Liquid water on exomoons of free-floating planets
2021-06-10
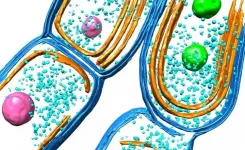
(Press-News.org) The moons of planets that have no parent star can possess an atmosphere and retain liquid water. Astrophysicists at LMU have calculated that such systems could harbor sufficient water to make life possible - and sustain it.
Water - in liquid form - is the elixir of life. It made life possible on Earth and is indispensable for the continuing existence of living systems on the planet. This explains why scientists are constantly on the lookout for evidence of water on other solid bodies in the Universe. Up to now, however, the existence of liquid water on planets other than Earth has not been directly proven. However, there are indications that several moons in the outer reaches of our own solar system - more specifically, Saturn's Enceladus and three of Jupiter's moons (Ganymede, Callisto and Europa) may possess subterranean oceans. What then are the prospects for the detection of water on the moons of planets beyond our solar system?
In cooperation with colleagues at the University of Concepción in Chile, LMU physicists Prof. Barbara Ercolano and Dr. Tommaso Grassi (both of whom are members of ORIGINS, a Cluster of Excellence) have now used mathematical methods to model the atmosphere and gas-phase chemistry of a moon in orbit around a free-floating planet (FFP). An FFP is a planet that is not associated with a star.
More than 100 billion planetary nomads
FFPs are of interest mainly because the evidence indicates that there are plenty of them out there. Conservative estimates suggest that our own galaxy hosts at least as many Jupiter-sized orphan planets as there are stars - and the Milky Way itself is home to well over 100 billion stars.
Ercolano and Grassi made use of a computer model to simulate the thermal structure of the atmosphere of an exomoon of the same size as the Earth in orbit around a FFP. Their results suggest that the amount of water present on the moon's surface would be about 10,000 times smaller than the total volume of our planet's oceans, but 100 times larger than that found in Earth's atmosphere. This would be enough to enable life to evolve and thrive.
The model from which this estimate was derived consists of an Earth-sized moon and a Jupiter-sized FFP. Such a system, which has no stellar companion nearby, is expected to be dark and cold. Unlike our solar system, there is no central star that can serve as a reliable source of energy to drive chemical reactions.
Cosmic radiation and tidal forces to the fore!
Rather, in the researchers' model, cosmic rays provide the chemical drive necessary to convert molecular hydrogen and carbon dioxide into water and other products. To keep the system stirred up, the authors invoke the tidal forces exerted by the planet on its moon as a source of heat - and assuming that carbon dioxide accounts for 90% of the moon's atmosphere, the resulting greenhouse effect would effectively retain a large part of the heat generated on the moon. Together, these energy sources would suffice to keep water in the liquid state.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-10
The increased use of ridesharing apps was linked to a decrease in motor vehicle collisions and impaired driving convictions in Houston, according to published research by The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
The findings were published today in JAMA Surgery.
Christopher Conner, MD, PhD, neurosurgery resident in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth and the study's lead author, said the research is timely as more individuals are utilizing ridesharing apps.
"Automobile accidents are the leading cause of death and disability among young people, so anything we can do to reduce those incidents ...
2021-06-10
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men, according to the American Cancer Society. It's also one of the trickiest cancers to diagnose and treat.
But new research from the University of Georgia has identified a protein that appears to prevent the cancer from spreading to and colonizing the bone, providing a new target for future therapeutics.
"Unfortunately, prostate cancer that has spread to the bone is very aggressive, often lethal and very difficult to treat," said Brian Cummings, corresponding author of the study and head of the College of Pharmacy's pharmaceutical and biomedical sciences department. "Even in cases of successful treatment, the patient's quality of life is severely lessened due to bone loss."
Prostate cancer that hasn't spread beyond nearby ...
2021-06-10
There are still many unsolved mysteries about the human brain and its development. Now, a novel study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry sheds new light on the neurobiological origins of our individual traits.
