(Press-News.org) Magnetic-spin interactions that allow spin-manipulation by electrical control allow potential applications in energy-efficient spintronic devices.
An antisymmetric exchange known as Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) is vital to form various chiral spin textures, such as skyrmions, and permits their potential application in energy-efficient spintronic devices.
Published this week, a Chinese-Australia collaboration has for the first time illustrated that DMI can be induced in a layered material tantalum-sulfide (TaS2) by intercalating iron atoms, and can further be tuned by gate-induced proton intercalation.
REALIZING AND TUNING DMI IN VAN-DER-WAALS MATERIAL TaS2
Searching for layered materials that harbour chiral spin textures, such as skyrmions, chiral domain Walls is vital for further low-energy nanodevices, as those chiral spin textures are building blocks for topological spintronic devices and can be driven by ultra-low current density.
Generally, chiral spin textures are stabilized by DMI. Therefore, introducing and controlling DMI in materials is key in searching and manipulating the chiral spin textures.
"Tantalum-sulfide is one of the large family of transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDCs) investigated by FLEET for low-energy applications," says the study's first author, FLEET Research Fellow Dr Guolin Zheng (RMIT).
The team firstly successfully realized a sizable DMI in the layered material tantalum-sulfide (TaS2) by intercalating Fe atoms.
However, electrically controlling the DMI turns out to be challenging:
"Both conventional electric-field gating, and the widely-used alternative technique of ion-liquid (Li+) gating have hit stumbling blocks in the electrical control of DMI in itinerant ferromagnets, because the electric-field and Li+ can only modulate the carriers close to the surface," explains Guolin.
To address this limitation in tuning the DMI, the group at RMIT recently developed a new protonic gate technique, and successfully illustrated that DMI can be dramatically controlled by gate-induced proton intercalations.
By increasing the intercalation of protons by gate voltage, the team were able to significantly change the carrier density and further tune the DMI via the Ruderman-Kittel-Kasuya-Yosida (RKKY) mechanism, which refers to the coupling of nuclear magnetic moments.
"The observed topological Hall resistivity after proton intercalation has been increased more than four-fold under a few volts, indicating a huge increase of DMI," says co-author A/Prof Lan Wang (also at RMIT).
"The successful tuning of DMI in chiral magnet Fe-intercalated TaS2 by protonic gate enables an electrical control of the chiral spin textures as well as the potential applications in energy-efficient spintronic devices," says co-author Prof Mingliang Tian, who is a FLEET Partner Investigator and Director of the Centre's partner organisation the High Magnetic Field Laboratory (Anhui Province, China).
INFORMATION:
THE STUDY
"Tailoring Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction in a transition metal dichalcogenide by dual-intercalation" was published in Nature Communications in June 2021. (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23658-z)
As well as support from the END
WASHINGTON --Just a small number of cells found in tumors can enable and recruit other types of cells nearby, allowing the cancer to spread to other parts of the body, report END ...
It sounds like a plot from a Quentin Tarantino movie -- something sets off natural killers and sends them on a killing spree.
But instead of characters in a movie, these natural killers are part of the human immune system and their targets are breast cancer tumor cells. The triggers are fusion proteins developed by Clemson University researchers that link the two together.
"The idea is to use this bifunctional protein to bridge the natural killer cells and breast cancer tumor cells," said Yanzhang (Charlie) Wei, a professor in the College of Science's Department of Biological Sciences. "If the two cells are brought close enough together through this receptor ligand connection, the natural killer cells can release what I call killing machinery to have the tumor cells killed."
It's ...
A group of researchers from the University of Jyvaskyla and Stanford University were part of an expedition to French Guiana to study tropical frogs in the Amazon. Various amphibian species of this region use ephemeral pools of water as their nurseries, and display unique preferences for specific physical and chemical characteristics. Despite species-specific preferences, researchers were surprised to find tadpoles of the dyeing poison frog surviving in an incredible range of both chemical (pH 3-8) and vertical (0-20 m in height) deposition sites. This research was published in the journal Ecology and Evolution in June 2021.
