(Press-News.org) When a fictional female journalist appears on screen, chances are she's about to sleep with one of her sources. It's a trope that infuriates actual women in news media -- and it can have real-life consequences, says University of Florida researcher Frank Waddell, Ph.D.
In shows like "House of Cards" and movies like "Thank You for Smoking," female reporters are quick to trade sex for information. Even when sex with sources has nothing to do with ambition -- such as the hookups in "Sharp Objects," "Top Five," "Trainwreck," and the "Gilmore Girls" reboot, to name a few -- it still portrays unethical behavior.
"In the past 20 to 30 years, Hollywood has really latched on to this. It's incredibly consistent," Waddell said.
At the same time, threats to female journalists have increased. A UNESCO study of 901 journalists from 125 countries shows that 73% experienced online harassment. And in a 2019 survey of women and gender non-conforming journalists in the United States and Canada, 70% experienced threats and 85% felt they had become less safe in past five years.
Waddell, an assistant professor in UF's College of Journalism and Communications, wanted to know who believes these sexist portrayals, as research shows we're most affected by media we perceive as realistic. In a study published in Journalism Studies, he was surprised to uncover no difference between men and women or liberals and conservatives, who tend to indicate lower levels of trust in mainstream media. Less surprising: People who already held sexist beliefs about women journalists found the portrayals believable. With repetition, Waddell explains, those views become more entrenched, creating a vicious cycle.
Understanding who falls for skewed portrayals of female journalists is the first step in finding solutions, he says.
"This is a very specific slice of the pie, but it's in the context of a larger conversation about declining trust in media overall," said Waddell, who is part of UF's multidisciplinary Consortium on Trust in Media and Technology.
In his original concept for the experiment, Waddell wanted to contrast reactions to sexist portrayals of women journalists in popular shows and movies with positive ones. He couldn't find any.
"I was actually struggling so badly to find positive examples that I couldn't do that part of the study," he said. ("Spotlight," the chronicle of the Boston Globe's reporting on child sex abuse in the Catholic church, is a rare exception, but Waddell was concerned that the subject matter could have skewed the data.)
Because most people have few, if any, first-hand encounters with reporters, Hollywood can have an outsized influence. Ways to counter that could include increased contact between regular folks and journalists, whether it's through town hall events, expanded social media interaction, or creative approaches to demystifying what goes on inside a newsroom, Waddell said.
"I'm also hoping that Hollywood can do a better job finding ways to dramatize the practice of journalism," he said. "People are treating women in the newsroom differently because they fail to recognize what they're seeing has nothing to do with real life."
INFORMATION:
A study of media coverage of 623 scientific papers on Alzheimer disease research conducted in mice reveals that the news media are more likely to write a story about alleged breakthroughs or medical research findings if research authors omit mice from their studies' titles. On the other hand, papers that acknowledge mice in their titles result in limited media coverage.
In addition, the study titled "What's not in the news headlines or titles of Alzheimer disease articles? #In mice" conducted by Dr Marcia Triunfol of Humane Society International and Dr Fabio Gouveia of the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Brazil, and published in PLoS ...
Discussions of a broken value system are ubiquitous in science, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic served to expose inequality globally. However, according to the authors of an article publishing 15th June 2021 in the open access journal PLOS Biology, science itself is not "broken," but it was built on deeply-entrenched, systemic sexist and racist values, which perpetuate biases through the continued focus on citation rates and impact factors.
The author maintain that while equity within science has advanced thanks to the tireless efforts of generations of systemically marginalized groups, the system remains outdated, colonialist, and patriarchal. ...
Financial toxicity, the financial strain experienced by patients accessing health care, impacts a large population of cancer patients according to prior research. A new study, published in JACC: CardioOncology, finds financial toxicity is often greater among heart disease patients compared to cancer patients, and those with both conditions suffer the highest burden.
