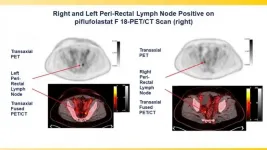
(Press-News.org) Reston, VA (Embargoed until 3:00 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 15, 2021)--A phase III clinical trial has validated the effectiveness of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radiotracer 18F-DCFPyL in detecting and localizing recurrent prostate cancer. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration last month, the radiotracer identified metastatic lesions with high positive predictive values regardless of anatomic region, adding to the evidence that PSMA-targeted radiotracers are the most sensitive and accurate agents for imaging prostate cancer. This study was presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) 2021 Annual Meeting.
Prostate cancer patients have high levels of PSMA expression, which makes PSMA an effective target for imaging the disease. In previous studies, the novel positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent 18F-DCFPyL was found to bind selectively with high affinity to PSMA. To demonstrate the diagnostic performance of 18F-DCFPyL for regulatory approval, a prospective, multicenter study was conducted in 14 sites across the United States and Canada.
The study sought to determine the positive predictive value (the probability that patients with a positive screening test actually have the disease) and detection rate of 18F-DCFPyL PET/computed tomography (CT) by anatomic region, specifically the prostate/prostate bed, pelvic lymph nodes, and regions outside the pelvis. Study participants included men who had rising prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels after local therapy as well as negative or equivocal conventional imaging results.
Patients were imaged with 18F-DCFPyL PET/CT, then imaged again after 60 days to verify suspected lesions using a composite "standard of truth," which consisted of histopathology, correlative imaging findings and PSA response. Comparing findings between the 18F-DCFPyL imaging and the "standard of truth," the positive predictive value and detection rate were measured.
18F-DCFPyL-PET/CT was found to successfully detect and pinpoint metastatic lesions with high positive predictive value, regardless of their location in the body, in men with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer who had negative or equivocal baseline imaging. Higher positive predictive values were observed in extra-pelvic lymph nodes and bone compared to soft tissue regions.
With the recent approval of 18F-DCFPyL (now referred to as piflufolastat F-18) by the FDA, the impact of this research may be realized in the very near future. As these agents become more widely available, patients with newly diagnosed, recurrent, and metastatic prostate cancer may have new therapeutic approaches available to them. The results of the study will be presented at the SNMMI meeting by Steven Rowe, MD, PhD, associate professor of radiology and radiological science at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland.
Abstract 123. "A Phase 3 study of 18F-DCFPyL-PET/CT in Patients with Biochemically Recurrent Prostate Cancer (CONDOR): An Analysis of Disease Detection Rate and Positive Predictive Value (PPV) by Anatomic Region," Steven Rowe and Michael Gorin, Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, Maryland; Lawrence Saperstein, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut; Frederic Pouliot, Departement de Chirurgie, Division d'Urologie, University of Quebec, Quebec, Canada; David Josephson, Tower Urology, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California; Peter Carroll, UCSF, San Francisco, California; Jeffrey Wong, City of Hope, Sierra Madre, California; Austin Pantel, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Morand Piert, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan; Kenneth Gage, Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Radiology, H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute, Tampa, Florida; Steve Cho, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wisconsin; Andrei Iagaru, Stanford University, Stanford, California; Janet Pollard, University of Iowa Hospital, Iowa City, Iowa; Vivien Wong, Jessica Jensen and Nancy Stambler, Progenics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., New York, New York; Michael Morris, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York; and Barry Siegel, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri.
INFORMATION:
All 2021 SNMMI Annual Meeting abstracts can be found online at https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/62/supplement_1.
About the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, vital elements of precision medicine that allow diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes.
SNMMI's members set the standard for molecular imaging and nuclear medicine practice by creating guidelines, sharing information through journals and meetings and leading advocacy on key issues that affect molecular imaging and therapy research and practice. For more information, visit http://www.snmmi.org.
The demand for detecting infrared (IR) light, invisible to human eyes, is constantly growing, due to a wide variety of applications ranging from food quality control and remote sensing to night vision devices and lidar. Commercial IR cameras require the conversion of infrared light to electrons and the projection of the resultant image on a display. This display blocks the transmission of visible light, thereby disrupting normal vision. Moreover, such IR detectors require low temperature and even cryogenic cooling due to the low energies of the IR photons, making IR detectors bulky and heavy.
An all-optical alternative to traditional cameras is the use of a nonlinear optical process to convert IR light into visible. In this case, electrical signals are no ...
