Observing quantum coherence from photons scattered in free-space
2021-06-10
(Press-News.org) Quantum coherence is a key ingredient in many fundamental tests and applications of quantum technology including quantum communication, imaging, computing, sensing and metrology. However, the transfer of quantum coherence in free-space has so far been limited to direct line-of-sight channels as atmospheric turbulence and scattering degrade the quality of coherence severely.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, researchers from the University of Waterloo have successfully demonstrated the transfer and recovery of quantum coherence using photons scattered in free-space for the first time, enabling new research opportunities and applications in fields ranging from quantum communication to imaging and beyond.
"The ability to transfer quantum coherence via scattered photons means that now you can do many things that previously required direct line-of-sight free-space channels," said Shihan Sajeed, lead author on the paper and a postdoctoral fellow at the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) and in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada.
Normally, if you try to send and receive photons through the air (free-space) for quantum communication or any other quantum-encoded protocol, you need a direct line-of-sight between transmitter and receiver. Any objects--from as big as a wall to as small as a molecule--in the optical path will reflect some photons and scatter others, depending on how reflective the surface is. Any quantum information encoded in the photons is typically lost in the scattered photons, interrupting the quantum channel.
Together with Thomas Jennewein, principal investigator of the Quantum Photonics lab at IQC, Sajeed found a way to encode quantum coherence in pairs of photon pulses sent one after the other so that they would maintain their coherence even after scattering from a diffuse surface.
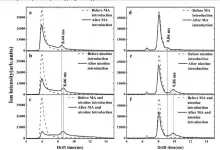
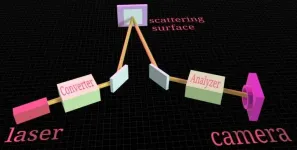
The researchers emitted a train of pulse pairs with a specific phase-coherence that could be measured from the scattered photons using quantum interference. They also used a single-photon-detector-array sensor that, in addition to solving wavefront distortions caused by atmospheric turbulence, acted as an imager thereby allowing to observe single-photon interference and imaging simultaneously. They placed the detector where they would only absorb scattered photons from the laser pulses, and observed a visibility of over 90%, meaning that the scattered photons maintained their quantum coherence even after smashing against an object.
Their novel technique required custom hardware to make use of the coherent light they were generating. The single photon detector array could detect one billion photons every second with a precision of 100 picoseconds. Only cutting-edge time-tagging electronics could handle the demands of this flow of light, and the team had to design their own electronics adapter board to communicate between the detectors and the computer that would process the data.
"Our technique can help image an object with quantum signals or transmit a quantum message in a noisy environment," said Sajeed. "Scattered photons returning to our sensor will have a certain coherence, whereas noise in the environment will not, and so we can reject everything except the photons we originally sent."
Sajeed expects their findings will stimulate new research and new applications in quantum sensing, communication, and imaging in free space environments. The duo demonstrated quantum communication and imaging in their paper, but Sajeed said further research is required to find out how their techniques could be used in various practical applications.
"We believe this could be used in quantum enhanced Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging), quantum sensing, non-line-of-sight imaging, and many other areas--the possibilities are endless," said Sajeed.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-10
Recently, a research group led by CHU Yannan and HUANG Chaoqun from the Institute of Health & Medical Technology of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) developed an effective method for on-site detection of methamphetamine (MA) in the presence of nicotine by a homemade ion mobility spectrometry. Relevant results were published in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
MA is a highly addictive stimulant that affects the central nervous system. The on-site rapid detection of trace amounts of MA and screening illicit drugs in clandestine laboratories are important for drug enforcement agencies and the forensic community in general. However, detecting MA in the ...
2021-06-10
Lack of water, floods, or crop losses: As a result of climate change, pronounced periods of drought and rainfall are occurring more frequently and more intensively all around the world, causing human suffering and major economic damage. The more precise seasonal forecasts for the coming months are, the more effectively these consequences can be mitigated. A research team from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) has now been able to improve global forecasts using statistical methods so that they can be used on the regional level. The researchers describe the new approach and the economic benefits of ...
2021-06-10
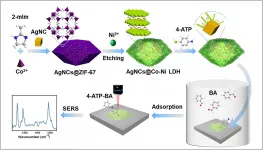
Prof. HUANG Qing's group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) developed a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) gas sensor to detect aldehyde with high sensitivity and selectivity, which provided a new detection method for studying the adsorption of gas molecules on porous materials. The relevant research results have been published in Analytical Chemistry.
