(Press-News.org) The period preceding the emergence of behaviourally modern humans was characterised by dramatic climatic and environmental variability - it is these pressures, occurring over hundreds of thousands of years that shaped human evolution.
New research published today in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal proposes a new theory of human cognitive evolution entitled 'Complementary Cognition' which suggests that in adapting to dramatic environmental and climactic variabilities our ancestors evolved to specialise in different, but complementary, ways of thinking.
Lead author Dr Helen Taylor, Research Associate at the University of Strathclyde and Affiliated Scholar at the McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research, University of Cambridge, explained: "This system of complementary cognition functions in a way that is similar to evolution at the genetic level but instead of underlying physical adaptation, may underlay our species' immense ability to create behavioural, cultural and technological adaptations. It provides insights into the evolution of uniquely human adaptations like language suggesting that this evolved in concert with specialisation in human cognition."
The theory of complementary cognition proposes that our species cooperatively adapt and evolve culturally through a system of collective cognitive search alongside genetic search which enables phenotypic adaptation (Darwin's theory of evolution through natural selection can be interpreted as a 'search' process) and cognitive search which enables behavioural adaptation.
Dr Taylor continued, "Each of these search systems is essentially a way of adapting using a mixture of building on and exploiting past solutions and exploring to update them; as a consequence, we see evolution in those solutions over time. This is the first study to explore the notion that individual members of our species are neurocognitively specialised in complementary cognitive search strategies."
Complementary cognition could lie at the core of explaining the exceptional level of cultural adaptation in our species and provides an explanatory framework for the emergence of language. Language can be viewed as evolving both as a means of facilitating cooperative search and as an inheritance mechanism for sharing the more complex results of complementary cognitive search. Language is viewed as an integral part of the system of complementary cognition.
The theory of complementary cognition brings together observations from disparate disciplines, showing that they can be viewed as various faces of the same underlying phenomenon.
Dr Taylor continued: "For example, a form of cognition currently viewed as a disorder, dyslexia, is shown to be a neurocognitive specialisation whose nature in turn predicts that our species evolved in a highly variable environment. This concurs with the conclusions of many other disciplines including palaeoarchaeological evidence confirming that the crucible of our species' evolution was highly variable."
Nick Posford, CEO, British Dyslexia Association said, "As the leading charity for dyslexia, we welcome Dr Helen Taylor's ground-breaking research on the evolution of complementary cognition. Whilst our current education and work environments are often not designed to make the most of dyslexia-associated thinking, we hope this research provides a starting point for further exploration of the economic, cultural and social benefits the whole of society can gain from the unique abilities of people with dyslexia."
At the same time, this may also provide insights into understanding the kind of cumulative cultural evolution seen in our species. Specialisation in complementary search strategies and cooperatively adapting would have vastly increased the ability of human groups to produce adaptive knowledge, enabling us to continually adapt to highly variable conditions. But in periods of greater stability and abundance when adaptive knowledge did not become obsolete at such a rate, it would have instead accumulated, and as such Complementary Cognition may also be a key factor in explaining cumulative cultural evolution.
Complementary cognition has enabled us to adapt to different environments, and may be at the heart of our species' success, enabling us to adapt much faster and more effectively than any other highly complex organism. However, this may also be our species' greatest vulnerability.
Dr Taylor concluded: "The impact of human activity on the environment is the most pressing and stark example of this. The challenge of collaborating and cooperatively adapting at scale creates many difficulties and we may have unwittingly put in place a number of cultural systems and practices, particularly in education, which are undermining our ability to adapt. These self-imposed limitations disrupt our complementary cognitive search capability and may restrict our capacity to find and act upon innovative and creative solutions."
"Complementary cognition should be seen as a starting point in exploring a rich area of human evolution and as a valuable tool in helping to create an adaptive and sustainable society. Our species may owe our spectacular technological and cultural achievements to neurocognitive specialisation and cooperative cognitive search, but our adaptive success so far may belie the importance of attaining an equilibrium of approaches. If this system becomes maladjusted, it can quickly lead to equally spectacular failures to adapt - and to survive, it is critical that this system be explored and understood further."
INFORMATION:
CHARLESTON, S.C. (June 15, 2021) - It's not every day that someone discovers a new-to-science bird migration spectacle. It's even more unexpected that such an encounter - in this case, tens of thousands of shorebirds gathering during their annual journey north - would be just a stone's throw from a metropolitan area. But two years ago, that's exactly what happened in coastal South Carolina.
In May 2019, South Carolina Department of Natural Resources (SCDNR) biologist Felicia Sanders and a team of researchers confirmed that approximately 20,000 whimbrel were roosting at night on a small island during their spring migration. The team documented similar numbers again in 2020. This single ...
