Semiconductor technology mitigates fire risk in electric vehicle batteries
Convergence of semiconductor physics and electrochemistry leads to effective inhibition of dendrite formation using semiconducting passivation layers
2021-06-16
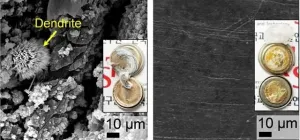
(Press-News.org) Despite rapid development of electric vehicles (EVs), the safety of the lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries remains a concern as they are as a fire and explosion risk. Among the various approaches to tackle this issue, Korean researchers have used semiconductor technology to improve the safety of Li-ion batteries. A research team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) led by Dr. Joong Kee Lee of the Center for Energy Storage Research has succeeded in inhibiting the growth of dendrites, crystals with multiple branches that cause EV battery fires by forming protective semiconducting passivation layers on the surface of Li electrodes.
When Li-ion batteries are charged, Li ions are transported to the anode (the negative electrode) and are deposited on the surface as Li metal; at this point, tree-like dendrites are formed. These Li dendrites are responsible for the uncontrollable volumetric fluctuations and leads to reactions between the solid electrode and the liquid electrolyte, which causes a fire. Unsurprisingly, this severely degrades battery performance.
To prevent dendrite formation, the research team exposed fullerene (C60), a highly electronic conductive semiconductor material, to plasma, resulting in the formation of semiconducting passivation carbonaceous layers between the Li electrode and the electrolyte. The semiconducting passivation carbonaceous layers allow Li-ions to pass through while blocking electrons due to generation of Schottky barrier, and by preventing electrons and ions from interacting on the electrode surface and inside, they stops the formation of Li crystals and the consequent growth of dendrites.
*fullerene : a particular physical form of carbon in which 60 carbon atoms are connected by single and double bonds in a pentagonal shape to form a soccer ball-like shape
The stability of the electrodes with the semiconducting passivation carbonaceous layers was tested using Li/Li symmetric cells in extreme electrochemical environments where typical Li electrodes remain stable for up to 20 charge/discharge cycles. The newly developed electrodes showed significantly enhanced stability, with Li dendrite growth suppressed for up to 1,200 cycles. Moreover, using a lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) cathode in addition to the developed electrode, approximately 81% of the initial battery capacity was maintained after 500 cycles, representing an improvement of approximately 60% over conventional Li electrodes.
Lead researcher Dr. Joong Kee Lee said, "The effective suppression of dendrite growth on Li electrodes is instrumental for improving battery safety. The technology for developing highly safe Li-metal electrodes proposed in this study provides a blueprint for the development of next-generation batteries that do not pose a fire risk." As Dr. Lee explains, his team's next goal is improving the commercial viability of this technology, "We aim to make the fabrication of the semiconducting passivation carbonaceous layers more cost-effective by substituting fullerene with less expensive materials."
INFORMATION:
This research was carried out as part of a KIST's institutional R&D project and a mid-career researcher project. It also received funding as an outstanding new overseas research project from the National Research Foundation of Korea with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). The results of this study are published in the latest issue of 'ACS Energy Letters' (IF: 19.003, Top 1.852% in JCR), a highly respected international journal in the field of materials science.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-16
Chestnut Hill, Mass. (6/16/2021) - In unconventional superconductors, electrons often exhibit a tendency towards spatial ordering within their atomic structure.
In high-temperature superconductors, this comes in the form of the electronic structure exhibiting a pronounced difference in the lattice-bound directions along which atoms are ordered.
Within these materials, this electronic activity in turn breaks the rotational symmetry of the crystal, a phase known as electronic nematicity. Researchers have sought to better understand this novel electronic state, which co-exists with superconductivity.
Boston College Associate Professor of Physics Ilija Zeljkovic and an international team of researchers set out to better understand the atomic-scale signature ...
2021-06-16
The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are found in oily fish. Researchers from the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre assessed the effects of high doses of EPA and DHA in lab-grown neurones and then in patients to help clarify how they reduce inflammation and depression. This novel approach allowed the scientists to identify an important molecular mechanism which can help inform the development of potential new treatments involving omega-3 fatty acids for patients with depression.
Lead author Dr Alessandra Borsini, NIHR Maudsley BRC Senior Postdoctoral ...
