One step towards a daily-use deep UV light source for sterilization and disinfection
Researchers construct a gallium nitride optical microcavity with high reflectivity distributed Bragg reflectors to double the frequency of incoming light, which may be utilized for a safe and practical deep UV light source with bactericidal effects
2021-06-14
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and the Center for Quantum Information and Quantum Biology at Osaka University unveiled a new solid state second-harmonic generation (SHG) device that converts infrared radiation into blue light. This work may lead to a practical daily-use deep ultraviolet light source for sterilization and disinfection.
Recently, deep ultraviolet (DUV) light sources have been attracting much attention in sterilization and disinfection. In order to realize a bactericidal effect while ensuring user safety, a wavelength range of 220-230 nm is desirable. But DUV light sources in this wavelength range that are both durable and highly efficient have not yet been developed. Although wavelength conversion devices are promising candidates, conventional ferroelectric wavelength conversion materials cannot be applied to DUV devices due to absorption edge.
Since nitride semiconductors such as gallium nitride and aluminum nitride have relatively high optical nonlinearity, they can be applied to wavelength conversion devices. Due to its transparency to 210 nm, aluminum nitride is particularly suitable for DUV wavelength conversion devices. However, realizing structures with periodically inverted polarity like conventional ferroelectric wavelength conversion devices has proven quite difficult.
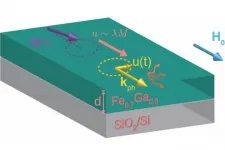
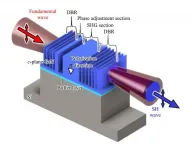
The researchers proposed a novel monolithic microcavity wavelength conversion device without a polarity-inverted structure. A fundamental wave is enhanced significantly in the microcavity with two distributed Bragg reflectors (DBR), and counter-propagating second harmonic waves are efficiently emitted in phase from the one side. As the first step towards a practical DUV light source, a gallium nitride microcavity device was fabricated via microfabrication technology, including dry etching and anisotropic wet etching for vertical and smooth DBR sidewalls. By obtaining a blue SH wave, the effectiveness of the proposed concept was successfully demonstrated.
"Our device can be adapted to use a broader range of materials. They can be applied to deep ultraviolet light emission or even broadband photon pair generation," senior author Masahiro Uemukai says. The researchers hope that because this approach does not rely on materials or periodically inverted structures, it will make future nonlinear optical devices easier to construct.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Monolithic microcavity second harmonic generation device using low birefringence paraelectric material without polarity-inverted structure" was published in Applied Physics Express at DOI: https://doi.org/10.35848/1882-0786/abff9e
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-14
Singapore, 14 June 2021 - Many butterfly species bear distinct circular markings known as eyespots on their wings, and the functions of these rings of contrasting colours vary. A long-standing theory is that they serve as anti-predator defences - small eyespots along the wing margin can protect butterflies by directing predators to attack less important parts of the body, such as the hindwings, enabling them to escape.
Most nymphalid family butterflies have half as many eyespots on their forewings compared to their hindwings. In particular, this has been observed in the bush brown butterfly Bicyclus anynana.
A recent research by biologists from the National University of Singapore (NUS) sought to understand the impact of uneven distribution of eyespots. ...
2021-06-14
A team of scientists has shown that the healing of skin blisters is driven by hair follicle stem cells, which delay their own development in the process.
The healing process of the tissues in the human body is particularly well-studied in skin, especially as skin serves as a layer of protection from the environment. However, there remain some specific types of skin injuries where the healing process is not well understood.
A team of scientists from Japan and Italy, including Associate Professor Ken Natsuga from the Graduate School of Medicine at Hokkaido University, have used models of skin blisters to explore the effects of injury on developing skin tissue. Their discoveries ...
2021-06-14
Nearly 12,000 people in Sweden received sickness benefit from the Swedish Social Insurance Agency for COVID-19 during the first wave of the pandemic. The median duration of sick leave in this group was 35 days, but for many it was considerably more long-drawn-out, according to a University of Gothenburg study.
