(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. - Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated that a class of interwoven composite materials called semi-interpenetrating polymer networks (sIPNs) can be produced by living cells. The approach could make these versatile materials more biologically compatible for biomedical applications such as time-delayed drug delivery systems.
The research appears online on June 8 in the journal Nature Communications.
The concept of sIPNs has been around for more than 100 years and has been used in automotive parts, medical devices, molding compounds and engineering plastics. The general idea is for one or more polymers to assemble around another polymer scaffold in such a way that they become interlocked. Even though the polymers are not chemically bonded, they cannot be pulled apart and form a new material with properties greater than the simple sum of its parts.
Traditional methods for manufacturing sIPNs typically involve producing the constituent parts called monomers and mixing them together in the right chemical conditions to control their assembly into large networks in a process called polymerization.
"When it works, it's a fantastic platform that can incorporate different functionalities into the self-assembled layer for biomedical or environmental applications," said Lingchong You, professor of biomedical engineering at Duke. "But the process is often not as biocompatible as you might want. So we thought why not use living cells to synthesize the second layer to make it as biocompatible as possible?"
In the new paper, Zhuojun Dai, a former postdoc in the You lab who is now an associate professor at the Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology, uses a platform that the lab has been developing for several years called "swarmbots" to do just that.
The swarmbots are living cells that are programmed to produce biological molecules within their walls and then explode once their population reaches a certain density. In this case, they're programmed to produce monomers called elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) fused to functional features called SpyTag and SpyCatcher. These two molecular structures form a lock-and-key system, allowing the ELPs to self-assemble into a polymer chain when mixed. As they grow, these polymers entangle themselves with the polymeric microcapsules containing the cells to form sIPNs.
Each monomer can contain multiple SpyTags or SpyCatchers and can also be fused to proteins that generate a readout or have specific functions. It's sort of like making a chain-link fence out of many tiny charm bracelets that have room for clasps and charms.
The researchers first program the cells to fill this accessorizable feature with a fluorescent protein to prove that the system can lock them into place. After that successful demonstration, they turn their attention to engineering a useful drug delivery system with their new invention.
"You could replace the fluorescent marker with anything that has a function you want to feature," said You. "We decided to touch on antibiotics because it's one of the other focuses of our lab."
Beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillin and its derivatives, are some of the most commonly used antibiotics in the world. They're also often overused and can have negative effects such as destroying the natural microbiome that lives within our guts.
To demonstrate one way in which their new cell-built sIPNs could be useful, the researchers fill the accessorizable spot with beta-lactamase, which can degrade beta-lactam antibiotics. By injecting the newly functionalized sIPNs into mice, the researchers showed the platform could slowly release the otherwise short-lived protective molecule to help the mice's gut microbiomes ward off negative side effects from the antibiotics.
"Nobody has used living cells as a factory to produce monomers in real-time for sIPNs before," said You. "The proof-of-principle demonstration shows that, not only can we fabricate these types of functional materials with live cells, but they can exhibit medically relevant functions."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (ZD: 2018YFA0903000, ZD: 2020YFA0908100, LD: 2019YFA09006700), the U.S. Army Research Of?ce (LY: W911NF-14-1-0490), the National Institutes of Health (LY: 2R01-GM098642, 1RO1AI25604), a David and Lucile Packard Fellowship (LY), Shenzhen Peacock Team Project (ZD: KQTD20180413181837372), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (ZD:32071427, LD: 31971513).
CITATION: "Living Fabrication of Functional Semi-Interpenetrating Polymeric Materials," Zhuojun Dai, Xiaoyu Yang, Feilun Wu, Lihua Wang, Kun Xiang , Pengcheng Li, Qingqing Lv, Jinhui Tang, Anders Dohlman, Lei Dai, Xiling Shen & Lingchong You. Nature Communications, June 8, 2021. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23812-7
Humans expect that AI is Benevolent and trustworthy. A new study reveals that at the same time humans are unwilling to cooperate and compromise with machines. They even exploit them.
Picture yourself driving on a narrow road in the near future when suddenly another car emerges from a bend ahead. It is a self-driving car with no passengers inside. Will you push forth and assert your right of way, or give way to let it pass? At present, most of us behave kindly in such situations involving oth-er humans. Will we show that same kindness towards autonomous vehicles?
Using methods ...
As COVID-19 restrictions ease nationwide and more people host indoor gatherings, investing in a high efficiency particulate air (HEPA) purifier might not be a bad idea, says a University of Cincinnati College of Medicine researcher.