A new article analyzes Chile's transition in 1990 from dictatorship to democracy, the nature of democracy between 1990 and 2019, and the appearance of several social movements geared to expanding this democracy. The article, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), appears in The Latin Americanist, a publication of the Southeastern Council of Latin American Studies.
"Our goal is to locate the October 2019 protest movement in the context of Chile's very slow and incomplete transition to democracy, as well as amid social movements that have consistently challenged the economic ...
Dr. Igor Ivanishin, a postdoctoral researcher in the Harold Vance Department of Petroleum Engineering at Texas A&M University, has firsthand experience with the frustrations of oil production. He spent nine years as a hydraulic fracturing engineer with operating and service companies in Russia. A few years ago, he came to Texas A&M to get his doctoral degree while delving into a reoccurring recovery problem in carbonate reservoirs: why don't they produce oil as predicted?
Ivanishin is investigating variations in the chemical composition of dolomite and calcite ...
CHAPEL HILL, NC - A group of scientists led by researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian reported that the Moderna mRNA vaccine and a protein-based vaccine candidate elicited durable neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in pre-clinical research. There were no adverse effects.
The research, published June 15 in Science Immunology, suggests that vaccines for young children are likely important, safe tools to curtail the pandemic.
The co-senior authors of the paper are Kristina De Paris, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at the UNC School ...
Instead of looking at the reasons child welfare caseworkers leave their jobs, Oregon State University researchers examined the common factors among workers who stay in the field, and what makes them feel most satisfied in their work.
In their recent study, researchers found that quality supervisory support and strong relationships with coworkers helped caseworkers feel appreciated and understood, while having adequate technology and equipment helped them manage their workload effectively
They hope child welfare agencies can use this information to support ...
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - Clinical evaluation of three COVID-19 vaccine candidates in 2020-21 during a worldwide pandemic that killed or sickened millions was unprecedented in terms of urgency and scope. Responsibility for the safety, integrity and scientific validity of the trials in the United States fell to 12 experts of the federally appointed COVID-19 Vaccine Data and Safety Monitoring Board, or COVID-19 DSMB, who in turn report to an oversight group.
This COVID-19 DSMB team -- which included co-contributing author Richard Whitley, M.D., distinguished professor of pediatrics in the University of Alabama ...
For the first time, researchers have used precariously-balanced rocks to set the formal design earthquake motions for a major existing engineered structure--the Clyde Dam, the largest concrete dam in New Zealand.
Mark Stirling of the University of Otago and colleagues identified and assessed the ages of these gravity-defying rock formations located about 2 kilometers from the dam site, using these data to determine the peak ground accelerations that the rocks could withstand before toppling.
This in turn was used to set the Safety Evaluation Earthquake (SEE) spectrum for the dam, or ...
An underwater archaeologist from The University of Texas at Arlington is part of a research team studying 9,000-year-old stone tool artifacts discovered in Lake Huron that originated from an obsidian quarry more than 2,000 miles away in central Oregon.
The obsidian flakes from the underwater archaeological site represent the oldest and farthest east confirmed specimens of western obsidian ever found in the continental United States.
"In this case, these tiny obsidian artifacts reveal social connections across North America 9,000 years ago," said Ashley Lemke, assistant professor of sociology and anthropology at UT Arlington. "The artifacts found below the Great Lakes come from a geological source in Oregon, 4,000 kilometers away---making it one of the longest distances ...
"So, no one told you life was going to be this way.
Your job's a joke, you're broke, you're love life's DOA.
It's like you're always stuck in second gear,
When it hasn't been your day, your week, your month, or even your year..."
If you have watched TV since the 1990s, the sitcom theme song, "I'll Be There for You," has likely been stuck in your head at one point or another. New research from UC Davis suggests these experiences are more than a passing nuisance -- they play an important role in helping memories form, not only for the song, but also related life events like hanging out with friends ...
When a fictional female journalist appears on screen, chances are she's about to sleep with one of her sources. It's a trope that infuriates actual women in news media -- and it can have real-life consequences, says University of Florida researcher Frank Waddell, Ph.D.
In shows like "House of Cards" and movies like "Thank You for Smoking," female reporters are quick to trade sex for information. Even when sex with sources has nothing to do with ambition -- such as the hookups in "Sharp Objects," "Top Five," "Trainwreck," and the "Gilmore Girls" reboot, to name a few -- it still portrays unethical behavior.
"In the past 20 to 30 years, Hollywood has really latched on to this. ...