Adsorption technology is one of the main technologies for treating Volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Over the past years, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted high interest for their outstanding adsorption property. Closely related to MOFs, layered double hydroxides (LDHs), also known as hydrotalcite-like ...
2021-06-10
The annual number of new HIV infections among men who have sex with men (MSM) in England is likely to have fallen dramatically, from 2,770 in 2013 to 854 in 2018, showing elimination of HIV transmission by 2030 to be within reach - suggests work by researchers from the MRC Biostatistics Unit at the University of Cambridge and Public Health England (PHE), published in The Lancet HIV.
To manage the HIV epidemic among MSM in England, enhanced testing and earlier treatment strategies were scaled-up between 2011 and 2015 and supplemented from 2015 by pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). The researchers examined the effect of these interventions on the number of new infections and investigated ...
2021-06-10
Researchers have made progress towards a G7 commitment to establish safe standards for the release of antimicrobials into the environment, by developing a new framework that establishes safe thresholds.
The threat of bacteria developing resistance to antimicrobial drugs (often called antibiotics) used to treat infection is one of the greatest global health challenges, potentially resulting in 10 million deaths per year by 2050.
A major issue is the spread of antimicrobials and resistant bacteria through water systems. When we take antibiotics, 70 per cent passes through our bodies into wastewater. Farm animals are treated with antibiotics which ...
2021-06-10
Plants use numerous mechanisms for their pollination. Now botanists have discovered a particularly sophisticated system among pipevines that is based purely on deception.
The flowers of the Greek plant Aristolochia microstoma emit a foul, musty scent that seems to mimic the smell of decaying insects. The fly pollinators from the genus Megaselia likely get attracted to this odor while searching for arthropod corpses to potentially mate over and lay their eggs. Then, when entering the tube of an Aristolochia flower, the flies are guided by downward-pointing hairs into a small chamber, which holds the female and male floral organs. Trapped inside, they deposit pollen they carry onto the stigma, before the stamens ripen and ...
2021-06-10
It eventually became a Nobel prize-winning revolution when researchers first engineered CRISPR as a gene editing technology for bacterial, plant, animal and human cells. The potential of the technology is great and span from curing genetically disposed diseases to applications in agricultural and industrial biotechnology, but there are challenges.
One such challenge consists of selecting a so-called gRNA molecule which should be designed to guide the Cas9 protein to the right location in the DNA where it will make a cut in relation to the gene editing.
"Typically, there are multiple possible gRNAs and they are not all equally efficient. Therefore, ...
2021-06-10
Using a new 3D printing process, University of Nottingham researchers have discovered how to tailor-make artificial body parts and other medical devices with built-in functionality that offers better shape and durability, while cutting the risk of bacterial infection at the same time.
Study lead, Dr Yinfeng He, from the Centre for Additive Manufacturing, said: "Most mass-produced medical devices fail to completely meet the unique and complex needs of their users. Similarly, single-material 3D printing methods have design limitations that cannot produce a bespoke device with multiple biological or mechanical functions.
"But for the first time, using a computer-aided, multi-material ...
2021-06-10
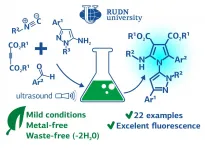
RUDN and Shahid Beheshti University(SBU) chemist proposed an eco-friendly method for the synthesis of pyrrole and pyrazole derivatives with a wide range of applications in medicine: from antidepressants to anticancer. Moreover, the synthesized compounds possess interesting fluorescence features, and the bioactive scaffolds might attract great interest in the fields of clinical diagnostics and biomedical research in the future. The results are published in the Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry.
Heterocyclic compounds expose remarkable chemistry with significant applications in medicinal and organic chemistry, industry, and pharmaceutical. These compounds are widely ...
2021-06-10
Wine grape growers in California and elsewhere face increasing labor costs and severe labor shortages, making it difficult to manage and harvest a vineyard while maintaining profitability. Growers are increasingly turning to machines for pruning, canopy management and harvesting, but how well these practices are executed can substantially affect yield and quality. A new review by researchers at the University of California, Davis, published in the journal Catalyst, provides guidelines for growers to make the best use of machines.
"Wine grape laborers have been virtually nonexistent. People don't want to work in vineyards anymore because it's remote, tough work," said Kaan Kurtural, professor of viticulture and enology and extension ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Observing quantum coherence from photons scattered in free-space