Machine learning reduces microscope data processing time from months to just seconds
2021-06-08
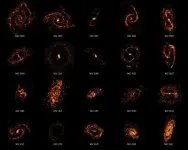
(Press-News.org) Ever since the world's first ever microscope was invented in 1590 by Hans and Zacharias Janssen --a Dutch father and son-- our curiosity for what goes on at the tiniest scales has led to development of increasingly powerful devices. Fast forward to 2021, we not only have optical microscopy methods that allow us to see tiny particles in higher resolution than ever before, we also have non-optical techniques, such as scanning force microscopes, with which researchers can construct detailed maps of a range of physical and chemical properties. IBEC's Nanoscale bioelectrical characterization group, led by UB Professor Gabriel Gomila, in collaboration with members of the IBEC's Nanoscopy for nanomedicine group, have been analysing cells using a special type of microscopy called Scanning Dielectric Force Volume Microscopy, an advanced technique developed in recent years with which they can create maps of an electrical physical property called the dielectric constant. Each of the biomolecules that make up cells --that is, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids-- has a different dielectric constant, so a map of this property is basically a map of cell composition. The technique that they developed has an advantage over the current gold standard optical method, which involves applying a fluorescent dye that can disrupt the cell being studied. Their approach doesn't require the addition of any potentially disruptive external agent. However, the application of this technique requires a complex post-processing process to convert the measured observables into the physical magnitudes, which for eukaryotic cells involves huge amounts of computation time. In fact, it can take months to process just one image in a workstation computer, since the dielectric constant is analysed pixel by pixel using local reconstructed geometrical models.
Months to seconds
In this new study, recently published in the journal Small Methods, the researchers opted for a new technique to speed up the microscope data processing. This time, they used machine learning algorithms instead of conventional computational methods. The result was drastic: once trained, the machine learning algorithm was able to produce a dielectric biochemical composition map of the cells in just seconds. In the study, no external substances were added to the sample, a long-sought goal in the composition imaging in cell biology. They achieved these rapid results by using a powerful type of algorithm called neural networks, which mimics the way that neurons in the human brain operate.
The study was first-authored by Martí Checa, who carried it out as part of his PhD in Gomila's group at IBEC. He is now a postdoctoral researcher at the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2). "It is one of the first studies to provide such a rapid label-free biochemical composition map of dry eukaryotic cells", Checa explains. Indeed, in this proof-of-concept study, the researchers used dried out cells, to prevent the huge effects of water in the dielectric measurements due to its high dielectric constant. In a recently published follow-up study, they also analysed fixed cells in their natural in-liquid state. Here they were able to compare the values obtained in the dry and liquid models in order to render an accurate map of the biomolecules that make up eukaryotic cells. These are the multi-structured cells that animals, plants, fungi and other organisms are composed of. "The next step in this research is to apply the method to electrically excitable living cells, such as neurons, where intense electrical activity occurs. We are excited to see what can be obtained with our technique in these systems" Prof. Gomila adds.
Biomedical applications
The researchers validated their methodology by comparing their findings to well-known facts about the composition of cells, such as the lipid-rich nature of the cell membrane or the high quantity of nucleic acids present in the nucleus. With this work, they have opened up the possibility of analysing large quantities of cells in record time.
This study is expected to provide an invaluable tool to biologists to conducting basic research, as well as, to open up potential medical applications. For example, changes in the dielectric properties of cells are currently being studied as possible biomarkers of some illnesses, such as cancer or neurodegenerative diseases.
"It is the first study to provide such a rapid nanoscale biochemical composition map from dielectric measurements of dry eukaryotic cells, which are classically seen as being extremely difficult to map due to their complex three-dimensional topography", declares Martí Checa, first author of the paper.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-08
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of vision loss in people over 50. Up to 12 percent of those over 80 have the chronic disease. An estimated 16.4 million adults are affected by retinal vein occlusion (RVO) worldwide, a condition caused by a thrombosis of a retinal vein. It is the second most common cause of blindness from retinal vascular disease after diabetic retinopathy (DR). DR in turn is the leading cause of blindness in developed countries and affects up to 80 percent of people with more than 20 years of diabetes. It can lead ...
2021-06-08
A defining characteristic of all life is its ability to evolve. However, the fact that biologically engineered systems will evolve when used has, to date, mostly been ignored. This has resulted in biotechnologies with a limited functional shelf-life that fail to make use of the powerful evolutionary capabilities inherent to all biology.
Sim Castle, first author of the research, published in Nature Communications, and a PhD student in the School of Biological Sciences at Bristol, explained the motivation for the work: "The thing that has always fascinated me about biology is that it changes, it is chaotic, it adapts, it evolves. Bioengineers therefore do not just design static artefacts - they design living populations that ...
