Sensitive and specific detecting biomarker of radiation-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma
2021-06-17
(Press-News.org) In a paper published in NANO, a team of researchers from Jiangnan University, China have prepared a convenient sensing platform which can detect microRNA-205 (MiR-205) with high sensitivity and excellent selectivity using TpTta-COF nanosheet and fluorescent oligonucleotide probes.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a kind of malignant cancer derived from the epithelial cells, which shows an apparent regional aggregation with a high prevalence in Southern China and Southeast Asia. With the ongoing improvement of radiotherapy technology, the therapeutic effect of NPC patients has been increased significantly. However, the easy recurrence and metastasis still cause the poor prognosis of NPC patients. Many researches indicated that radiation resistance may be a major obstacle leading to residual or recurring of tumor continues and it was also thought to be the main cause of treatment failure for NPC. An important attribute of MiR-205 is their potential use as predictive biomarker for anti-radiation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), and it is pivotal to monitor the dynamic change of MiR-205 for personalized precise treatment.
There are several methods aiming at detecting MiR-205 while rarely has worked out questions such as limited complex detection processes, poor sample detection limit or spending lots of time. Therefore, a method for detecting MiR-205 based on 2D COF nanosheets and fluorescent oligonucleotide probe was constructed and invested of the fluorescent single-stranded DNA (ss-DNA) probes through fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET).
2D COF materials could adsorb single-stranded DNA (ss-DNA) because of π?π stacking interaction. The fluorescence of the dyes will be quenched through fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Dye-labeled ss-DNA binds to 2D COF, and the fluorescence is recovered upon its specific interaction with the target biomolecules. The degree of fluorescence recovery is dependent on the conditions in the reaction environment, and it is also affected by the concentration of COF particles. By monitoring the fluorescence intensity of the biosensing platform, the concentration of target miRNA in the solution can be reflected, which indicated the feasibility of constructing the foundation for the quantitative determination of miRNA.
The results show that the method enables to capture MiR-205 sensitively in aqueous solution with a detection limit of 4.78 nM in the range 0-500 nM and R2= 0.989, and the method offers great specificity in that it can distinguish the target miRNA from mismatch non-target miRNAs. Considering its simple operability and excellent specificity, it has great application prospects in the detection of miRNA biomarker in clinical diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
INFORMATION:
This research was supported in part by the Top-notch Academic Programs Project of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PPZY2015B146), Wuxi Science and Technology Development Fund (N20192044), 2018 Innovative research team of Jiangsu Province, Construction project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging (18DZ2260400), and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (Class II Plateau Disciplinary Construction Program of Medical Technology of SUMHS, 2018-2020).
Corresponding authors for this study are Zhaoqi Yang (zhaoqiyang@jiangnan.edu.cn) and Gang Huang (huanggang@sumhs.edu.cn). Additional co-authors of the paper are Sen Li, Shaoxian Yin, Yanfei Cai and Jian Jin from Jiangnan University.
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-17
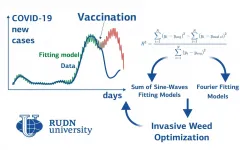
RUDN University mathematicians built a model of COVID-19 spreading based on two regression models. The mathematicians divided the countries into three groups, depending on the spreading rate and on the climatic conditions, and found a suitable mathematical approximation for each of them. Based on the model, the mathematicians predicted the subsequent waves. The forecast was accurate in countries where mass vaccination was not introduced. The results are published in Mathematics.
The epidemy spreading rate within the country depends, among other things, on the climatic ...
2021-06-17
In recent years, significant progress has been made towards the use of high-resolution peripheral computed tomography (HR-pQCT) imaging in research, and new potential for applications in the clinic have emerged, particularly with the advent of second generation devices.
A newly published state-of-the-art publication on the use and future directions of HR-PQCT provides a concise overview of current clinical applications as well as valuable guidance on the interpretation of results.
Specifically, it gives an overview of:
differences and reference data for HR-pQCT variables by age, sex, body composition and race/ethnicity;
fracture risk prediction using HR-pQCT, specifically in regard to bone microarchitecture in individuals ...