"Heart disease and cancer are the leading causes of death in the United States, yet most research on financial toxicity has focused on cancer patients. It is important to consider that cancer patients may have short bursts of high expenditures for treatments, while heart disease patients are often incurring ...
The number of people dying from cardiovascular disease (CVD) in Asia is increasing rapidly, with over half of all CVD deaths globally in 2019 occurring in Asian countries, according to a state-of-the-art review paper published in the inaugural issue of JACC: Asia. The data demonstrates an urgent need to understand the burdens and epidemiological features of CVD in Asian countries to develop localized CVD prevention strategies to combat the epidemic.
From 1990 to 2019, the number of CVD deaths in Asia rose from 5.6 million to 10.8 million. Nearly 39% of these CVD deaths were premature, meaning they occurred in a person less than 70 years old, which was significantly higher than premature CVD deaths in the U.S. (23%). Most ...
There is increasing scrutiny around how science is communicated to the public, but what is the relationship between how scientists report their findings and how media reports it to the public? A study published in PLOS Biology by Marcia Triunfol at Humane Society International, in Washington, DC and Fabio Gouveia at Oswaldo Cruz Foundation in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil suggests that when authors of scientific papers omit the basic fact that a study was conducted in mice (and not in humans) from the article title, journalists reporting on the paper tend to do the same.
Alzheimer's Disease is an exclusively ...
What will the Earth be like for our children and grandchildren, as temperatures continue to rise? We can be fairly certain of some things: Some regions will become inhospitable, as heat drives their inhabitants away or causes massive declines and changes in their ecosystems. Many other physical, chemical and biological processes will also be affected by rising temperatures that threaten critical ecosystem services such as food production, biodiversity and energy security.
But what these changes will be and exactly how they impact the Earth -- and ultimately us humans -- are still difficult to predict. Many of them are so gradual and happen over such a long timescale that they wouldn't be noticeable ...
Federal agencies that regulate drug pricing and healthcare insurance are concerned that an industry practice of using rebates to lower drug costs for insurers has led to increases in list prices and out-of-pockets costs for patients.
To investigate whether patients with or without insurance were paying more because of rebates to insurers, researchers led by the University of Washington examined cost and price data on more than 400 branded drugs. The study found that rebates were associated with increases in out-of-pocket costs for patients by an average of $6 for those with commercial insurance, $13 for Medicare ...
In 1943, two scientists named Max Delbrück and Salvador Luria conducted an experiment to show that bacteria can mutate randomly, independent of external stimulus, such as an antibiotic that threatens a bacterial cells' survival. Today the Luria-Delbrück experiment is widely used in laboratories for a different purpose--scientists use this classic experiment to determine microbial mutation rates. When performing the Luria-Delbrück experiment, scientists need efficient computer algorithms to extract reliable estimates of mutation rates from data, and they also need well-designed software tools to access these sophisticated algorithms.
Through the years, several web tools that allow researchers to more easily input and analyze data on a computer were developed to increase ...
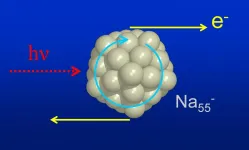
Photoemission is a property of metals and other materials that emit electrons when struck by light. Electron emission after light absorption was already explained by Albert Einstein. But since this effect is a highly complex process, scientists have still not been able to fully elucidate its details. Prof. Dr. Bernd von Issendorff and his team at the University of Freiburg's Institute of Physics have now succeeded in detecting a previously unknown quantum effect in the angular distributions of photoelectrons from cryogenic mass-selected metal clusters. ...
Washington, D.C. - June 15, 2021 - Viral genome sequencing of wastewater can provide an early warning system of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants that is independent of investigations of identified clinical cases, according to a new study published in mSystems, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. In the study, researchers describe the detection and quantification of variant B.1.1.7, first identified in southeast England, in sewage samples from London, United Kingdom before widespread transmission of this variant was obvious from clinical cases.
"Wastewater sampling and environmental surveillance ...