(Press-News.org) A team of neuroscientists are calling for greater support of neuroscience research in Africa following a long-term analysis of research outputs in the continent.
The findings detail important information about funding and international collaboration comparing activity in the continent to the US, UK and areas of Europe. It's hoped that the study will provide useful data to help shape and grow science in Africa.
Africa has the world's largest human genetic diversity which carries important implications for understanding human diseases, including neurological disorders.
Co-lead Senior author - Tom Baden, Professor of Neuroscience in the School of Life Sciences and the Sussex Neuroscience research group at the University of Sussex said: "One beautiful thing about science is that there is no such thing as a truly local problem. But that also means that there should be no such thing as a local solution - research and scientific communication by their very nature must be a global endeavour.
"And yet, currently the vast majority of research across most disciplines is carried out by a relatively small number of countries, located mostly in the global north. This is a huge waste of human potential."
The team, made up of experts from the University of Sussex, the Francis Crick Institute and institutions from across Africa, analysed all of the continent's Neuroscience outputs over two decades, thoroughly curating local and international collaborations, research citation, visibility and funding.
Lead author Mahmoud Bukar Maina, a Research Fellow in the School of Life Sciences and the Sussex Neuroscience research group at the University of Sussex and visiting scientist at Yobe State University, Nigeria, said: "Even though early progress in neuroscience began in Egypt, Africa's research in this area has not kept pace with developments in the field around the world. There are a number of reasons behind this and, for the first time, our work has provided a clear picture of why - covering both strengths and weaknesses of neuroscience research in Africa and comparing this to other continents.
"We hope it will provide useful data to guide governments, funders and other stakeholders in helping to shape science in Africa, and combat the 'brain drain' from the region."
Co-lead Senior author Lucia Prieto-Godino, a Group Leader at the Francis Crick Institute, said: "One of the reasons why this work is so important, is that the first step to solve any problem is understanding it. Here we analyse key features and the evolution of neuroscience publications across all 54 African countries, and put them in a global context. This highlights strengths and weaknesses, and informs which aspects will be key in the future to support the growth and global integration of neuroscience research in the continent."?
The study, published in Nature Communications, clearly details the African countries with the highest research outputs and reveals that the majority of research funding comes from external sources such as the USA and UK.
The researchers argue that local funding is vital in order to establish a sustainable African neuroscience research environment, suggesting greater government backing as well as support from the philanthropic sector.
Professor Baden added: "One pervasive problem highlighted in our research was the marked absence of domestic funding. In most African countries, international funding far predominates. This is doubly problematic.
"Firstly, it takes away the crucial funding stability that African researchers would need to meaningfully embark on large-scale and long-term research projects, and secondly, it means that the international, non-African funders essentially end up deciding what research is performed across the continent. Such as system would generate profound outrage across places like Europe - how then can it be acceptable for Africa?"
INFORMATION:
Many of the researchers involved in the analysis are active members of TReND Africa, a charity co-founded by Lucia and Tom, which supports scientific capacity building across Africa through biomedical training courses, networking opportunities, outreach and workshops.
Hurricanes that make landfall typically decay but sometimes transition into extratropical cyclones and re-intensify, causing widespread damage to inland communities
The presence of a cold core is currently used to identify this transition, but a new study has now found that a cold core naturally forms in all landfalling hurricanes
The cold core was detected when scientists ran simulations of landfalling hurricanes that accounted for moisture stored within the cyclone
Over time, the scientists saw a cold core growing from the bottom of the hurricane, replacing the warm core
The research could help forecasters make more ...
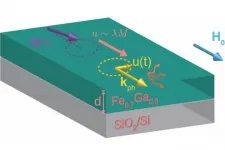
A study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers uncovered a property of magnetic materials that will allow engineers to develop more efficient spintronic devices in the future. Spintronics focuses on using the magnetic "spin" property of electrons instead of their charge, which improves the speed and efficiency of devices used for computing and data storage.
The research is published in Physical Review B, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Physical Society.
One of the major roadblocks in developing better spintronic devices is an effect called "damping," in which the magnetic energy essentially leaks out of the materials, causing them to be less efficient. Traditionally, scientists ...
