(Press-News.org) WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Many animals have evolved camouflage tactics for self-defense, but some butterflies and moths have taken it even further: They've developed transparent wings, making them almost invisible to predators.
A team led by Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) scientists studied the development of one such species, the glasswing butterfly, Greta oto, to see through the secrets of this natural stealth technology. Their work was published in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
Although transparent structures in animals are well established, they appear far more often in aquatic organisms. "It's an interesting biological question because there just aren't that many transparent organisms on land," notes lead author END
How butterflies make transparent wings: MBL scientists see the invisible
2021-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
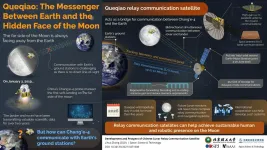
Queqiao: The bridge between Earth and the far side of the moon
2021-06-10
Because of a phenomenon called gravitational locking, the Moon always faces the Earth from the same side. This proved useful in the early lunar landing missions in the 20th century, as there was always a direct line of sight for uninterrupted radiocommunications between Earth ground stations and equipment on the Moon. However, gravitational locking makes exploring the hidden face of the moon--the far side--much more challenging, because signals cannot be sent directly across the Moon towards Earth.
Still, in January 2019, China's lunar probe Chang'e-4 marked the first time a spacecraft landed on the far side of the Moon. Both the lander and the lunar rover it carried have been gathering and sending back images and ...
Cell Phone Use While Driving May Be Tied to Other Risky Road Behaviors in Young Adults
2021-06-10
Philadelphia, June 10, 2021 - A new study from researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the University of Pennsylvania's Annenberg Public Policy Center found that 18- to 24-year-olds who use cell phones while driving are more likely to engage in other risky driving behaviors associated with "acting-without-thinking," a form of impulsivity. These findings suggest the importance of developing new strategies to prevent risky driving in young adults, especially those with impulsive personalities. The study was recently published in the International Journal of Environmental Research Public Health.
Cell phone use while driving has been linked to increased crash and near-crash risk. Despite bans on handheld cell phone use ...
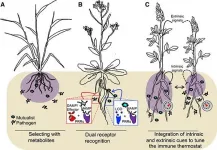
How do plants balance microbial friends and foes?
2021-06-10
Plants are constantly exposed to microbes: pathogens that cause disease, commensals that cause no harm or benefit, and mutualists that promote plant growth or help fend off pathogens. For example, most land plants can form positive relationships with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to improve nutrient uptake. How plants fight off pathogens without also killing beneficial microbes or wasting energy on commensal microbes is a largely unanswered question.
In fact, when scientists within the field of Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions were asked to come up with their Top 10 Unanswered Questions, the #1 question was "How do plants engage with beneficial microorganisms while at the same time restricting ...
Like night and day: Animal studies may not translate to humans without time considerations
2021-06-10
MORGANTOWN, W.Va. -- Imagine being woken up at 3 a.m. to navigate a corn maze, memorize 20 items on a shopping list or pass your driver's test.
According to a new analysis out of West Virginia University, that's often what it's like to be a rodent in a biomedical study. Mice and rats, which make up the vast majority of animal models, are nocturnal. Yet a survey of animal studies across eight behavioral neuroscience domains showed that most behavioral testing is conducted during the day, when the rodents would normally be at rest.
"There are these dramatic daily fluctuations--in metabolism, in immune function, in learning and ...
Saliva can be more effective than nasopharyngeal swabs for COVID-19 testing
2021-06-10
Philadelphia, June 10, 2021 - The collection of nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) samples for COVID-19 diagnostic testing poses challenges including exposure risk to healthcare workers and supply chain constraints. Saliva samples are easier to collect but can be mixed with mucus or blood, and some studies have found they produce less accurate results. A team of researchers has found that an innovative protocol that processes saliva samples with a bead mill homogenizer before real-time PCR (RT-PCR) testing results in higher sensitivity compared to NPS samples. Their protocol appears in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier.
"Saliva as a sample type for COVID-19 testing ...
Printing flexible wearable electronics for smart device applications
2021-06-10
WASHINGTON, June 10, 2021 -- The demand for flexible wearable electronics has spiked with the dramatic growth of smart devices that can exchange data with other devices over the internet with embedded sensors, software, and other technologies. Researchers consequently have focused on exploring flexible energy storage devices, such as flexible supercapacitators (FSCs), that are lightweight and safe and easily integrate with other devices. FSCs have high power density and fast charge and discharge rates.
Printing electronics, manufacturing electronics devices and systems by using conventional printing techniques, has proved to be an economical, simple, and scalable strategy for fabricating FSCs. Traditional micromanufacturing ...
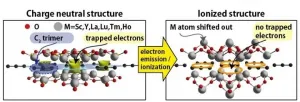
New family of atomic-thin electride materials discovered
2021-06-10
An exploratory investigation into the behavior of materials with desirable electric properties resulted in the discovery of a structural phase of two-dimensional (2D) materials. The new family of materials are electrides, wherein electrons occupy a space usually reserved for atoms or ions instead of orbiting the nucleus of an atom or ion. The stable, low-energy, tunable materials could have potential applications in nanotechnologies.
The international research team, led by Hannes Raebiger, associate professor in the Department of Physics at Yokohama National University in Japan, published their results on June 10th as frontispiece in Advanced Functional Materials.
Initially, the team ...
Study shows how permafrost releases methane in the warming Arctic
2021-06-10
Researchers from Skoltech have designed and conducted experiments measuring gas permeability under various conditions for ice-containing sediments mimicking permafrost. Their results can be useful both in modeling and testing techniques for gas production from Arctic reservoirs and in tracing methane emission in high latitudes. The paper was published in the journal Energy&Fuels.
Permafrost, even though it sounds very stable and permanent, is actually quite diverse: depending on the composition of the frozen ground, pressure, temperature and so on, it can have varying properties, which are extremely important if you want to build something on permafrost, ...
'Roadmaps' of the brain reveal regions vulnerable to Alzheimer's disease
2021-06-10
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (JUNE 10, 2021) -- Much like a supply truck crossing the countryside, the misfolded proteins that damage neurons in Alzheimer's disease travel the "roads" of the brain, sometimes stopping and sometimes re-routing to avoid roadblocks, reports a study published in END ...
COVID-19 creates hearing, balance disorders, aggravates tinnitus symptoms
2021-06-10
MELVILLE, N.Y., June 10, 2021 -- The physiological impacts of COVID-19 seem almost limitless. Complications can range from loss of taste to respiratory distress, with many effects lasting for months. Evidence suggests auditory and vestibular effects should be added to the growing list of symptoms.
During the 180th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, which will be held virtually June 8-10, Colleen Le Prell, from the University of Texas at Dallas, will talk about hearing and balance disorders associated with coronavirus infection and how pandemic-related stress ...