Into the belly of the bee
2021-06-14
(Press-News.org) Environmental bacteria and fungi that end up in the belly of honeybees may be essential to their survival in a changing world as bee populations dwindle due to pesticides, poor nutrition, habitat destruction and declining genetic diversity.
Like many animals, bees have an internal armory. Their guts are home to a multitude of microbes that perform vital functions, from aiding digestion to breaking down toxins and fending off parasites. "A healthy gut microbiota makes bees more resilient to threats such as pathogens and climate change," says KAUST research scientist Ramona Marasco, "highlighting the need to understand how different microbes help their host."
Extensive research into the microbiome of the European honeybee (Apis mellifera) has focused on several bee-specific (core) bacteria whose functions and distribution throughout the gut are now well understood. However, overlooked are the minor members of the microbiome, such as bacteria and fungi that the bees inadvertently ingest while foraging.
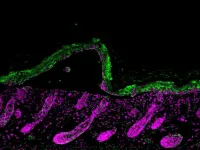
The team, led by Daniele Daffonchio, gathered hundreds of honeybees that had been freely foraging from local flowers and fields at sites in Italy and Saudi Arabia. The researchers removed the whole gut from each bee and used genome sequencing to analyze the bacterial community in each of the four main gut sections. "The challenge was to separate each gut section without releasing intestinal content that could contaminate the microbial communities of the other sections," says postdoc and co-first author Matteo Callegari, "so we froze the guts at -20 degrees Celsius before carefully cutting them up."
As expected, core bacteria accounted for up to 98 percent of the total bacterial community. However, the small remaining portion included 164 operational taxonomic units, a proxy for species, of bacteria and 118 of fungi, compared to just 32 from the core species.
The team was surprised to find that the diversity and abundance of all three microbial components varied along the gut. "Each gut compartment has different physical and environmental properties, such as pH, sugar concentration and oxygen levels," says Marasco. "Consequently, only bacteria and fungi that can cope with a compartment's unique conditions can survive and be metabolically active there."
The team used previous taxonomy data to predict how each of the environmental bacteria helps their honeybee host. Possible functions included producing antibiotics, breaking down toxic substances, metabolizing carbohydrates, digesting amino acids and fats, and distributing nutrients. The fungi were largely fermentative yeasts that are often important in digestion.
"Our findings suggest that these rather neglected minor microbes may become important players under unusual environmental conditions, such as climatic stress," says Daffonchio. "We are currently studying their functions so we can understand how honeybees respond in such a variable world."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-14
Some 42% of patients attending a dedicated diabetes clinic have signs of established chronic kidney disease, the first detailed research of its kind in Ireland has revealed.
The study was carried out by academics at NUI Galway and clinicians at University Hospital Galway Diabetes Centre and involved more than 4,500 patients in the west of Ireland.
The findings suggest that, despite careful medical management, a relatively high proportion of people with diabetes in Ireland are developing chronic kidney disease over time and are at risk of kidney failure and other complications of poor kidney function.
Diabetes ...
2021-06-14
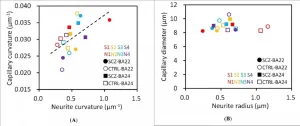
Drs. Itokawa, Mizutani and colleagues performed microtomography experiments the BL20XU beamline of the SPring-8 synchrotron radiation facility and found that brain capillary structures show a correlation with their neuron structures.
Brain blood vessels constitute a micrometer-scale vascular network responsible for supply of oxygen and nutrition. In this study, we analyzed cerebral tissues of the anterior cingulate cortex and superior temporal gyrus of schizophrenia cases and age/gender-matched controls by using synchrotron radiation microtomography or micro-CT in order to examine the three-dimensional structure of cerebral vessels.
All post-mortem human cerebral tissues were collected ...
2021-06-14
A new species of large prehistoric croc that roamed south-east Queensland's waterways millions of years ago has been documented by University of Queensland researchers.
PhD candidate Jorgo Ristevski, from UQ's School of Biological Sciences, led the team that named the species Gunggamarandu maunala after analysing a partial skull unearthed in the Darling Downs in the nineteenth century.
"This is one of the largest crocs to have ever inhabited Australia," Mr Ristevski said.
