(Press-News.org) Exposure to the rhinovirus, the most frequent cause of the common cold, can protect against infection by the virus which causes COVID-19, Yale researchers have found.
In a new study, the researchers found that the common respiratory virus jump-starts the activity of interferon-stimulated genes, early-response molecules in the immune system which can halt replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus within airway tissues infected with the cold.
Triggering these defenses early in the course of COVID-19 infection holds promise to prevent or treat the infection, said Ellen Foxman, assistant professor of laboratory medicine and immunobiology at the Yale School of Medicine and senior author of the study. One way to do this is by treating patients with interferons, an immune system protein which is also available as a drug.
"But it all depends upon the timing," Foxman said.
The results were published June 15th in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Previous work showed that at the later stages of COVID-19, high interferon levels correlate with worse disease and may fuel overactive immune responses. But recent genetic studies show that interferon-stimulated genes can also be protective in cases of COVID-19 infection.
Foxman's lab wanted to study this defense system early in the course of COVID-19 infection.
Since earlier studies by Foxman's lab showed that common cold viruses may protect against influenza, they decided to study whether rhinoviruses would have the same beneficial impact against the COVID-19 virus. For the study, her team infected lab-grown human airway tissue with SARS-CoV-2 and found that for the first three days, viral load in the tissue doubled about every six hours. However, replication of the COVID-19 virus was completely stopped in tissue which had been exposed to rhinovirus. If antiviral defenses were blocked, the SARS-CoV-2 could replicate in airway tissue previously exposed to rhinovirus.
The same defenses slowed down SARS-CoV-2 infection even without rhinovirus, but only if the infectious dose was low, suggesting that the viral load at the time of exposure makes a difference in whether the body can effectively fight the infection.
The researchers also studied nasal swab samples from patients diagnosed close to the start of infection. They found evidence of rapid growth of SARS-CoV-2 in the first few days of infection, followed by activation of the body's defenses. According to their findings, the virus typically increased rapidly for the first few days of infection, before host defenses kicked in, doubling about every six hours as seen in the lab; in some patients the virus grew even faster.
"There appears to be a viral sweet spot at the beginning of COVID-19, during which the virus replicates exponentially before it triggers a strong defense response," Foxman said.
Interferon treatment holds promise but it could be tricky, she said, because it would be mostly effective in the days immediately after infection, when many people exhibit no symptoms. In theory, interferon treatment could be used prophylactically in people at high risk who have been in close contact with others diagnosed with COVID-19. Trials of interferon in COVID-19 are underway, and so far show a possible benefit early in infection, but not when given later.
These findings may help explain why at times of year when colds are common, rates of infections with other viruses such as influenza tend to be lower, Foxman said. There are concerns that as social distancing measures ease, common cold and flu viruses -- which have been dormant over the past year -- will come back in greater force. Interference among respiratory viruses could be a mitigating factor, creating an "upper limit" on the degree to which respiratory viruses co-circulate, she said.
"There are hidden interactions between viruses that we don't quite understand, and these findings are a piece of the puzzle we are just now looking at," Foxman said.
INFORMATION:
Nagarjuna R. Cheemarla, a postdoctoral associate in Foxman's lab, was first author of the study, which was carried out by a team of Yale scientists in the Departments of Laboratory Medicine, Immunobiology, and Genetics.
Other Yale authors included Timothy Watkins, Valia Mihaylova, Bao Wang, Marie Landry, Dejian Zhao, and Guilin Wang.
Researchers from The Australian National University (ANU) have developed new technology that allows people to see clearly in the dark, revolutionising night-vision.
The first-of-its-kind thin film, described in a new article published in Advanced Photonics, is ultra-compact and one day could work on standard glasses.
The researchers say the new prototype tech, based on nanoscale crystals, could be used for defence, as well as making it safer to drive at night and walking home after dark.
The team also say the work of police and security guards - who regularly employ night vision - will be easier and safer, reducing chronic neck injuries from currently bulk night-vision devices.
"We have made the invisible visible," lead researcher Dr Rocio Camacho Morales said. ...
Data collected for over two decades shows that rising Baltic Sea water temperature is one of the main factors in the increasingly earlier appearance and faster growth of Baltic herring larvae.
Baltic herring (Clupea harengus membras) is commercially the most important fish species in Finland, and an important part of the Baltic marine ecosystem. Conditions during herring spawning may have cascading effects on the whole Baltic ecosystem.
According to a recent research, both developmental stages in Baltic herring larvae, small and large, have shifted their timing to earlier dates.
"This suggests that herring spawn earlier and larvae grow faster, by about 7.7 days per decade. Water ...