Functional connectivity is the coordinated activity - activation or deactivation - through time between separate brain regions, regardless of their physical closeness or the type of neural connections between them. Changes in functional connectivity can be a sign of mental health disorders such as depression, eating disorders, and schizophrenia, and are thought to have developmental origins.
We know that mental health is characterized by three functional brain networks. The first is hypoconnectivity ...
2021-06-10
People who have a high sensation-seeking personality trait may be more likely to develop an addiction to cocaine, according to a Rutgers study.
"Although many people try illicit drugs like cocaine or heroin, only a small proportion develop an addiction," said lead author Morgan James, a member of the Rutgers Brain Health Institute and an assistant professor in the department of psychiatry at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. "The interaction found between sensation-seeking traits and the drug-taking experience show that predisposition to addiction has a genetic basis, and that this interacts with environmental factors such as patterns of drug use. The sensation-seeking trait was predictive of rats' likelihood to exhibit stronger ...
2021-06-10
For older adults, participating in social activities can protect against physical and mental signs of aging, but it may also pose risks, especially for women.
A new analysis of national data led by UC San Francisco found that older women who were broadly engaged in social activities before the COVID pandemic had 76 percent higher odds of experiencing emotional abuse or mistreatment than women who were less engaged.
The paper is published June 9, 2021 in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
"Given widespread discussion about the negative effects of social isolation of ...
2021-06-10
Research from the University of Washington shows that endangered blue whales are present and singing off the southwest coast of India. The results suggest that conservation measures should include this region, which is considering expanding tourism.
Analysis of recordings from late 2018 to early 2020 in Lakshadweep, an archipelago of 36 low-lying islands west of the Indian state of Kerala, detected whales with a peak activity in April and May.
The study was published in May in the journal Marine Mammal Science.
"The presence of blue whales in Indian waters is well known from several strandings and some live sightings of blue whales," said lead author Divya Panicker, a ...
2021-06-10
A new study conducted by the researchers at the University of Liverpool reveals how the ancient photosynthetic organisms - cyanobacteria - evolve their photosynthetic machinery and organise their photosynthetic membrane architecture for the efficient capture of solar light and energy transduction.
Oxygenic photosynthesis, carried out by plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, produces energy and oxygen for life on Earth and is arguably the most important biological process. Cyanobacteria are among the earliest phototrophs that can perform oxygenic photosynthesis and make significant contributions to the Earth's atmosphere and primary production.
Light-dependent photosynthetic reactions are performed by a set of photosynthetic ...
2021-06-10
Laser-produced high energy density plasmas, akin to those found in stars, nuclear explosions, and the core of giant planets, may be the most extreme state of matter created on Earth. Now scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), building on nearly a decade of collaboration with the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the DOE's Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), have designed a novel X-ray crystal spectrometer to provide high-resolution measurements of a challenging feature of NIF-produced HED plasmas.
Most powerful lasers
The ...
2021-06-10
An international research team led by members from the Technical University of Munich, the Deutsches Museum, Munich, and the Swedish Linköping University has developed a method to manufacture two-dimensional polymers with the thickness of a single molecule. The polymers are formed on a surface by the action of light. The discovery paves the way to new ultrathin and functional materials.
The quest for new two-dimensional materials has rapidly intensified after the discovery of graphene - a supermaterial whose excellent properties include high conductivity and strength, making it incredibly versatile.
Two main ...
2021-06-10
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers demonstrate an automated, easy-to-operate quantum key distribution (QKD) system using the fiber network in the city of Padua, Italy. The field test represents an important step toward implementing this highly secure quantum communication technology using the type of communication networks already in place in many regions around the world.
QKD offers impenetrable encryption for data communication because it uses the quantum properties of light to generate secure random keys for encrypting and decrypting data.
"QKD can be useful in any situation where security is paramount because it offers unconditional security for the key exchange process," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Liquid water on exomoons of free-floating planets