"At the moment it's difficult to estimate the exact overall size of Gunggamarandu since all we have is the back of the skull - but it was big.
"We estimate the skull would have been at least 80 centimetres long, and based on comparisons with living crocs, this indicates a total ...
2021-06-14
Summer picnics and barbecues are only a few weeks away! As excited as you are to indulge this summer, Escherichia coli bacteria are eager to feast on the all-you-can-eat buffet they are about to experience in your gut.
However, something unexpected will occur as E. coli cells end their journey through your digestive tract. Without warning, they will find themselves swimming in your toilet bowl, clinging to the last bits of nutrients attached to their bodies. How do these tiny organisms adapt to survive sudden starvation? Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis wondered.
Close examination of nutrient-deprived E. coli ...
2021-06-14
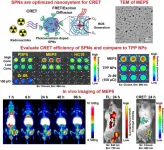
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 12:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021) - Researchers have successfully developed a novel cancer treatment approach that utilizes Cerenkov radiation energy to target and destroy cancer cells more effectively. The approach uses light from decaying radiopharmaceuticals, known as Cerenkov luminescence, as an energy source to activate semiconducting polymer nanoparticles that kill cancer cells. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging's 2021 Virtual Annual Meeting.
Over the past several decades, many studies have been conducted on photodynamic therapy, ...
2021-06-14
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia and is characterized by neurodegeneration in regions of the brain involved in memory and learning. Amyloid beta and tau are two toxic proteins that build up in disease and cause eventual neuronal death, but little is known about how other cells in the brain react during disease progression.
A new study from the ASU-Banner Neurodegenerative Research Center (NDRC) and MIT/Koch Institute sheds new light on how disease processes manifest in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Diego Mastroeni of the NDRC teamed up Forest White and Douglas Lauffenburger, colleagues in MIT's Department of Biological Engineering, to explore how protein ...
2021-06-14
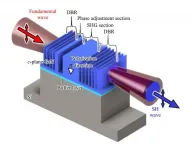
Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and the Center for Quantum Information and Quantum Biology at Osaka University unveiled a new solid state second-harmonic generation (SHG) device that converts infrared radiation into blue light. This work may lead to a practical daily-use deep ultraviolet light source for sterilization and disinfection.
Recently, deep ultraviolet (DUV) light sources have been attracting much attention in sterilization and disinfection. In order to realize a bactericidal effect while ensuring user safety, a wavelength range of 220-230 nm is desirable. ...
2021-06-14
Singapore, 14 June 2021 - Many butterfly species bear distinct circular markings known as eyespots on their wings, and the functions of these rings of contrasting colours vary. A long-standing theory is that they serve as anti-predator defences - small eyespots along the wing margin can protect butterflies by directing predators to attack less important parts of the body, such as the hindwings, enabling them to escape.
Most nymphalid family butterflies have half as many eyespots on their forewings compared to their hindwings. In particular, this has been observed in the bush brown butterfly Bicyclus anynana.
A recent research by biologists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) sought to understand the impact of uneven distribution of eyespots. ...
2021-06-14
A team of scientists has shown that the healing of skin blisters is driven by hair follicle stem cells, which delay their own development in the process.
The healing process of the tissues in the human body is particularly well-studied in skin, especially as skin serves as a layer of protection from the environment. However, there remain some specific types of skin injuries where the healing process is not well understood.
A team of scientists from Japan and Italy, including Associate Professor Ken Natsuga from the Graduate School of Medicine at Hokkaido University, have used models of skin blisters to explore the effects of injury on developing skin tissue. Their discoveries ...
2021-06-14
Nearly 12,000 people in Sweden received sickness benefit from the Swedish Social Insurance Agency for COVID-19 during the first wave of the pandemic. The median duration of sick leave in this group was 35 days, but for many it was considerably more long-drawn-out, according to a University of Gothenburg study.
A research group in rehabilitation medicine at the University of Gothenburg has studied sick-leave patterns. The study now presented in the scientific journal BMC Public Health.
The study included all recipients of sickness benefit from the Social Insurance Agency for COVID-19 diagnoses in Sweden during the first pandemic wave, from 1 March to 31 August 2020, and monitored them for 4 months from the start of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Into the belly of the bee