A research group in rehabilitation medicine at the University of Gothenburg has studied sick-leave patterns. The study now presented in the scientific journal BMC Public Health.
The study included all recipients of sickness benefit from the Social Insurance Agency for COVID-19 diagnoses in Sweden during the first pandemic wave, from 1 March to 31 August 2020, and monitored them for 4 months from the start of ...
2021-06-14
Artemisone is a promising substance in the fight against malaria. However, the active ingredient has yet to be used due its instability and because it is not easily absorbed by the body. A team from Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem has now pushed this a bit further. They have developed a very simple method for preparing the active ingredient that makes it easier to administer and store. The researchers report on their work in the scientific journal "Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy".
Malaria is caused ...
2021-06-14
High running capacity is associated with health and longevity. However, whether high genetic running capacity promotes more efficient metabolism with aging is not known. A new study conducted in collaboration between the universities of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (China) and Jyväskylä (Finland) investigated the effects of genetic running capacity and aging on tissue metabolism. The study reveals that adipose tissue may have a key role in healthy aging.
Running capacity, expressed as aerobic capacity, refers to an individual's capacity to utilize oxygen and is known to decrease with age, thereby affecting the whole body metabolism and health.
"We currently lack the information ...
2021-06-14
A team of neuroscientists are calling for greater support of neuroscience research in Africa following a long-term analysis of research outputs in the continent.
The findings detail important information about funding and international collaboration comparing activity in the continent to the US, UK and areas of Europe. It's hoped that the study will provide useful data to help shape and grow science in Africa.
Africa has the world's largest human genetic diversity which carries important implications for understanding human diseases, including neurological disorders.
Co-lead ...
2021-06-14
Hurricanes that make landfall typically decay but sometimes transition into extratropical cyclones and re-intensify, causing widespread damage to inland communities
The presence of a cold core is currently used to identify this transition, but a new study has now found that a cold core naturally forms in all landfalling hurricanes
The cold core was detected when scientists ran simulations of landfalling hurricanes that accounted for moisture stored within the cyclone
Over time, the scientists saw a cold core growing from the bottom of the hurricane, replacing the warm core
The research could help forecasters make more ...
2021-06-14
A study led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers uncovered a property of magnetic materials that will allow engineers to develop more efficient spintronic devices in the future. Spintronics focuses on using the magnetic "spin" property of electrons instead of their charge, which improves the speed and efficiency of devices used for computing and data storage.
The research is published in Physical Review B, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Physical Society.
One of the major roadblocks in developing better spintronic devices is an effect called "damping," in which the magnetic energy essentially leaks out of the materials, causing them to be less efficient. Traditionally, scientists ...
2021-06-14
Humans often cooperate, but ample research has shown that they're conditionally cooperative; that is, they are far more likely to cooperate with those who they consider "good."
In large societies, however, people don't always know the reputations of the people with whom they interact. That's where reputation monitoring systems--such as the star ratings for eBay sellers or the scores assigned by credit bureaus--come into play, helping guide people's decisions about whether or not they want to help or interact with another person.
In a new paper in the journal Nature Communications, a team from Penn uses mathematical modeling to study how public institutions of reputation monitoring can foster cooperation and also encourage participants to adhere to its assessments instead ...
2021-06-14
In fighting the COVID-19 pandemic, it's not just the vaccines that require complicated cold supply chains and refrigerated storage. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests -- often considered the "gold standard" of testing -- also have enzymes and reagents that need to be frozen.
Northwestern University researchers have discovered that commercially available PCR tests can withstand the freeze-drying process, making them shelf-stable for up to 30 days and 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit), without sacrificing sensitivity and accuracy.
The researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] One step towards a daily-use deep UV light source for sterilization and disinfection
Researchers construct a gallium nitride optical microcavity with high reflectivity distributed Bragg reflectors to double the frequency of incoming light, which may be utilized for a safe and practical deep UV light source with bactericidal effects