2021-06-17
AURORA, COLORADO, June 16, 2021 -- Foresight Diagnostics, the emerging leader in blood-based lymphoma disease monitoring, announced today that clinical performance of its minimal residual disease (MRD) detection platform in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) will be presented at the 16th International Conference on Malignant Lymphoma (ICML) on June 18-22, 2021. The oral presentation demonstrates the utility of Foresight Diagnostics' proprietary PhasED-Seq technology to improve MRD detection rates in DLBCL patients in low-disease burden settings.
"Foresight's MRD testing platform can detect relapsing disease 200 ...
2021-06-17
Cancer cells can develop resistance to therapy through both genetic and non-genetic mechanisms. But it is unclear how and why one of these routes to resistance prevails. Understanding this 'choice' by the cancer cells may help us devise better therapeutic strategies. Now, the team of Prof. Jean-Christophe Marine (VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology) shows that the presence of certain stem cells correlates with the development of nongenetic resistance mechanisms. Their study is published in the prestigious journal Cancer Cell.
Two routes to resistance
Even though cancer therapy has made great strides in the ...
2021-06-17
African American mothers continue to have the lowest breastfeeding rates, even as the breastfeeding rates have risen in the U.S. over the past 25 years. Racism is an important barrier to breastfeeding, as examined in Part 2 of a special issue on "Breastfeeding and the Black/African American Experience: Cultural, Sociological, and Health Dimensions Through an Equity Lens," published in the peer-reviewed journal Breastfeeding Medicine. Click here to read the issue now.
The special issue is led by Guest Editor Sahira Long, MD, a pediatrician and lactation consultant.
Exploring how racism creates barriers to breastfeeding for Black mothers and how Black women resist racism during their quest to breastfeed are Catasha Davis, PhD and Aubrey Van Kirk Villalobos, DrPH, Milken Institute School ...
2021-06-17
Since 2005, the guidelines for the care of unconscious cardiac arrest patients have been to cool the body temperature down to 33 degrees Celsius. A large, randomised clinical trial led by Lund University and Region Skåne in Sweden has shown that this treatment does not improve survival. The study is published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"These results will affect the current guidelines", says Niklas Nielsen, researcher at Lund University and consultant in anaesthesiology and intensive care at Helsingborg Hospital, who led the study.
In the early 2000s, two studies in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that induced hypothermia in unconscious cardiac arrest patients ...
2021-06-17
Conservationists have long warned of the dangers associated with bears becoming habituated to life in urban areas. Yet, it appears the message hasn't gotten through to everyone.
News reports continue to cover seemingly similar situations -- a foraging bear enters a neighbourhood, easily finds high-value food and refuses to leave. The story often ends with conservation officers being forced to euthanize the animal for public safety purposes.
Now, a new study by sustainability researchers in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science uses computer modelling to look at the best strategies to reduce human-bear conflict.
"It happens all the time, and unfortunately, humans are almost ...
2021-06-17
Research shows that inhibiting necroptosis, a form of cell death, could be a novel therapeutic approach for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an inflammatory lung condition, also known as emphysema, that makes it difficult to breathe.
Published in the prestigious American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, the study by a team of Australian and Belgian researchers, revealed elevated levels of necroptosis in patients with COPD.
By inhibiting necroptosis activity, both in the lung tissue of COPD patients as well as ...
2021-06-17
Electrons are ubiquitous among atoms, subatomic tokens of energy that can independently change how a system behaves--but they also can change each other. An international research collaboration found that collectively measuring electrons revealed unique and unanticipated findings. The researchers published their results on May 17 in Physical Review Letters.
"It is not feasible to obtain the solution just by tracing the behavior of each individual electron," said paper author Myung Joon Han, professor of physics at KAIST. "Instead, one should describe or track all the entangled electrons at once. This requires a clever way of treating this entanglement."
Professor Han and the researchers used a recently developed "many-particle" theory to account for the ...
2021-06-17
New UMD study suggests that everywhere tyrannosaurs rose to dominance, their juveniles took over the ecological role of medium-sized carnivores
A new study shows that medium-sized predators all but disappeared late in dinosaur history wherever Tyrannosaurus rex and its close relatives rose to dominance. In those areas--lands that eventually became central Asia and Western North America--juvenile tyrannosaurs stepped in to fill the missing ecological niche previously held by other carnivores.
The research conducted by Thomas Holtz, a principal lecturer in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sensitive and specific detecting biomarker of radiation-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma