(Press-News.org) Thirty state-of-the-art IPCC-climate models predict dramatically different climates for the Northern Hemisphere, especially Europe. An analysis of the range of responses now reveals that the differences are mostly down to the individual model's simulations of changes to the North Atlantic ocean currents and not only - as normally assumed - atmospheric changes. The work, by Katinka Bellomo, National Research Council of Italy, Institute of Atmospheric Sciences and Climate, and colleagues is published today in Nature Communications and is part of the European science collaboration, TiPES, coordinated by the University of Copenhagen.
All climate models vary in the details. Variables such as atmospheric pressure, cloud cover, temperature gradients, sea surface temperatures, and many more are tuned to interact slightly differently for every model. This means, the predictions of the many models also vary.
International modelling centers run a coordinated set of climate model simulations, which are then assessed by the IPCC and summarized in a balanced report. But naturally, an uncertainty remains, reflecting the many different tunings of models.
"We want to understand the differences among these models. Why does one model project an overall global temperature change of two degrees while another one of four degrees? Our objective is to narrow down this inter-model uncertainty. We also want to understand the differences in these models in terms of regional climate change," explains Dr. Katinka Bellomo.
Two types of climate scenarios
Bellomo and colleagues analyzed simulations from thirty different climate models and found an important difference. There is disagreement among the models on the rate of the decline in the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC), a large system of ocean currents in the North Atlantic which overturns surface water to a deep ocean current and plays a crucial role in the distribution of heat from the tropics to the Northern Hemisphere.
"To see how this difference was reflected in projections of the future climate, we grouped together the top ten models (from a total of thirty) in which the AMOC decline is smaller. We then compared the group with the average of the 10 models that have the largest decline," explains Bellomo.
The analysis revealed two distinct types of climate scenarios. In models where the AMOC decline is large, Europe warms only slightly, but wind patterns in Europe and precipitation patterns in the tropics change dramatically. However, in models where the AMOC decline is smaller, the Northern hemisphere heats up considerably, and a well-known pattern of wet-regions-get- wetter, dry-get-dryer emerges.
Tease mechanisms apart
This means, that the uncertainties in predictions of the future climate may to a large degree depend on how climate models predict changes in the overturning circulation in the North Atlantic. Thus, the result challenges the previous understanding of mechanisms controlling climate change over the North Atlantic, in which parameterizations of the atmosphere have been suspected to cause the main part of the uncertainty.
"This is important because it points to the AMOC as one of the largest sources of uncertainties in climate prediction," says Katinka Bellomo.
"I am excited about this research. Because there is so much more that can be done in addition to this. We need to investigate the processes leading to the inter-model differences in the ocean circulation response, the link between the ocean circulation response and precipitation change, and we also need to compare this with near-future projections of climate change," says Bellomo.
The TiPES project, investigating tipping points in the Earth system has received funding from the EU Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme.
INFORMATION:
Additional information:
Listen to the Tipes podcast - Katinka Bellomo explains her findings: https://www.tipes.dk/the-tipes-podcast-is-on-air/ (available when embargo lifts).
Visit the TiPES homepage Tipes.dk for more information on the TiPES project and and stories on tipping points in the Earth system.
The TiPES project is an EU Horizon 2020 interdisciplinary climate science project on tipping points in the Earth system. 18 partner institutions work together in more than 10 countries. TiPES is coordinated and led by The Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark. The TiPES project has received funding from the European Horizon 2020 research and innovation program, grant agreement number 820970.
A study led by Fernando Colchero, University of Southern Denmark and Susan Alberts, Duke University, North Carolina, that included researchers from 42 institutions across 14 countries, provides new insights into the aging theory "the invariant rate of ageing hypothesis", which states that every species has a relatively fixed rate of aging.
- Human death is inevitable. No matter how many vitamins we take, how healthy our environment is or how much we exercise, we will eventually age and die, said Fernando Colchero.
He is an expert in applying statistics and mathematics to population biology and an associate professor at Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Southern Denmark.
"We were able to shed light on the invariant rate of ageing hypothesis by combining ...