Humans often cooperate, but ample research has shown that they're conditionally cooperative; that is, they are far more likely to cooperate with those who they consider "good."
In large societies, however, people don't always know the reputations of the people with whom they interact. That's where reputation monitoring systems--such as the star ratings for eBay sellers or the scores assigned by credit bureaus--come into play, helping guide people's decisions about whether or not they want to help or interact with another person.
In a new paper in the journal Nature Communications, a team from Penn uses mathematical modeling to study how public institutions of reputation monitoring can foster cooperation and also encourage participants to adhere to its assessments instead ...
In fighting the COVID-19 pandemic, it's not just the vaccines that require complicated cold supply chains and refrigerated storage. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests -- often considered the "gold standard" of testing -- also have enzymes and reagents that need to be frozen.
Northwestern University researchers have discovered that commercially available PCR tests can withstand the freeze-drying process, making them shelf-stable for up to 30 days and 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit), without sacrificing sensitivity and accuracy.
The researchers ...
In 2007, the American housing boom ended, and there was heightened risk of a housing crisis. Private securitizers withdrew from purchasing high-risk mortgages, while government-sponsored enterprises, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, dramatically increased their acquisitions of risky mortgages. By 2008, the agencies reversed course, decreasing their high-risk acquisitions.
In a new article, an economist proposes a scenario in which large lenders temporarily boost high-risk activity at the end of a boom. According to her model, lenders with many outstanding mortgages have incentives to extend risky credit to prop up housing prices, which lessens the losses on their outstanding portfolio of mortgages. As the bust continues, lenders slowly wind down their mortgage exposure.
The ...
BOSTON - The cost of cancer care in United States was an estimated $183 billion in 2015 and is projected to rise by 30 percent by 2030, according to the American Cancer Society. While private and government insurance may cover much of the cost of care, even patients with insurance can struggle to pay for office visit co-payments, prescription medications or other cancer-related expenses. Yet limited data describes how financial hardship impacts patient behavior and how that in turn may impact patient health.
In a new study designed to provide a more comprehensive picture of how a diverse cohort of gynecologic cancer patients are affected by financial distress -- also called "financial toxicity" in acknowledgment of the health ...
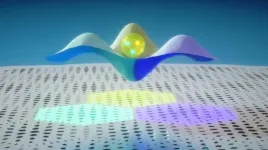
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- When two similar atomic layers with mismatching lattice constants -- the constant distance between a layer's unit cells -- and/or orientation are stacked together, the resulting bilayer can exhibit a moiré pattern and form a moiré superlattice.
Moiré patterns are interference patterns that typically arise when one object with a repetitive pattern is placed over another with a similar pattern. Moiré superlattices, formed by atomic layers, can exhibit fascinating phenomena not found in the individual layers, opening the door to technological revolutions in many areas, including electricity transmission, information engineering, and ...
White men who had a Black neighbor when they were growing up are more likely to be Democrats and less likely to be Republican, an influence that can last several decades later.
That's according to a Harvard study published Friday in Science Advances that takes individual level data from 650,000 Americans recorded in the 1940 U.S. Census. Using machine learning, the analysis links those records to contemporary voter files to see if there are correlations between having a Black neighbor as a child and political views later in life. The paper includes only men because the common practice of surname changes at marriage made it difficult to accurately track women.
The scientists found that those 650,000 white men who had a Black neighbor growing up are believed to be more likely ...
There is no question that the pandemic has been immensely stressful for health care workers, especially for those on the frontline of patient care. Yet, even before the pandemic, the regular demands of many health care industry jobs put these workers at risk for burnout.
Now, a new study from the University of Georgia suggests that investing in more physical activity programming could mitigate the effects of stress and improve worker mental and emotional health.
Tackling burnout in health care is critical to ensuring patient safety, said lead author Marilyn ...
(Boston)-- Prevalence rates of opioid use disorder (OUD) have increased dramatically, accompanied by a surge of overdose deaths--nearly 50,000 in the U.S. in 2019. While opioid dependence has been extensively studied in preclinical models, an understanding of the biological alterations that occur in the brains of people who chronically use opioids and who are diagnosed with OUD remains limited.
To address this issue, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have conducted the largest transcriptomic (the study of all the RNA molecules within a cell) study to date using postmortem ...