(Press-News.org) When young adults are more interested in socializing and casually dating, they tend to drink more alcohol, according to a new paper led by a Washington State University professor.
On the other hand, scientists found that when young adults are in serious relationships, are not interested in dating or place less importance on friendship, their alcohol use was significantly lower.
Published June 15 in the journal Substance Use & Misuse, the study included more than 700 people in the Seattle area aged 18-25 who filled out surveys every month for two years. The study used a community sample that was not limited to college students.
"Young adults shift so much in terms of social relationships that having this monthly data really allowed us to hone in on nuances and see these changes in alcohol use depending on social situations," said Jennifer Duckworth, the lead author on the paper. "The idea is to understand whether young adults may be viewing alcohol as a way to facilitate relationships. They may think of alcohol as a way to make hanging out easier or more fun."
Being able to look at young adult behavior over a longer period allowed the research team to see how alcohol use was related to socializing and relationships.
"If a college student has mid-terms, they may have less interest in spending time with friends," said Duckworth, an assistant professor in WSU's Department of Human Development. "But if it's spring break, they may place more importance on those friendships. And when friendships become more important, we found alcohol use tends to be higher."
For relationships, Duckworth and her co-authors separated single young adults into two groups: casually dating and not interesting in dating. That distinction showed a significant difference in alcohol use. Since the survey tracked people every month, they could study changes as participants moved in and out of different relationship statuses.
"For instance, one month, someone may not be interested in dating and their alcohol use tended to be lower," Duckworth said. "Then, if they start dating, alcohol use tended to be higher."
Previous research has shown that young adults in relationships tend to drink less than single people, but those studies didn't separate the term single into two separate groups based on whether or not the young adults were interested in dating.
Young adults have more high-risk alcohol use than any other age group, she said. The overall goal of this research is to understand the context for greater alcohol use by young adults.
"Understanding what's going on in their lives across time is very useful if we want to mitigate high-risk use of alcohol," Duckworth said. "We can focus on interventions that help educate young adults on what is motivating their behaviors. We're bridging alcohol use with development research in a meaningful way that can really help people."
INFORMATION:
The young adults in the study filled out confidential monthly online surveys and received a stipend at the end of the two-year study. That combination of confidentiality, financial incentive and ease of use led to a very high retention rate, Duckworth said.
Co-authors on the paper were principal investigator Christine M. Lee, Isaac Rhew, and Anne Fairlie at the University of Washington, Megan Patrick and John Schulenberg at the University of Michigan and Jennifer L. Maggs at Pennsylvania State University.
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (R01AA022087) provided funding for the study.
Nearly one in four teachers may leave their job by the end of the current (2020-'21) school year, compared with one in six who were likely to leave prior to the pandemic, according to a new RAND Corporation survey. Teachers who identified as Black or African American were particularly likely to consider leaving.
U.S. public-school teachers surveyed in January and February 2021 reported they are almost twice as likely to experience frequent job-related stress as the general employed adult population and almost three times as likely to experience depressive symptoms as the general adult population.
These results suggest potential immediate and long-term threats to the teacher supply.
"Teacher stress was a concern prior ...
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - June 15, 2021 - With preseason football training on the horizon, a new study shows that head impacts experienced during practice are associated with changes in brain imaging of young players over multiple seasons.
The research, conducted by scientists at Wake Forest School of Medicine and the University of Texas Southwestern, is published in the June 15 issue of the Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics.
"Although we need more studies to fully understand what the measured changes mean, from a public health perspective, it is motivation to further reduce head impact drills used during practice in youth football," said the study's corresponding author Jill Urban, Ph.D., assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Wake Forest ...
In the heart of their Antarctic habitat, krill populations are projected to decline about 30% this century due to widespread negative effects from human-driven climate change. However, these effects on this small but significant species will be largely indistinguishable from natural variability in the region's climate until late in the 21st century, finds new University of Colorado Boulder research.