Teachers play a key role in supporting children's development in early childhood education classrooms such as Head Start. Research shows significant associations between teachers' depressive symptoms and their students' social and emotional development. However, little research has focused on the associations between teachers' depressive symptoms and academic outcomes of preschoolers from low-income families. Specifically, one important pathway that has not been examined is whether teacher depressive symptoms have implications for the quality of family-teacher relationships. This in turn could affect how supportive parents ...
An herbicide widely used in agriculture, forestry and other applications can cause deleterious effects on the reproductive health of a common perennial plant found in forests in British Columbia, Canada. Researchers reported in the journal END ...
Despite rapid development of electric vehicles (EVs), the safety of the lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries remains a concern as they are as a fire and explosion risk. Among the various approaches to tackle this issue, Korean researchers have used semiconductor technology to improve the safety of Li-ion batteries. A research team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) led by Dr. Joong Kee Lee of the Center for Energy Storage Research has succeeded in inhibiting the growth of dendrites, crystals with multiple branches that cause EV battery fires by forming protective semiconducting passivation layers on the surface of Li electrodes.
When ...
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (6/16/2021) - In unconventional superconductors, electrons often exhibit a tendency towards spatial ordering within their atomic structure.
In high-temperature superconductors, this comes in the form of the electronic structure exhibiting a pronounced difference in the lattice-bound directions along which atoms are ordered.
Within these materials, this electronic activity in turn breaks the rotational symmetry of the crystal, a phase known as electronic nematicity. Researchers have sought to better understand this novel electronic state, which co-exists with superconductivity.
Boston College Associate Professor of Physics Ilija Zeljkovic and an international team of researchers set out to better understand the atomic-scale signature ...
The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are found in oily fish. Researchers from the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre assessed the effects of high doses of EPA and DHA in lab-grown neurones and then in patients to help clarify how they reduce inflammation and depression. This novel approach allowed the scientists to identify an important molecular mechanism which can help inform the development of potential new treatments involving omega-3 fatty acids for patients with depression.
Lead author Dr Alessandra Borsini, NIHR Maudsley BRC Senior Postdoctoral ...
Killer whales have complex social structures including close "friendships", according to a new study that used drones to film the animals.
The findings show that killer whales spend more time interacting with certain individuals in their pod, and tend to favour those of the same sex and similar age.
The study, led by the University of Exeter and the Center for Whale Research (CWR), also found that the whales become less socially connected as they get older.
"Until now, research on killer whale social networks has relied on seeing the whales when they surface, and recording which whales are together," said lead author Dr Michael Weiss, of the University of Exeter.
"However, because resident killer whales stay in the social groups into which they're born, how closely related whales ...
The period preceding the emergence of behaviourally modern humans was characterised by dramatic climatic and environmental variability - it is these pressures, occurring over hundreds of thousands of years that shaped human evolution.
New research published today in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal proposes a new theory of human cognitive evolution entitled 'Complementary Cognition' which suggests that in adapting to dramatic environmental and climactic variabilities our ancestors evolved to specialise in different, but complementary, ways of thinking. ...
CHARLESTON, S.C. (June 15, 2021) - It's not every day that someone discovers a new-to-science bird migration spectacle. It's even more unexpected that such an encounter - in this case, tens of thousands of shorebirds gathering during their annual journey north - would be just a stone's throw from a metropolitan area. But two years ago, that's exactly what happened in coastal South Carolina.
In May 2019, South Carolina Department of Natural Resources (SCDNR) biologist Felicia Sanders and a team of researchers confirmed that approximately 20,000 whimbrel were roosting at night on a small island during their spring migration. The team documented similar numbers again in 2020. This single ...
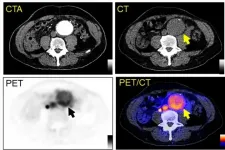
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 6:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 15, 2021)--A new positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer can detect abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) and potentially predict when they will rupture, according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting. Targeting a novel biomarker associated with AAA, the radiotracer is effective both in diagnosis and in providing information to assist in the development of AAA treatments, of which there currently are none.
AAA is a life-threatening degenerative vascular disease. It occurs when blood vessels weaken and ...