2021-06-16
Killer whales have complex social structures including close "friendships", according to a new study that used drones to film the animals.
The findings show that killer whales spend more time interacting with certain individuals in their pod, and tend to favour those of the same sex and similar age.
The study, led by the University of Exeter and the Center for Whale Research (CWR), also found that the whales become less socially connected as they get older.
"Until now, research on killer whale social networks has relied on seeing the whales when they surface, and recording which whales are together," said lead author Dr Michael Weiss, of the University of Exeter.
"However, because resident killer whales stay in the social groups into which they're born, how closely related whales ...
2021-06-16
The period preceding the emergence of behaviourally modern humans was characterised by dramatic climatic and environmental variability - it is these pressures, occurring over hundreds of thousands of years that shaped human evolution.
New research published today in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal proposes a new theory of human cognitive evolution entitled 'Complementary Cognition' which suggests that in adapting to dramatic environmental and climactic variabilities our ancestors evolved to specialise in different, but complementary, ways of thinking. ...
2021-06-16
CHARLESTON, S.C. (June 15, 2021) - It's not every day that someone discovers a new-to-science bird migration spectacle. It's even more unexpected that such an encounter - in this case, tens of thousands of shorebirds gathering during their annual journey north - would be just a stone's throw from a metropolitan area. But two years ago, that's exactly what happened in coastal South Carolina.
In May 2019, South Carolina Department of Natural Resources (SCDNR) biologist Felicia Sanders and a team of researchers confirmed that approximately 20,000 whimbrel were roosting at night on a small island during their spring migration. The team documented similar numbers again in 2020. This single ...
2021-06-16
Reston, VA (Embargoed until 6:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 15, 2021)--A new positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer can detect abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) and potentially predict when they will rupture, according to research presented at the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021 Annual Meeting. Targeting a novel biomarker associated with AAA, the radiotracer is effective both in diagnosis and in providing information to assist in the development of AAA treatments, of which there currently are none.
AAA is a life-threatening degenerative vascular disease. It occurs when blood vessels weaken and ...
2021-06-16
Persisting symptoms thought to be complex interplay between effects of new injury and underlying conditions
Strict rest after a sports related concussion slows recovery and may prolong symptoms, says a consensus statement drawn up by a US expert panel on how best to treat and manage the condition, and published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Most of these concussions get better within a month and can be effectively treated, it says.
Persisting symptoms are thought to be a complex interplay between the physical and psychological effects of the new injury and underlying conditions.
The consensus statement was developed by the Team Physician Consensus Conference (TPCC), an annual project-based alliance of six major professional associations,* with the aim ...
2021-06-16
A junk food diet may increase the risk of dangerous driving among truck/lorry drivers by boosting fatigue, which is often a key factor in vehicle collisions, suggests research published online in the journal Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Some 1.35 million people die in road traffic collisions every year, with professional drivers at greater risk because of the time they spend behind the wheel.
There are several known contributory factors, among which gender, age, experience, driving skills and attitudes seem to be important, note the researchers. But lifestyle ...
2021-06-16
In a new study, North Carolina State University researchers demonstrated they could print layers of electrically conductive ink on polyester fabric to make an e-textile that could be used in the design of future wearable devices.
Since the printing method can be completed at room temperature and in normal atmospheric conditions, researchers believe inkjet printing could offer a simpler and more effective method of manufacturing electronic textiles, also known as e-textiles. In addition, researchers said the findings suggest they could extend techniques common in the flexible electronic industry to textile manufacturing. They reported their findings in the journal ACS Applied ...
2021-06-15
New research from Syracuse University Newhouse School of Public Communications reveals a relationship between political biases and attitudes about sexual assault.
Authored by assistant professor Rebecca Ortiz and PhD student Andrea Smith, the article "A social identity threat perspective on why partisans may engage in greater victim blaming and sexual assault myth acceptance in the #MeToo era," was published in the peer-reviewed journal Violence Against Women.
Ortiz and Smith found that the stronger the partisan identity of Republicans and Democrats, the more likely they were to engage in victim blaming attitudes, which was then related to a lesser likelihood to perceive the #MeToo ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Semiconductor technology mitigates fire risk in electric vehicle batteries
Convergence of semiconductor physics and electrochemistry leads to effective inhibition of dendrite formation using semiconducting passivation layers