Rising numbers of liver cancer in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities has led experts at Flinders University to call for more programs, including mobile liver clinics and ultrasound in rural and remote Australia.
The Australian study just published in international Lancet journal EClinicalMedicine reveals the survival difference was largely accounted for by factors other than Indigenous status - including rurality, comorbidity burden and lack of curative therapy.
The study of liver cancer, or Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), included 229 Indigenous and 3587 non-Indigenous HCC cases in South Australia, Queensland and the ...
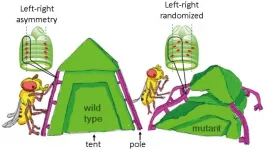
Osaka, Japan - On the outside, animals often appear bilaterally symmetrical with mirror-image left and right features. However, this balance is not always reflected internally, as several organs such as the lungs and intestines are left-right (LR) asymmetrical. Researchers at Osaka University, using an innovative technique for imaging movement of cell nuclei in living tissue, have determined the patterns of nuclear alignment responsible for LR-asymmetrical shaping of internal organs in the developing embryo.
Embryogenesis involves complex genetic and molecular processes that transform a single-celled zygote into a complete, living individual with multiple functional axes, including the LR axis. A long-standing conundrum of Developmental ...
Researchers at the University of Helsinki and the Beatson Institute for Cancer Research in Glasgow have discovered how mutated cells promote their chances to form cancer. Typically, the accumulation of harmful cells is prevented by active competition between multiple stem cells in intestinal glands, called crypts.
"The functioning of intestinal stem cells relies on growth factors, named Wnts, produced by the surrounding environment. Intestinal cancers typically originate from stem cells where mutations allow growth independent of these factors. When we removed a gene called Notum, which renders Wnts inactive, from mutated stem cells, the number of precancerous adenomas in the intestine was greatly reduced. We found that ...
Echoing through history by reviving fungal specimens originally preserved and described a flabbergasting quarter of a millenium ago by the "Father of Modern Taxonomy" Carl Linnaeus, this study highlights the untapped potential of museum collections in modern research programmes. The results have just been published in the renowned Cell Press journal iScience.
The "desert coprinus" fungus Podaxis has fascinated scientists and explorers for centuries, still the genus has been subjected to relatively little research. These large mushrooms thrive in hostile and mostly species-free environments and while they occur seasonally ...
Hypertension is a widespread comorbidity of patients with obesity that greatly increases the risk of mortality and disability. In recent years, researchers have found that a high-calorie diet increases the density of blood vessels (hypervascularization) in the hypothalamus - an important "eating control" area in our brain. Researchers hypothesized that elevated hormone levels of leptin are associated with a higher risk of developing hypertension. However, the exact mechanisms that contribute to the condensed growth of blood vessels in the hypothalamus were unknown.
New research conducted by Cristina García-Cáceres' research group at Helmholtz Zentrum ...
Solar activities, such as CME(Coronal Mass Ejection), cause geomagnetic storm that is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere. Geomagnetic storms can affect GPS positioning, radio communication, and power transmission system. Solar explosions also emit radiation, which can affect satellite failures, radiation exposure to aircraft crew, and space activity. Therefore, it is important to understand space weather phenomena and their impact on the Earth.
Space weather research by continuous observation of cosmic rays on the ground is mainly conducted using observation data from neutron monitors and multi-directional muon detectors. Since the phenomenon of space weather is on a short-term, days-long scale, it is effective to investigate changes in the flow ...
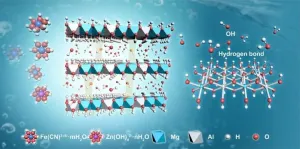
Alkaline zinc-iron flow battery (AZIFB) is well suitable for stationary energy storage applications due to its advantages of high open-cell voltage, low cost, and environmental friendliness. However, it surfers from zinc dendrite/accumulation and relatively low operation current density.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LI Xianfeng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS) developed layered double hydroxide (LDH) membrane with high hydroxide conductivity and ion selectivity for alkaline-zinc iron flow battery.
The ...
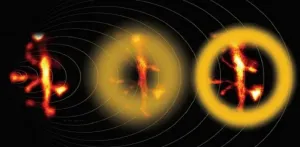
Light--and all waves--can bend around the corners of obstacles found along its path. Because of this phenomenon, called diffraction, it is impossible to focus light onto a spot that is smaller than half its wavelength. In other words, the highest resolution one can theoretically achieve using an optical microscope is approximately 250 nm, a barrier called the diffraction limit. Unfortunately, this resolution is not enough for observing fine cellular structures, such as those found in neurons.
Over more than a century, microscopists were hamstrung by this classic barrier until the invention of super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. One particularly powerful ...