Several published studies evaluating aerosols and submicron particles similar in size to the SARS-CoV-2 virion have shown that portable HEPA purifiers are able to significantly reduce airborne COVID-19 particles, says Ahmad Sedaghat, MD, PhD, director of the UC Division of Rhinology, Allergy and Anterior Skull Base Surgery.
Sedaghat identified the medical literature showing published studies on the effectiveness ...
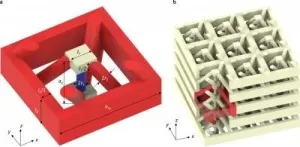
Acoustic waves in gases, liquids, and solids usually travel at an almost constant speed of sound. So-called rotons are an exception: their speed of sound changes significantly with the wavelength, and it is also possible that the waves travel backwards. Researchers at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) are studying the possibilities of using rotons in artificial materials. These computer-designed metamaterials, produced by ultra-precise 3D laser printing, might be used in the future to manipulate or direct sound in ways that have never been possible before. A report on the researchers' work has been published in Nature Communications. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23574-2)
Rotons are quasiparticles, which means that they behave ...
New Orleans, LA - Research conducted at LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center of Excellence reports that Elovanoids, bioactive chemical messengers made from omega-3 very-long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids discovered by the Bazan lab in 2017, may block the virus that causes COVID-19 from entering cells and protect the air cells (alveoli) of the lung. Their findings are published online in Scientific Reports, available here.
"Because the compounds are protective against damage in the brain and retina of the eye and the COVID-19 virus clearly damages the lung, ...
Fraud is going uninvestigated by police who are "hiding behind the veil" of the Action Fraud national crime reporting agency.
In his paper published this week in Policing, Professor Mark Button, director of the Centre for Counter Fraud Studies at the University of Portsmouth argues that, Action Fraud, which has been widely derided, has become a useful veil from which the police can hide their inadequate response.
Figures from Action Fraud, the arm of the police responsible for recording scams and fraud, show that between 2019 and 2020, over 800,000 people reported being a victim of fraud, with £2.3bn finding its way into criminal hands. However, Professor Button calculated just 0.6 per cent of police officers ...
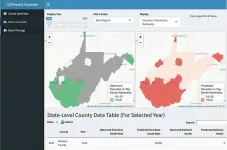
For two decades, the number of Americans who die each year from drug overdoses has steadily risen, from less than 20,000 in 1999 to more than 80,000 in 2020. By studying patterns of these drug-related fatalities, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, San Diego State University (SDSU), and international collaborators have designed and validated a prediction model to signal counties at risk of future overdose death outbreaks. The goal of the open-source tool is to predict and prevent deaths through early deployment of public health resources.
Findings were published June 9, 2021 by Lancet Public Health.
"A big challenge for public health experts is figuring out which parts of the country are at greatest risk of ...
WASHINGTON -- In a new study, researchers show that the fiber optic cables that carry data across the world's oceans can also be used to sense geophysical events and monitor ocean and seafloor conditions.
Although buoys and cabled observatories can be used to monitor parts of the ocean, the information they provide is limited to their immediate surroundings. The new approach could offer a way to use the global network of subsea fiber optic cables to study otherwise inaccessible parts of the ocean.
"Once perfected, this new technique will allow geophysical sensing in the ocean depths, which are largely unexplored because of a lack of instrumentation that works in this environment," said Zhongwen Zhan, assistant professor of geophysics at Caltech. ...
A CABI-led study has revealed that the success of Classical Biological Control (CBC) in Europe, North Africa and the Middle East is only rarely dependent on the released biological control agent, but more often on other factors, such as the target pest, its host plant, or the circumstances of the releases.
The research - published in the journal NeoBiota - suggests that the overall success of biological control introductions of insect predators and parasitoids against herbivorous insects in the Western Paleartic ecozone is comparable to the success of CBC worldwide. However, over 100 years of CBC in this region, has resulted in no overall rise in success in the fight against insect pests - including those of crops such as citrus, olive, potato, ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has made clear the importance of understanding precisely how diseases spread throughout networks of transportation. However, rigorously determining the connection between disease risk and changing networks--which either humans or the environment may alter--is challenging due to the complexity of these systems. In a paper publishing on Thursday in the END ...
Quantum coherence is a key ingredient in many fundamental tests and applications of quantum technology including quantum communication, imaging, computing, sensing and metrology. However, the transfer of quantum coherence in free-space has so far been limited to direct line-of-sight channels as atmospheric turbulence and scattering degrade the quality of coherence severely.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, researchers from the University of Waterloo have successfully demonstrated the transfer and recovery of quantum coherence using photons scattered in free-space ...