(Press-News.org) White men who had a Black neighbor when they were growing up are more likely to be Democrats and less likely to be Republican, an influence that can last several decades later.
That's according to a Harvard study published Friday in Science Advances that takes individual level data from 650,000 Americans recorded in the 1940 U.S. Census. Using machine learning, the analysis links those records to contemporary voter files to see if there are correlations between having a Black neighbor as a child and political views later in life. The paper includes only men because the common practice of surname changes at marriage made it difficult to accurately track women.
The scientists found that those 650,000 white men who had a Black neighbor growing up are believed to be more likely to skew toward more racially liberal politics and hold other more liberal stances because of their noted party affiliation as registered Democrats than those who did not have a Black neighbor.
"What we identified here was a way to say does [cross-ethnic exposure] matter over a really long-life period -- over a period that people never had a chance to look at before," said government Professor Ryan D. Enos. "We asked: 'Is there a relationship between their contact with African Americans early in life and their politics way later in life?' What we found is that there is. If white Americans are exposed by having a neighbor that is African Americans early in life, they're more likely to be Democrats, which is the party of racial liberalism in the United States, almost eight decades later."
The team of social scientists from Harvard's Institute for Quantitative, Department of Government, and Boston University found that white men with a Black next-door neighbor in 1940 were 1.5 percentage points to 4.2 percentage points more likely to be Democrats in 2005 and 2009. In 2017, that percentage point range became 2.8 to 5.3 compared to those without a Black, next-door neighbor.
Even when it came to the inverse --a decreased likelihood to register as a Republican -- the statistics almost mirrored each other for the same years.
The statistics are significant because of how strict partisan lines have become in the U.S., acting essentially one of the strongest predictors of nearly every political attitude and many nonpolitical lifestyle choices, according to the report.
Researchers point out that their findings are only based on what party the white men they tracked are registered as and they can't be sure what beliefs, attitudes, and policy preferences they actually hold. But because of history and their registered affiliation, they believe those views are likely more liberal ones when it comes to issues like race.
"There is no doubt that racial attitudes are correlated with partisanship in the United States," Enos said. "We see this across all kinds of scholarship where, in many ways, the modern parties in the U.S., Democrats and Republicans, their membership was shaped by their position on racial issues....The fact is we know these things drive people towards these parties. That's not true of everybody but on average, a person that is more racially liberal is more likely to be a Democrat, and that's just what we see here, something consistent with that."
Employing a wide range of statistical techniques and controls to try and account for outliers that would explain the reasoning behind their numbers, researchers could account for moral, ethical, and tolerance values taught to the children by others, like their parents, for example. While they could not eliminate these as explanations they believe they do not interfere with the findings and that it was the interracial contact the men experienced as children that was affecting the politics of these men later in life.
The researchers also compared people who lived in the same neighborhoods. Each time the statistics held up: the person who had a black neighbor was more likely to be Democrat than the one that didn't.
The study provides what's believed to be some of the first quantifiable proof that early exposure to people of different ethnicities can be a predictor and influencer of long-term political behavior.
Whether contact across social groups influences sociopolitical behavior in the long run is among the most studied in the social sciences because of its implication for the harmony of diverse societies. Many social scientists believe that interpersonal relationships across ethnic, racial, or any type of sort of diverse groups especially during adolescence leads to this increased harmony. Social scientists call it the contact hypothesis.
Evidence for this popular theory has traditionally been limited because researchers tend to only observe a small amount of people over very short time periods and often in laboratory settings. A common experiment has been mixing different groups of people together to see if they walk away from the lab feeling a little better about the other groups. The problem is researchers don't know what happens the next week or the next year. This new study focuses on that long-term influence.
To get their findings, researchers constructed a dataset capturing many of the early-life experiences, including demographics like exact address, race, age, and socioeconomic status, of nearly every child in the U.S. living in 1940. The 1940 census became public record in 72 years after the 2012 census was taken.
Researchers found white men still living and registered to vote based on contemporary voter file data. Machine learning algorithms matched the available variables from the census data with the voter file data to track the individuals for over 77 years. Most commonly these variables were name, age, gender, and place of birth.
Researchers are currently looking to expand the project by adding white women who weren't included in the original study and expanding to other ethnicities. They are also beginning to reach out to the people they tracked to gauge their actual sociopolitical views to see if they match their findings.
Outside of politics, the paper suggests deep implications for diversity programs in schools, and activities that people do to shape things like intergroup attitudes.