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 6:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 15, 2021)--A new positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer can detect abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) and potentially predict when they will rupture, according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting. Targeting a novel biomarker associated with AAA, the radiotracer is effective both in diagnosis and in providing information to assist in the development of AAA treatments, of which there currently are none.
AAA is a life-threatening degenerative vascular disease. It occurs when blood vessels weaken and ...
Persisting symptoms thought to be complex interplay between effects of new injury and underlying conditions
Strict rest after a sports related concussion slows recovery and may prolong symptoms, says a consensus statement drawn up by a US expert panel on how best to treat and manage the condition, and published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Most of these concussions get better within a month and can be effectively treated, it says.
Persisting symptoms are thought to be a complex interplay between the physical and psychological effects of the new injury and underlying conditions.
The consensus statement was developed by the Team Physician Consensus Conference (TPCC), an annual project-based alliance of six major professional associations,* with the aim ...
A junk food diet may increase the risk of dangerous driving among truck/lorry drivers by boosting fatigue, which is often a key factor in vehicle collisions, suggests research published online in the journal Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Some 1.35 million people die in road traffic collisions every year, with professional drivers at greater risk because of the time they spend behind the wheel.
There are several known contributory factors, among which gender, age, experience, driving skills and attitudes seem to be important, note the researchers. But lifestyle ...
In a new study, North Carolina State University researchers demonstrated they could print layers of electrically conductive ink on polyester fabric to make an e-textile that could be used in the design of future wearable devices.
Since the printing method can be completed at room temperature and in normal atmospheric conditions, researchers believe inkjet printing could offer a simpler and more effective method of manufacturing electronic textiles, also known as e-textiles. In addition, researchers said the findings suggest they could extend techniques common in the flexible electronic industry to textile manufacturing. They reported their findings in the journal ACS Applied ...
New research from Syracuse University Newhouse School of Public Communications reveals a relationship between political biases and attitudes about sexual assault.
Authored by assistant professor Rebecca Ortiz and PhD student Andrea Smith, the article "A social identity threat perspective on why partisans may engage in greater victim blaming and sexual assault myth acceptance in the #MeToo era," was published in the peer-reviewed journal Violence Against Women.
Ortiz and Smith found that the stronger the partisan identity of Republicans and Democrats, the more likely they were to engage in victim blaming attitudes, which was then related to a lesser likelihood to perceive the #MeToo ...
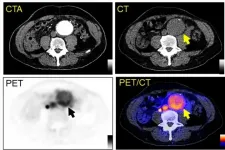
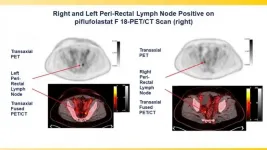
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 3:00 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 15, 2021)--A phase III clinical trial has validated the effectiveness of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radiotracer 18F-DCFPyL in detecting and localizing recurrent prostate cancer. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration last month, the radiotracer identified metastatic lesions with high positive predictive values regardless of anatomic region, adding to the evidence that PSMA-targeted radiotracers are the most sensitive and accurate agents for imaging prostate cancer. This study was presented at the ...
The demand for detecting infrared (IR) light, invisible to human eyes, is constantly growing, due to a wide variety of applications ranging from food quality control and remote sensing to night vision devices and lidar. Commercial IR cameras require the conversion of infrared light to electrons and the projection of the resultant image on a display. This display blocks the transmission of visible light, thereby disrupting normal vision. Moreover, such IR detectors require low temperature and even cryogenic cooling due to the low energies of the IR photons, making IR detectors bulky and heavy.
An all-optical alternative to traditional cameras is the use of a nonlinear optical process to convert IR light into visible. In this case, electrical signals are no ...
A new article analyzes Chile's transition in 1990 from dictatorship to democracy, the nature of democracy between 1990 and 2019, and the appearance of several social movements geared to expanding this democracy. The article, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), appears in The Latin Americanist, a publication of the Southeastern Council of Latin American Studies.
"Our goal is to locate the October 2019 protest movement in the context of Chile's very slow and incomplete transition to democracy, as well as amid social movements that have consistently challenged the economic ...
Dr. Igor Ivanishin, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harold Vance Department of Petroleum Engineering at Texas A&M University, has firsthand experience with the frustrations of oil production. He spent nine years as a hydraulic fracturing engineer with operating and service companies in Russia. A few years ago, he came to Texas A&M to get his doctoral degree while delving into a reoccurring recovery problem in carbonate reservoirs: why don't they produce oil as predicted?
Ivanishin is investigating variations in the chemical composition of dolomite and calcite ...