Eco-friendly smart farms based on nutrient solution recirculation
UV sterilization and microbial stability analysis used to recycle nutrient solution; proposed method minimizes the use fertilizers and water by hydroponic farms
2021-06-15
(Press-News.org) The development of new urban agriculture technologies, such as vertical and smart farms, has accelerated rapidly in recent years. These technologies are based on hydroponic cultivation in which plants are grown using nutrient-rich solutions rather than soil. Approximately 20-30% of the nutrient solutions used during hydroponic cultivation are discharged without being absorbed by the crops, and because most farmers in South Korea do not treat the discharged solutions, hydroponic farms contribute significantly to environmental pollution.
This problem can be reduced if hydroponic farms use a recirculating hydroponic cultivation method that reuses the nutrient solutions after sterilizing them with ultraviolet (UV) light, instead of discharging them. However, two main issues complicate the implantation of such recirculation systems. First, the potential for diseases and nutrient imbalances to develop owing to microbial growth in the recycled nutrient solutions must be eliminated. Second, the initial investment required to set up a recirculating hydroponic cultivation system is often prohibitive, costing hundreds of millions of Korean won per hectare.
However, a new study conducted by researchers at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST)proposes a method that can stably manage the microbial population in recirculating hydroponic cultivation systems. The research team, led by Drs. Ju Young Lee and Tae In Ahn of the Smart Farm Research Center, KIST Gangneung Institute of Natural Products, conducted an integrated analysis of the microbial growth characteristics by constructing a model that simulates the flow of water and nutrients, and the inflow, growth, and discharge of microorganisms in recirculating and non-circulating hydroponic cultivation systems. Their simulations revealed that the microbial population in recirculating hydroponic cultivation systems can be controlled by adjusting the UV output and the water supply. On the contrary, in non-circulating hydroponic cultivation, the microbial population fluctuates considerably depending on the amount of water used, increasingly sharply if there is too little water.
High cost has restricted the use of UV sterilization systems in hydroponic farming in Korea And prompted the research team to develop their own UV sterilization system, with further studies underway to commercialize this system as an economical alternative to imported systems.
The results of the study have already received strong interest: the rights to the operation and management software technology for recirculating hydroponic cultivation has been acquired by Dooinbiotech Co., Ltd. for an advance fee of 80 million won (8.5% of the operating revenue), while an agreement is in place with Shinhan A-Tec Co., Ltd. for the advanced recirculating hydroponic cultivation technology for an advance fee of 200 million won (1.5% of the operating revenue). Commercializing the recirculating hydroponic cultivation system is expected to reduce fertilizer costs by approximately 30~40%, which equates to 30 million won per year based on a 1-hectare farm.
Commenting on the envisaged impacts of the study, Dr. Ju Young Lee said, "The developed system makes the transition to eco-friendly recirculating hydroponic cultivation systems an affordable option for many more farmers." Dr. Tae In Ahn added, "We are also developing software and operation manuals to guide farmers in managing the nutrient balance in the solutions to increase the number of farms using the recirculating hydroponic cultivation system."
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry) and the Innovative Smart Farm Technology Development Program of Multi-agency Package. The research results are published in the latest issue of the Journal of Cleaner Production (IF: 7.24, ranked in the top 6.9% by JCR), a highly respected international journal in the field of environmental science.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-15
Niigata, Japan - The loss of muscle tissue - referred to as muscle atrophy in medical terms - can occur as a result of lack of physical activity for an extended period of time; aging; alcohol-associated myopathy - a pain and weakness in muscles due to excessive drinking over long periods of time; burns; injuries; malnutrition; spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries; stroke; and long-term corticosteroid therapy. While muscle atrophy due to disuse is well known and studied, the underlying cellular mechanisms, particularly the status of mitochondrial degradation by mitophagy during disuse-induced muscle atrophy has been a subject ...
2021-06-15
Researchers from University of Texas at Dallas and Emory University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines the issue of encroachment in the hotel industry.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Can Encroachment Benefit Hotel Franchisees?" and is authored by TI Tongil Kim and Sandy Jap.
For decades, the issue of encroachment, or adding an outlet in proximity to existing outlets, has been contentious. A new outlet increases competition for customers, causing concerns for franchisors and franchisees that the existing outlet's sales will be cannibalized. Franchising is a key means for growth and market expansion for many companies. ...