"What this really speaks to is the long-term viability and the long-term stability of diverse societies," Enos said. "We now know there's a potential now for those to have lifelong consequences in terms of how they shape people's attitudes."
INFORMATION:
There is no question that the pandemic has been immensely stressful for health care workers, especially for those on the frontline of patient care. Yet, even before the pandemic, the regular demands of many health care industry jobs put these workers at risk for burnout.
Now, a new study from the University of Georgia suggests that investing in more physical activity programming could mitigate the effects of stress and improve worker mental and emotional health.
Tackling burnout in health care is critical to ensuring patient safety, said lead author Marilyn ...
(Boston)-- Prevalence rates of opioid use disorder (OUD) have increased dramatically, accompanied by a surge of overdose deaths--nearly 50,000 in the U.S. in 2019. While opioid dependence has been extensively studied in preclinical models, an understanding of the biological alterations that occur in the brains of people who chronically use opioids and who are diagnosed with OUD remains limited.
To address this issue, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have conducted the largest transcriptomic (the study of all the RNA molecules within a cell) study to date using postmortem ...
People with end-stage renal disease often undergo hemodialysis, a life-sustaining blood-filtering treatment. To make the process as fast and efficient as possible, many people have "hemodialysis grafts" surgically implanted. These grafts are like bypasses, connecting a vein to a major artery, making it easier to access blood and ensuring the same blood doesn't get filtered twice.
But the grafts have a notorious problem: Clots tend to form where the graft is attached to the vein. For the person undergoing dialysis, this means not only a break from treatment, but also surgery to remove the graft and then surgery to implant another.
A multidisciplinary team from Washington University School of Medicine ...
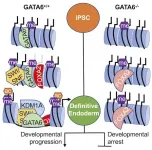
Scientists know that developing cells in a healthy embryo will transform into a variety of cell types that will make up the different organ systems in the human body, a process known as cell differentiation. But they don't know how the cells do it.
A Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) study in Cell Reports led by Stephen Duncan, D.Phil., examines how an endodermal cell - a type of developing cell - becomes a liver cell and not some other type of cell. Duncan and his team found that the development of naive cells into differentiated liver cells ...
Researchers have developed a new approach to gene therapy that leans on the common pain reliever acetaminophen to force a variety of genetic diseases into remission.
A paper published in Science Translational Medicine describes how the novel technique successfully treated the blood-clotting disorder hemophilia and the debilitating metabolic disease known as phenylketonuria, or PKU, in mice.
The approach uses a benign lentivirus to both correct disease-causing mutations and to insert a new gene that makes liver cells immune to the potentially toxic effects of acetaminophen. The latter ...
CINCINNATI--The disease is so rare and complex that its acronym is hard to pronounce. But for infants unlucky enough to be born with this lung disease, the outcome is usually fatal.
The disease is called alveolar capillary dysplasia with misalignment of the pulmonary veins (ACDMPV). Research indicates the disease is linked to mutations in the FOXF1 gene. Worldwide, medical experts have documented about 200 cases, but an unknown number of infants may have died without the condition ever being diagnosed, according to the National Organization for Rare Disorders.
The disease is caused by genetic variations that prevent proper blood vessel formation in the lungs. Within ...
Los Alamos, N.M., June 10, 2021 - For the first time, the boundary of the heliosphere has been mapped, giving scientists a better understanding of how solar and interstellar winds interact.
Video link: https://youtu.be/w__vzNXSFoI
"Physics models have theorized this boundary for years," said Dan Reisenfeld, a scientist at Los Alamos National Laboratory and lead author on the paper, which was published in the Astrophysical Journal today. "But this is the first time we've actually been able to measure it and make a three-dimensional map of it."
The heliosphere is a bubble created by the solar wind, a stream ...
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- An international research team has described a new species of Oculudentavis, providing further evidence that the animal first identified as a hummingbird-sized dinosaur was actually a lizard.
The new species, named Oculudentavis naga in honor of the Naga people of Myanmar and India, is represented by a partial skeleton that includes a complete skull, exquisitely preserved in amber with visible scales and soft tissue. The specimen is in the same genus as Oculudentavis khaungraae, whose original description as the smallest known bird was retracted last year. The two fossils were found in the same area and are about 99 million years ...
What The Study Did: The results suggest assisted living residents experienced increased mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic consistent with increases observed among nursing home residents.
Authors: Kali S. Thomas, Ph.D., of Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.13411)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the association between the amount of ultra-processed food consumed by children and their weight in early adulthood.
Authors: Kiara Chang, Ph.D., of Imperial College London, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1573)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: ...