenia is properly detected and patients are encouraged to get further evaluation at the hospital, ...
Scientists have observed for the first time what it looks like in the key memory region of the brain when a mistake is made during a memory trial. The findings have implications for Alzheimer's disease research and advancements in memory storage and enhancement, with a discovery that also provides a view into differences between the physiological events in the brain during a correct memory versus a faulty one.
The study was published today in the journal Nature Communications.
In both correct and incorrect recall of a spatial memory, researchers could observe patterns of cell activation in the brain that were similar, though the pace of activation differed.
"We could see the memories activating," said Laura Colgin, an associate professor of neuroscience at The University ...
SAN RAMON, Calif., June 8, 2021--CooperVision today announced its scientific research program for the 2021 British Contact Lens Association Virtual Clinical Conference and Exhibition, which begins Sunday, June 13. For the first time, the biennial event will be streamed live over the course of 30 hours, welcoming members of the global eye care community to experience and discuss the latest category advancements.
More than 20 CooperVision-authored and sponsored investigations were accepted by the conference committee. The papers and posters span a range of topics that underpin the contact lens industry's evolution, including new data and insights on the complex lifestyle factors involved with addressing presbyopia, misperceptions surrounding soft toric lens fitting, ...