2021-06-15
Researchers have discovered a new and more efficient computing method for pairing the reliability of a classical computer with the strength of a quantum system.
This new computing method opens the door to different algorithms and experiments that bring quantum researchers closer to near-term applications and discoveries of the technology.
"In the future, quantum computers could be used in a wide variety of applications including helping to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, developing artificial limbs and designing more efficient pharmaceuticals," said Christine Muschik, a principal investigator at the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) and a faculty member in physics and astronomy at the University of Waterloo.
The research team from ...
2021-06-15
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--A protein that is critical in cancer cell metabolism has been imaged for the first time with a newly developed radiopharmaceutical, 18F-DASA-23. Imaging with this novel agent has the potential to improve the assessment of treatment response for patients, specifically those with brain tumors. This study was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tumor cells go through various changes to survive and prosper in the body. One of the key changes they make is modifying a master switch, known as pyruvate kinase ...
2021-06-15
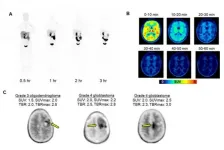
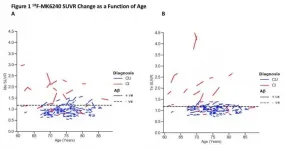
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--A novel positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer has been shown to effectively measure increases in brain tau--a distinguishing characteristic of Alzheimer's disease--before any symptoms of the disease are observed. With the potential to measure increases in tau over a long period of time, this tracer offers an important tool to assess the effectiveness of Alzheimer's disease treatments in clinical trials. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tau is a protein commonly ...
2021-06-15
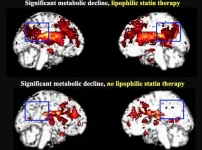
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--In patients with mild cognitive impairment, taking lipophilic statins more than doubles their risk of developing dementia compared to those who do not take statins. According to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting, positron emission tomography (PET) scans of lipophilic statin users revealed a highly significant decline in metabolism in the area of the brain that is first impacted by Alzheimer's disease.
Statins are medications used to lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke. They are the most commonly used drugs in the developed world, and nearly 50 percent of Americans over age 75 use a statin. Different types ...
2021-06-15
The use of 'ice' flavoured e-cigarettes may be common and positively associated with conventional smoking and nicotine dependence among young adults, suggests research published online in the journal Tobacco Control.
And it's unclear where these' hybrid' vapes, combining fruit/sweet and cooling flavours, fit into current or future regulatory frameworks, which apply restrictions according to distinct flavour categories, point out the study authors.
'Ice' flavoured e-cigarettes--marketed as a combination of fruity/sweet and cooling flavours, such as 'blueberry ice' or 'melon ice'--recently entered the US market. Previous research ...
2021-06-15
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. A third dose of COVID-19 vaccine increased antibody levels in organ transplant recipients with a suboptimal response following standard 2-dose vaccination
Study is the first to report on response to a third vaccine ...
2021-06-15
KINGSTON, R.I. - June 14, 2021 - The rarest frog in Rhode Island may not be as rare as scientists once thought after a study by University of Rhode Island researchers using a seldom-used methodology turned up many more of the endangered animals than they expected.
Eastern spadefoots - often called spadefoot toads, though they are actually frogs - have long been considered highly secretive and difficult to find outside of their one- or two-day annual breeding periods on rainy nights. In some years, they don't breed at all. But after scientists reported just 50 sightings of the frogs over the previous 70 years, the Rhode Island researchers observed 42 spadefoots ...
2021-06-14
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a way to dynamically switch the surface of liquid
metal between reflective and scattering states. This technology could one day be used to create electrically controllable mirrors or illumination devices.
Liquid metals combine the electrical, thermal and optical properties of metals with the fluidity of a liquid. The new approach uses an electrically driven chemical reaction to create switchable reflective surfaces on a liquid metal. No optical coatings nor polishing steps, which are typically required to make reflective optical components, are necessary to make the liquid metal highly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Eco-friendly smart farms based on nutrient solution recirculation
UV sterilization and microbial stability analysis used to recycle nutrient solution; proposed method minimizes the use fertilizers and water by hydroponic farms