2021-06-08
The presence of amino acids on the prebiotic Earth is widely accepted, either coming from endogenous chemical processes or being delivered by extraterrestrial material. On the other hand, plausibly prebiotic pathways to peptides often rely on different aqueous approaches where condensation of amino acids is thermodynamically unfavorable. Now, chemists from the Ruđer Bošković Institute (RBI), in collaboration with colleagues from Xellia Pharmaceuticals, have shown that solid-state mechanochemical activation of glycine and alanine in combination with mineral surfaces leads to the formation of peptides. ...
2021-06-08
A team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) has completed the first census of molecular clouds in the nearby Universe, revealing that contrary to previous scientific opinion, these stellar nurseries do not all look and act the same. In fact, they're as diverse as the people, homes, neighborhoods, and regions that make up our own world.
Stars are formed out of clouds of dust and gas called molecular clouds, or stellar nurseries. Each stellar nursery in the Universe can form thousands or even tens of thousands of new stars during its lifetime. Between 2013 and 2019, astronomers on the PHANGS-- Physics at High Angular Resolution in Nearby GalaxieS-- project conducted the first systematic survey of 100,000 stellar nurseries ...
2021-06-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Astronomers have taken a big step forward in understanding the dark and violent places where stars are born.
Over the past five years, an international team of researchers has conducted the first systematic survey of "stellar nurseries" across our part of the universe, charting the more than 100,000 of these nurseries across more than 90 nearby galaxies and providing new insights into the origins of stars.
"Every star in the sky, including our own sun, was born in one of these stellar nurseries," said Adam Leroy, associate professor of astronomy at The Ohio State University and one of ...
2021-06-08
Researchers from the University of Arizona will present findings from radio-astronomical observations of organic molecules at the 238th Meeting of the American Astronomical Society, or AAS, during a press conference titled "Molecules in Strange Places" at the 238th AAS Meeting on Tuesday, June 8, at 12:15 p.m. EDT.
A team led by Lucy Ziurys at the University of Arizona reports observations of organic molecules in planetary nebulae in unprecedented detail and spatial resolution. Using the Atacama Large Millimeter Array, or ALMA, Ziurys and her team observed radio emissions from hydrogen cyanide (HCN), formyl ion (HCO+) and carbon monoxide (CO) in five planetary nebulae: M2-48, M1-7, M3-28, K3-45 and K3-58.
The ...
2021-06-08
Researchers have developed a 'library of properties' to help identify the environmental impact of nanomaterials faster and more cost effectively.
Whilst nanomaterials have benefited a wide range of industries and revolutionised everyday life, there are concerns over potential adverse effects - including toxic effects following accumulation in different organs and indirect effects from transport of co-pollutants.
The European Union H2020-funded NanoSolveIT project is developing a ground-breaking computer-based Integrated Approach to Testing and Assessment (IATA) for the environmental health and safety of nanomaterials.
Over ...
2021-06-08
A new global analysis says that greenhouse-gas emissions from food systems have long been systematically underestimated--and points to major opportunities to cut them. The authors estimate that activities connected to food production and consumption produced the equivalent of 16 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide in 2018--one third of the human-produced total, and an 8 percent increase since 1990. A companion policy paper highlights the need to integrate research with efforts to reduce emissions. The papers, developed jointly by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, NASA, New York University and experts at Columbia University, are part of a special issue of Environmental Research Letters on sustainable food systems.
The Center on Global Energy ...
2021-06-08
Stereotypes are knowledge structures integrated in our world representation, which have an influence on our decisions and which are hard to change. A team from the Faculty of Psychology of the University of Barcelona (UB) and the Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL), in collaboration with the Èpica Foundation - La Fura dels Baus analysed how a performing experience could have a positive impact in reducing the population's bias against physical illnesses. This performing experience is a pioneer one for it combines scientific training and theatre performance in the same working platform.
The study, published in the journal Frontiers in Psychology, shows that the participation ...
2021-06-08
After looking for just one-twentieth of a second, experts in camouflage breaking can accurately detect not only that something is hidden in a scene, but precisely identify the camouflaged target, a skill set that can mean the difference between life and death in warfare and the wild, investigators report.
They can actually identify a camouflaged target as fast and as well as individuals identifying far more obvious "pop-out" targets, similar to the concept used at a shooting range, but in this case using easy-to-spot scenarios like a black O-shaped target among a crowd of black C shapes.
In fact, the relatively rapid method for training civilian novices to become expert camouflage breakers developed by Medical College of Georgia neuroscientist ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Machine learning reduces microscope data processing time from months to just seconds