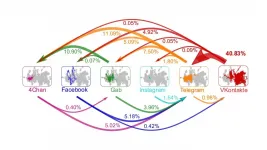
Malicious content exploits pathways between platforms to thrive online, subvert moderation
New research demonstrates how stopping the spread of harmful content will require inter-platform action
2021-06-15
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (June 15, 2021)--Malicious COVID-19 online content -- including racist content, disinformation and misinformation -- thrives and spreads online by bypassing the moderation efforts of individual social media platforms, according to new research published in the journal END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Snails carrying the world's smallest computer help solve mass extinction survivor mystery
2021-06-15
More than 50 species of tree snail in the South Pacific Society Islands were wiped out following the introduction of an alien predatory snail in the 1970s, but the white-shelled Partula hyalina survived.
Now, thanks to a collaboration between University of Michigan biologists and engineers with the world's smallest computer, scientists understand why: P. hyalina can tolerate more sunlight than its predator, so it was able to persist in sunlit forest edge habitats.
"We were able to get data that nobody had been able to obtain," said David Blaauw, the Kensall D. Wise Collegiate Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. "And ...
Head impacts and abnormal imaging findings in youth football players over consecutive seasons
2021-06-15
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (JUNE 15, 2021). In this longitudinal study, researchers from Wake Forest School of Medicine and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas, Texas, examined the frequency and severity of head impacts experienced by youth football players and how exposure to head impacts changes from one year to the next in returning players. The researchers then compared the resulting data with findings on neuroimaging studies obtained over consecutive years in the same athletes. The comparison demonstrated a significant positive association between changes in head impact exposure (HIE) metrics and changes in abnormal findings on brain imaging studies. ...
New treatment stops progression of Alzheimer's disease in monkey brains
2021-06-15
A new therapy prompts immune defense cells to swallow misshapen proteins, amyloid beta plaques and tau tangles, whose buildup is known to kill nearby brain cells as part of Alzheimer's disease, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the investigation showed that elderly monkeys had up to 59 percent fewer plaque deposits in their brains after treatment with CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODN), compared with untreated animals. These amyloid beta plaques are protein fragments that clump together and clog the junctions between nerve cells (neurons).
Brains of treated animals also had a ...
Young adults' alcohol use increases when casually dating
2021-06-15
When young adults are more interested in socializing and casually dating, they tend to drink more alcohol, according to a new paper led by a Washington State University professor.
On the other hand, scientists found that when young adults are in serious relationships, are not interested in dating or place less importance on friendship, their alcohol use was significantly lower.
Published June 15 in the journal Substance Use & Misuse, the study included more than 700 people in the Seattle area aged 18-25 who filled out surveys every month for two years. The study used a community sample that was not limited to college students.
"Young adults shift so much in terms of social relationships ...
Job-related stress threatens the teacher supply - RAND survey
2021-06-15
Nearly one in four teachers may leave their job by the end of the current (2020-'21) school year, compared with one in six who were likely to leave prior to the pandemic, according to a new RAND Corporation survey. Teachers who identified as Black or African American were particularly likely to consider leaving.
U.S. public-school teachers surveyed in January and February 2021 reported they are almost twice as likely to experience frequent job-related stress as the general employed adult population and almost three times as likely to experience depressive symptoms as the general adult population.
These results suggest potential immediate and long-term threats to the teacher supply.
"Teacher stress was a concern prior ...
Study finds association between head impacts and imaging changes in youth football players
2021-06-15
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - June 15, 2021 - With preseason football training on the horizon, a new study shows that head impacts experienced during practice are associated with changes in brain imaging of young players over multiple seasons.
The research, conducted by scientists at Wake Forest School of Medicine and the University of Texas Southwestern, is published in the June 15 issue of the Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics.
"Although we need more studies to fully understand what the measured changes mean, from a public health perspective, it is motivation to further reduce head impact drills used during practice in youth football," said the study's corresponding author Jill Urban, Ph.D., assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Wake Forest ...
Human-driven climate change only half the picture for krill
2021-06-15
In the heart of their Antarctic habitat, krill populations are projected to decline about 30% this century due to widespread negative effects from human-driven climate change. However, these effects on this small but significant species will be largely indistinguishable from natural variability in the region's climate until late in the 21st century, finds new University of Colorado Boulder research.
Published today in Frontiers in Marine Science, the study has important implications for not only the local food web, but for the largest commercial fishery in the Southern Ocean: A booming ...
Psychologists identify 18 best measures to assess intimate partner violence
2021-06-15
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Millions of people experience intimate partner violence (IPV) in their lifetime and assessment is important in conducting therapy and assisting victims. A team of psychologists at Binghamton University, State University of New York have evaluated dozens of available measures used to assess intimate partner violence and have pinpointed the most effective ones.
IPV is a blanket term used to refer to not only acts of physical violence, but other abusive behaviors, such as psychological and emotional abuse or control tactics. According to estimates by the National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey, within the United States, 22.3% of women and 14% of men experience severe physical violence by an intimate partner in ...
Eco-friendly smart farms based on nutrient solution recirculation
2021-06-15
The development of new urban agriculture technologies, such as vertical and smart farms, has accelerated rapidly in recent years. These technologies are based on hydroponic cultivation in which plants are grown using nutrient-rich solutions rather than soil. Approximately 20-30% of the nutrient solutions used during hydroponic cultivation are discharged without being absorbed by the crops, and because most farmers in South Korea do not treat the discharged solutions, hydroponic farms contribute significantly to environmental pollution.
This problem can be reduced if hydroponic farms use a recirculating hydroponic cultivation method that reuses the nutrient solutions after sterilizing them with ...
A new reporter mouse line to detect mitophagy changes during muscle tissue loss
2021-06-15
Niigata, Japan - The loss of muscle tissue - referred to as muscle atrophy in medical terms - can occur as a result of lack of physical activity for an extended period of time; aging; alcohol-associated myopathy - a pain and weakness in muscles due to excessive drinking over long periods of time; burns; injuries; malnutrition; spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries; stroke; and long-term corticosteroid therapy. While muscle atrophy due to disuse is well known and studied, the underlying cellular mechanisms, particularly the status of mitochondrial degradation by mitophagy during disuse-induced muscle atrophy has been a subject ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Malicious content exploits pathways between platforms to thrive online, subvert moderationNew research demonstrates how stopping the spread of harmful content will require inter-platform action