INFORMATION:
Many prolonged sick leaves for COVID-19
2021-06-14
(Press-News.org) Nearly 12,000 people in Sweden received sickness benefit from the Swedish Social Insurance Agency for COVID-19 during the first wave of the pandemic. The median duration of sick leave in this group was 35 days, but for many it was considerably more long-drawn-out, according to a University of Gothenburg study.
A research group in rehabilitation medicine at the University of Gothenburg has studied sick-leave patterns. The study now presented in the scientific journal BMC Public Health.
The study included all recipients of sickness benefit from the Social Insurance Agency for COVID-19 diagnoses in Sweden during the first pandemic wave, from 1 March to 31 August 2020, and monitored them for 4 months from the start of the sick-leave period.
Sickness benefit from the Swedish Social Insurance Agency is normally paid from day 15 of a sick-leave period. People whose sick leave lasted two weeks or less, with sick pay from the employer, were not included in the study.
Data from the Social Insurance Agency, the National Board of Health and Welfare, and Statistics Sweden were used. Describing sick leaves is a way to investigate the impact of diseases on society and individuals, but few other studies have specifically looked at this repercussion of the pandemic.
The results show that 11,955 people received sickness benefit for COVID-19 during the first wave. For a sizable proportion, sick leave was lengthy. The median time was 35 days, and for 9% sick leave was still underway at the end of the follow-up period, i.e., after 4 months.
The proportion of participants who were on sick leave for more than 12 weeks, i.e., those who may have been affected by what is known as "long-term COVID-19," was 13.3%.
Inpatient hospital care for COVID-19 was the strongest predictor of prolonged sick leave. Another major factor was sick leave in the previous year, 2019. Age, too, appears to have a bearing on the duration of sick leave.
However, the study showed no socioeconomic factors that clearly and consistently predicted long-drawn-out sick leave.
The research group behind the study belongs to the Department of Clinical Neuroscience at the Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, Sahlgrenska Academy at the University of Gothenburg, and Sahlgrenska University Hospital. Hanna C Persson is the study's corresponding author.
"The results indicate that the category of people who had been on long-term sick leave due to COVID-19 is heterogeneous, and that the disease is complex. For us to understand the whole picture, more studies are needed in this subject, and with a longer follow-up period," Persson says.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Easy, inexpensive, efficient: Researchers improve efficacy of new malaria drug
2021-06-14
Artemisone is a promising substance in the fight against malaria. However, the active ingredient has yet to be used due its instability and because it is not easily absorbed by the body. A team from Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has now pushed this a bit further. They have developed a very simple method for preparing the active ingredient that makes it easier to administer and store. The researchers report on their work in the scientific journal "Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy".
Malaria is caused ...
High genetic running capacity promotes efficient metabolism with aging
2021-06-14
High running capacity is associated with health and longevity. However, whether high genetic running capacity promotes more efficient metabolism with aging is not known. A new study conducted in collaboration between the universities of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (China) and Jyväskylä (Finland) investigated the effects of genetic running capacity and aging on tissue metabolism. The study reveals that adipose tissue may have a key role in healthy aging.
Running capacity, expressed as aerobic capacity, refers to an individual's capacity to utilize oxygen and is known to decrease with age, thereby affecting the whole body metabolism and health.
"We currently lack the information ...
Two decade analysis of African neuroscience research prompts calls for greater support
2021-06-14
A team of neuroscientists are calling for greater support of neuroscience research in Africa following a long-term analysis of research outputs in the continent.
The findings detail important information about funding and international collaboration comparing activity in the continent to the US, UK and areas of Europe. It's hoped that the study will provide useful data to help shape and grow science in Africa.
Africa has the world's largest human genetic diversity which carries important implications for understanding human diseases, including neurological disorders.
Co-lead ...
