Novel materials: Sound waves traveling backwards
Researchers of the 3D matter made to order cluster of excellence use rotons for metamaterials - Nature Communications publishes first results
2021-06-10
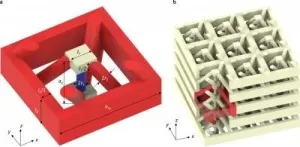
(Press-News.org) Acoustic waves in gases, liquids, and solids usually travel at an almost constant speed of sound. So-called rotons are an exception: their speed of sound changes significantly with the wavelength, and it is also possible that the waves travel backwards. Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) are studying the possibilities of using rotons in artificial materials. These computer-designed metamaterials, produced by ultra-precise 3D laser printing, might be used in the future to manipulate or direct sound in ways that have never been possible before. A report on the researchers' work has been published in Nature Communications. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23574-2)
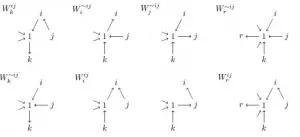
Rotons are quasiparticles, which means that they behave similarly to free particles. Unlike ordinary acoustic waves in gases, liquids, and solids, the speed of sound changes significantly with the wavelength. In addition, certain frequencies generate three different partial waves. "The slowest among them is a backward wave: the energy flow and the wavefronts run in exactly opposite directions," explains Professor Martin Wegener from the Institute of Applied Physics (APH) and KIT's Institute of Nanotechnology (INT). Understanding and benefiting from quasiparticles such as rotons is one of the great challenges of quantum physics. Physicist Lev Landau, who won a Nobel Prize in 1962 for his groundbreaking work, predicted their existence in the context of superfluidity, a condition in which a fluid loses its internal friction and becomes thermally conductive in a nearly ideal way. Until now, rotons could only be observed under special quantum-physical conditions at very low temperatures - and were therefore not suitable to technical applications.
Rotons without Any Quantum Effects
This might change in the future: in the 3D Matter Made to Order Cluster of Excellence of KIT and the University of Heidelberg, a group of researchers is working on metamaterials that "grow" rotons. Metamaterials exhibit optical, acoustic, electrical, or magnetic properties that are not found in nature. The scientists propose an artificial material that can produce rotons without any quantum effects under normal ambient conditions and at almost random frequencies or wavelengths. Thus, it might be possible in the future to better manipulate sound waves in air or in materials, for example, to bounce them back, redirect them, or create echoes. These materials have not been demonstrated experimentally yet; however, it should be possible to produce them by using technologies such as ultra-precise 3D laser printing. "We have even made some of these metamaterials in the meantime," Professor Martin Wegener says. "Currently, we are working intensively on the direct experimental proof for the existence of rotons."
3D printing - the Gateway from the Digital to the Physical World
Dr. Yi Chen, lead author of the publication, explains that the researchers relied on a combination of reflection, many discussions and numerical simulations and optimizations to devise the computer-aided virtual design of materials with such novel properties. His work as a post-doctoral researcher at KIT is funded by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and is integrated into a Helmholtz program entitled "Material Systems Engineering" launched in 2021. "In general, our dream is to design materials on the computer and then turn them directly into reality - without years of trial and error. So 3D printing is just an automated converter, as it were, from the digital to the physical world," Professor Martin Wegener explains.(or)
INFORMATION:
Original publication (Open Access):
Yi Chen, Muamer Kadic, and Martin Wegener: Roton-like acoustical dispersion relations in 3D metamaterials. Nature Communications, 2021. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23574-2
Link to the paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23574-2
More information on the "3D Matter Made to Order" Cluster of Excellence: https://www.3dmattermadetoorder.kit.edu
More about the KIT Materials Center: https://www.materials.kit.edu
Contact for this press release:
Regina Link, Press Officer, Phone: +49 721 608-41158, regina.link@kit.edu
Being "The Research University in the Helmholtz Association", KIT creates and imparts knowledge for the society and the environment. It is the objective to make significant contributions to the global challenges in the fields of energy, mobility, and information. For this, about 9,600 employees cooperate in a broad range of disciplines in natural sciences, engineering sciences, economics, and the humanities and social sciences. KIT prepares its 23,300 students for responsible tasks in society, industry, and science by offering research-based study programs. Innovation efforts at KIT build a bridge between important scientific findings and their application for the benefit of society, economic prosperity, and the preservation of our natural basis of life. KIT is one of the German universities of excellence.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-10
New Orleans, LA - Research conducted at LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center of Excellence reports that Elovanoids, bioactive chemical messengers made from omega-3 very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids discovered by the Bazan lab in 2017, may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from entering cells and protect the air cells (alveoli) of the lung. Their findings are published online in Scientific Reports, available here.