Neotropical frogs are special because, unlike species in temperate regions, many tropical frogs ...
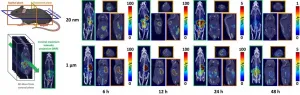
Postdoctoral Researcher Outi Keinänen from the University of Helsinki developed a method to radiolabel plastic particles in order to observe their biodistribution on the basis of radioactivity with the help of positron emission tomography (PET). As a radiochemist, Keinänen has in her previous radiopharmaceutical studies utilised PET imaging combined with computed tomography (CT), which produces a very accurate image of the anatomical location of the radioactivity signal.
In the recently completed study, radiolabelled plastic particles were fed to mice, and their elimination from the body was followed with PET-CT scans. This was the first time that ...
Research published today in the Journal of General Virology has identified missed cases of SARS-CoV-2 by retrospective testing of throat swabs.
Researchers at the University of Nottingham screened 1,660 routine diagnostic specimens which had been collected at a Nottingham hospital between 2 January and 11 March 2020 and tested for SARS-CoV-2 by PCR. At this stage of the pandemic, there was very little COVID-19 testing available in hospitals, and to qualify patients had to meet a strict criterion, including recent travel to certain countries in Asia or contact with a known positive case.
Three previously unidentified cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection were identified by the retrospective screening, including one from a 75-year-old ...
The phenomenon of quantum nonlocality defies our everyday intuition. It shows the strong correlations between several quantum particles some of which change their state instantaneously when the others are measured, regardless of the distance between them. While this phenomenon has been confirmed for slow moving particles, it has been debated whether nonlocality is preserved when particles move very fast at velocities close to the speed of light, and even more so when those velocities are quantum mechanically indefinite. Now, researchers from the University of Vienna, the Austrian Academy of Sciences and the Perimeter Institute report in the latest issue of Physical Review Letters that ...
Tokyo, Japan - Colloids--mixtures of particles made from one substance, dispersed in another substance--crop up in numerous areas of everyday life, including cosmetics, food and dyes, and form important systems within our bodies. Understanding the behavior of colloids therefore has wide-ranging implications, yet investigating the rotation of spherical particles has been challenging. Now, an international team including researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science has created particles with an off-center core or "eye" that can be tracked ...
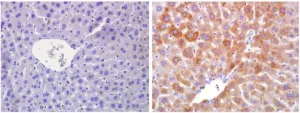
Getting energy and nutrients from the environment - that is, eating - is such an important function that it has been regulated through sophisticated mechanisms over hundreds of millions of years. Some of these mechanisms are only now beginning to be unravelled. A group at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) has found one of their key components - a switch that controls the ability of organisms to adapt to low cellular nutrient levels.
The protein involved is RagA, which is part of the mTOR molecular pathway, whose importance in metabolic activity regulation has been known for decades now. CNIO researchers have found that if RagA is continuously activated, cells do not know that there are no sufficient nutrients and so ...
The encryption algorithm GEA-1 was implemented in mobile phones in the 1990s to encrypt data connections. Since then, it has been kept secret. Now, a research team from Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB), together with colleagues from France and Norway, has analysed the algorithm and has come to the following conclusion: GEA-1 is so easy to break that it must be a deliberately weak encryption that was built in as a backdoor. Although the vulnerability is still present in many modern mobile phones, it no longer poses any significant threat to users, according to the researchers.
Backdoors not useful according to researchers
"Even though intelligence services and ministers of the interior understandably want such backdoors ...
ENVIRONMENT Diesel-polluted soil from now defunct military outposts in Greenland can be remediated using naturally occurring soil bacteria according to an extensive five-year experiment in Mestersvig, East Greenland, to which the University of Copenhagen has contributed.
Mothballed military outposts and stacks of rusting oil drums aren't an unusual sight in Greenland. Indeed, there are about 30 abandoned military installations in Greenland where diesel, once used to keep generators and other machinery running, may have seeped into the ground.
This is the case with Station 9117 Mestersvig, an abandoned military airfield ...