Scientists expose the cold heart of landfalling hurricanes
2021-06-14
Hurricanes that make landfall typically decay but sometimes transition into extratropical cyclones and re-intensify, causing widespread damage to inland communities
The presence of a cold core is currently used to identify this transition, but a new study has now found that a cold core naturally forms in all landfalling hurricanes
The cold core was detected when scientists ran simulations of landfalling hurricanes that accounted for moisture stored within the cyclone
Over time, the scientists saw a cold core growing from the bottom of the hurricane, replacing the warm core
The research could help forecasters make more ...
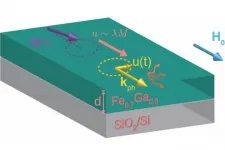
Researchers discover a key cause of energy loss in spintronic materials
2021-06-14
A study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers uncovered a property of magnetic materials that will allow engineers to develop more efficient spintronic devices in the future. Spintronics focuses on using the magnetic "spin" property of electrons instead of their charge, which improves the speed and efficiency of devices used for computing and data storage.
The research is published in Physical Review B, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Physical Society.
One of the major roadblocks in developing better spintronic devices is an effect called "damping," in which the magnetic energy essentially leaks out of the materials, causing them to be less efficient. Traditionally, scientists ...
Designing public institutions that foster cooperation
2021-06-14
Humans often cooperate, but ample research has shown that they're conditionally cooperative; that is, they are far more likely to cooperate with those who they consider "good."
In large societies, however, people don't always know the reputations of the people with whom they interact. That's where reputation monitoring systems--such as the star ratings for eBay sellers or the scores assigned by credit bureaus--come into play, helping guide people's decisions about whether or not they want to help or interact with another person.
In a new paper in the journal Nature Communications, a team from Penn uses mathematical modeling to study how public institutions of reputation monitoring can foster cooperation and also encourage participants to adhere to its assessments instead ...
COVID-19 PCR tests can be freeze dried
2021-06-14
In fighting the COVID-19 pandemic, it's not just the vaccines that require complicated cold supply chains and refrigerated storage. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests -- often considered the "gold standard" of testing -- also have enzymes and reagents that need to be frozen.
Northwestern University researchers have discovered that commercially available PCR tests can withstand the freeze-drying process, making them shelf-stable for up to 30 days and 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit), without sacrificing sensitivity and accuracy.
The researchers ...
New model identifies levers for stability for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac credit
2021-06-14
In 2007, the American housing boom ended, and there was heightened risk of a housing crisis. Private securitizers withdrew from purchasing high-risk mortgages, while government-sponsored enterprises, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, dramatically increased their acquisitions of risky mortgages. By 2008, the agencies reversed course, decreasing their high-risk acquisitions.
In a new article, an economist proposes a scenario in which large lenders temporarily boost high-risk activity at the end of a boom. According to her model, lenders with many outstanding mortgages have incentives to extend risky credit to prop up housing prices, which lessens the losses on their outstanding portfolio of mortgages. As the bust continues, lenders slowly wind down their mortgage exposure.
The ...
Financial toxicity impacts nearly 50% of women with gynecologic cancer
2021-06-14
BOSTON - The cost of cancer care in United States was an estimated $183 billion in 2015 and is projected to rise by 30 percent by 2030, according to the American Cancer Society. While private and government insurance may cover much of the cost of care, even patients with insurance can struggle to pay for office visit co-payments, prescription medications or other cancer-related expenses. Yet limited data describes how financial hardship impacts patient behavior and how that in turn may impact patient health.
In a new study designed to provide a more comprehensive picture of how a diverse cohort of gynecologic cancer patients are affected by financial distress -- also called "financial toxicity" in acknowledgment of the health ...
Trions exhibit novel characteristics in moiré superlattices
2021-06-14
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- When two similar atomic layers with mismatching lattice constants -- the constant distance between a layer's unit cells -- and/or orientation are stacked together, the resulting bilayer can exhibit a moiré pattern and form a moiré superlattice.
Moiré patterns are interference patterns that typically arise when one object with a repetitive pattern is placed over another with a similar pattern. Moiré superlattices, formed by atomic layers, can exhibit fascinating phenomena not found in the individual layers, opening the door to technological revolutions in many areas, including electricity transmission, information engineering, and ...