"Because the compounds are protective against damage in the brain and retina of the eye and the COVID-19 virus clearly damages the lung, ...
2021-06-10
Fraud is going uninvestigated by police who are "hiding behind the veil" of the Action Fraud national crime reporting agency.
In his paper published this week in Policing, Professor Mark Button, director of the Centre for Counter Fraud Studies at the University of Portsmouth argues that, Action Fraud, which has been widely derided, has become a useful veil from which the police can hide their inadequate response.
Figures from Action Fraud, the arm of the police responsible for recording scams and fraud, show that between 2019 and 2020, over 800,000 people reported being a victim of fraud, with £2.3bn finding its way into criminal hands. However, Professor Button calculated just 0.6 per cent of police officers ...
2021-06-10
For two decades, the number of Americans who die each year from drug overdoses has steadily risen, from less than 20,000 in 1999 to more than 80,000 in 2020. By studying patterns of these drug-related fatalities, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, San Diego State University (SDSU), and international collaborators have designed and validated a prediction model to signal counties at risk of future overdose death outbreaks. The goal of the open-source tool is to predict and prevent deaths through early deployment of public health resources.
Findings were published June 9, 2021 by Lancet Public Health.
"A big challenge for public health experts is figuring out which parts of the country are at greatest risk of ...
2021-06-10
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers show that the fiber optic cables that carry data across the world's oceans can also be used to sense geophysical events and monitor ocean and seafloor conditions.
Although buoys and cabled observatories can be used to monitor parts of the ocean, the information they provide is limited to their immediate surroundings. The new approach could offer a way to use the global network of subsea fiber optic cables to study otherwise inaccessible parts of the ocean.
"Once perfected, this new technique will allow geophysical sensing in the ocean depths, which are largely unexplored because of a lack of instrumentation that works in this environment," said Zhongwen Zhan, assistant professor of geophysics at Caltech. ...
2021-06-10
A CABI-led study has revealed that the success of Classical Biological Control (CBC) in Europe, North Africa and the Middle East is only rarely dependent on the released biological control agent, but more often on other factors, such as the target pest, its host plant, or the circumstances of the releases.
The research - published in the journal NeoBiota - suggests that the overall success of biological control introductions of insect predators and parasitoids against herbivorous insects in the Western Paleartic ecozone is comparable to the success of CBC worldwide. However, over 100 years of CBC in this region, has resulted in no overall rise in success in the fight against insect pests - including those of crops such as citrus, olive, potato, ...
2021-06-10
The COVID-19 pandemic has made clear the importance of understanding precisely how diseases spread throughout networks of transportation. However, rigorously determining the connection between disease risk and changing networks--which either humans or the environment may alter--is challenging due to the complexity of these systems. In a paper publishing on Thursday in the END ...
2021-06-10
Quantum coherence is a key ingredient in many fundamental tests and applications of quantum technology including quantum communication, imaging, computing, sensing and metrology. However, the transfer of quantum coherence in free-space has so far been limited to direct line-of-sight channels as atmospheric turbulence and scattering degrade the quality of coherence severely.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, researchers from the University of Waterloo have successfully demonstrated the transfer and recovery of quantum coherence using photons scattered in free-space ...
2021-06-10
Recently, a research group led by CHU Yannan and HUANG Chaoqun from the Institute of Health & Medical Technology of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) developed an effective method for on-site detection of methamphetamine (MA) in the presence of nicotine by a homemade ion mobility spectrometry. Relevant results were published in Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.
MA is a highly addictive stimulant that affects the central nervous system. The on-site rapid detection of trace amounts of MA and screening illicit drugs in clandestine laboratories are important for drug enforcement agencies and the forensic community in general. However, detecting MA in the ...
2021-06-10
Lack of water, floods, or crop losses: As a result of climate change, pronounced periods of drought and rainfall are occurring more frequently and more intensively all around the world, causing human suffering and major economic damage. The more precise seasonal forecasts for the coming months are, the more effectively these consequences can be mitigated. A research team from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) has now been able to improve global forecasts using statistical methods so that they can be used on the regional level. The researchers describe the new approach and the economic benefits of ...
2021-06-10
Prof. HUANG Qing's group from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) developed a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) gas sensor to detect aldehyde with high sensitivity and selectivity, which provided a new detection method for studying the adsorption of gas molecules on porous materials. The relevant research results have been published in Analytical Chemistry.
Adsorption technology is one of the main technologies for treating Volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Over the past years, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have attracted high interest for their outstanding adsorption property. Closely related to MOFs, layered double hydroxides (LDHs), also known as hydrotalcite-like ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel materials: Sound waves traveling backwards
Researchers of the 3D matter made to order cluster of excellence use rotons for metamaterials - Nature Communications publishes first results