Published today in Frontiers in Marine Science, the study has important implications for not only the local food web, but for the largest commercial fishery in the Southern Ocean: A booming ...
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Millions of people experience intimate partner violence (IPV) in their lifetime and assessment is important in conducting therapy and assisting victims. A team of psychologists at Binghamton University, State University of New York have evaluated dozens of available measures used to assess intimate partner violence and have pinpointed the most effective ones.
IPV is a blanket term used to refer to not only acts of physical violence, but other abusive behaviors, such as psychological and emotional abuse or control tactics. According to estimates by the National Intimate Partner and Sexual Violence Survey, within the United States, 22.3% of women and 14% of men experience severe physical violence by an intimate partner in ...
The development of new urban agriculture technologies, such as vertical and smart farms, has accelerated rapidly in recent years. These technologies are based on hydroponic cultivation in which plants are grown using nutrient-rich solutions rather than soil. Approximately 20-30% of the nutrient solutions used during hydroponic cultivation are discharged without being absorbed by the crops, and because most farmers in South Korea do not treat the discharged solutions, hydroponic farms contribute significantly to environmental pollution.
This problem can be reduced if hydroponic farms use a recirculating hydroponic cultivation method that reuses the nutrient solutions after sterilizing them with ...
Niigata, Japan - The loss of muscle tissue - referred to as muscle atrophy in medical terms - can occur as a result of lack of physical activity for an extended period of time; aging; alcohol-associated myopathy - a pain and weakness in muscles due to excessive drinking over long periods of time; burns; injuries; malnutrition; spinal cord or peripheral nerve injuries; stroke; and long-term corticosteroid therapy. While muscle atrophy due to disuse is well known and studied, the underlying cellular mechanisms, particularly the status of mitochondrial degradation by mitophagy during disuse-induced muscle atrophy has been a subject ...
Researchers from University of Texas at Dallas and Emory University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines the issue of encroachment in the hotel industry.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Can Encroachment Benefit Hotel Franchisees?" and is authored by TI Tongil Kim and Sandy Jap.
For decades, the issue of encroachment, or adding an outlet in proximity to existing outlets, has been contentious. A new outlet increases competition for customers, causing concerns for franchisors and franchisees that the existing outlet's sales will be cannibalized. Franchising is a key means for growth and market expansion for many companies. ...
Researchers have discovered a new and more efficient computing method for pairing the reliability of a classical computer with the strength of a quantum system.
This new computing method opens the door to different algorithms and experiments that bring quantum researchers closer to near-term applications and discoveries of the technology.
"In the future, quantum computers could be used in a wide variety of applications including helping to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, developing artificial limbs and designing more efficient pharmaceuticals," said Christine Muschik, a principal investigator at the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) and a faculty member in physics and astronomy at the University of Waterloo.
The research team from ...
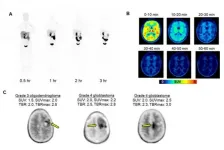
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--A protein that is critical in cancer cell metabolism has been imaged for the first time with a newly developed radiopharmaceutical, 18F-DASA-23. Imaging with this novel agent has the potential to improve the assessment of treatment response for patients, specifically those with brain tumors. This study was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tumor cells go through various changes to survive and prosper in the body. One of the key changes they make is modifying a master switch, known as pyruvate kinase ...
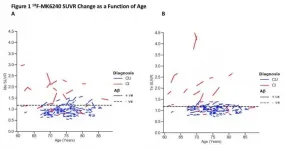
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 7:30 p.m. EDT, Monday, June 14, 2021)--A novel positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer has been shown to effectively measure increases in brain tau--a distinguishing characteristic of Alzheimer's disease--before any symptoms of the disease are observed. With the potential to measure increases in tau over a long period of time, this tracer offers an important tool to assess the effectiveness of Alzheimer's disease treatments in clinical trials. This research was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting.
Tau is a protein commonly ...