Anthropogenic forcing increases drought risks in Southeast Asia
2021-06-17
(Press-News.org) Southeast Asian monsoon region falls in the warm and humid tropics modulated by Asian monsoon. It is home to nearly 15% of the world's tropical forests and one of the biodiversity hotspots in the world.
With the unprecedented urbanization and population growing rate, water scarcity issues have already posed a serious challenge for sustainable development in Southeast Asian monsoon region. However, the impact of anthropogenic forcing, such as greenhouse gases and anthropogenic aerosols, on extreme drought events in the region is still unclear.
Scientists from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics (IAP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the observed drought changes over Southeast Asian monsoon region and impacts of anthropogenic forcing using the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project phase 6 (CMIP6) models.
Their findings were published in Geophysical Research Letters on June 1.
They revealed an increasing drought risk for 1951-2018 due to more frequent and wide-spread droughts over the Southeast Asian monsoon region.
They also detected the influence of anthropogenic forcing, which has increased the likelihood of the extreme droughts in historical simulation by reducing precipitation and enhancing evapotranspiration.
The time of emergence (ToE) of anthropogenic forcing in extreme drought frequency and affected area firstly appeared around the 1960s. Even though drought risk will start to decrease since the 2030s in the future under the lowest emission scenario of CMIP6, the projected drought risks are still beyond the changes caused by nature alone.
"The impact of anthropogenic forcing on drought risk over Southeast Asia has already exceeded internal climate variability in the late 20th century. It is urgent to take actions to reduce anthropogenic aerosol loading and greenhouse gas emissions to reduce drought risks in Southeast Asia." Said Dr. Lixia Zhang, the lead author of the study.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-17
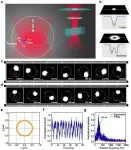
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have observed the absorption of a single electron by a levitated droplet with such a magnification that it is visible with the naked eye and can even be measured with a normal millimeter scaled ruler.
Matter in the universe is composed of elementary particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons. They are everywhere, but they are so small that the human eye cannot discern them. In the last century, physicists have proven the existence of these particles through different experiments, but in most cases the observation of the particles have been indirect.
- Electrons are one of these fundamental particles. In 1909, Robert Millikan proved that the charge of the electron is quantized. In other words, there exists a minimum, indivisible ...
2021-06-17
Researchers from Skoltech and Saratov State University have designed a simple and easily reproducible labeling system for individual cells that enables researchers to track single cell behavior and migration for tasks requiring extreme precision. The paper was published in the journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
Modern biomedical science and developmental biology often require scientists to track and trace individual cells, whether it is to establish the best purified cells from various types of cell lines, in particular to select mesenchymal stem/stromal cells best suited for tissue ...
2021-06-17
The production of chemicals is a cumbersome business. Often, only a small part of what is actually wanted is produced in the factory. The large remainder is unusable - or even worse. Examples? The defoliant "Agent Orange" used by the US army in the Vietnam War was produced in great hurry. It contained dioxin as an impurity. As a result, not only did trees in the combat zone lose their foliage, but US soldiers and Vietnamese civilians also fell ill with cancer years later.
There are also examples from agriculture: In the production of the insecticide lindane, ...
2021-06-17
As a new member of photovoltaic family, antimony trisulfide (Sb2S3) has the satisfactory bandgap of 1.7eV, benefiting the fabrication of the top absorber layer of tandem solar cells. Due to special quasi-one-dimensional structure, it shows advantages of less dangling bonds. Based on these advantages, the vacancy defects upon the surface causing the recombination of the carriers could be reduced sharply, which helps to solve the photovoltaic problems in solar cells.
In the previous studies, the relationships between conformation, chemical composition and ...
2021-06-17
Scientists have developed a new method that improves dispensing of viscoelastic fluids - a vital process for circuit board production, 3D printing and other industrial applications
Viscoelastic fluids are difficult to dispense as liquid bridges that form between the substrate and nozzle must be broken
New research has found that twisting these liquid bridges breaks them in a quicker and cleaner way than the conventional method of stretching them
Researchers used high speed imaging to observe that when twisted, a crack forms at the edge of the liquid bridge and propagates towards the center
The underlying mechanism that breaks the liquid bridge was found to be "edge fracture" and is the first time that ...
2021-06-17
During flock encounters, a single vocal interaction seems to be sufficient for making the decision of whether to recruit an individual or flock. Parrots are known for their splendid ability to imitate, including the contact calls of other individuals during vocal interactions. Such rapid vocal matching is hypothesised to precede and mediate the formation of new flocks. But how are such interactions perceived by others?
Heidi M. Thomsen, first author and PhD student at the Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen explains:
-"By using a novel experimental design, we were able ...
2021-06-17
Seiichi Shirai (1905-1983) was an influential architect whose work has affected the designs of significant architects of the 20th century. Associate Professor Kosuke Hato of the Department of Architecture, Faculty of Engineering, Shinshu University has studied the work of Shirai and examined why the architect worked extensively on calligraphy. Hato's strategy is to clarify the relationship between the architect and his activity of calligraphy through Shirai's Theory of Tradition.
The 1950s in Japan is known as a time when architects actively discussed traditions, and Shirai is a representative example. Hato, in his past article, clarified not only the ...
2021-06-17
Is it possible to drive nanoparticles to orbit below the light diffraction limit using a Gaussian beam? A recent joint research project reported in Nature Communications says yes.
It is well known that light possesses not only energy but also momentum. When light irradiates an object, momentum is transferred to the object, thus generating light pressure on the object. At the microscopic scale, microparticles and nanoparticles (such as biocells and macromolecules) can be manipulated by the light force. Atoms can be cooled by light pressure to achieve atomic clocks, Bose-Einstein condensation, and so on.
In addition to the linear momentum of light being transferable, the angular momentum of light can also be transferred to an object, thus causing object rotation. Since ...
2021-06-17
Tissue-engineering scaffolds built around ultrashort peptides provide a new platform for studying bone regeneration in the lab.
The peptides developed at KAUST self-assemble into a cartilage-like hydrogel that mimics the natural matrix that underpins bone formation in the body. Its physiologically relevant properties enable this cell-friendly biomaterial to support the growth and development of bone marrow precursor cells. It also enables tubular blood vessels to take shape, which is a critical part of bone health and repair.
"Our system is a simple, efficient and robust model that closely resembles the complex architecture of native bone tissue," says Ph.D. student Salwa Alshehri. "Using these peptide-based ...
2021-06-17
Thousands of years ago, archaic humans such as Neanderthals and Denisovans went extinct. But before that, they interbred with the ancestors of present-day humans, who still to this day carry genetic mutations from the extinct species.
Over 40 percent of the Neanderthal genome is thought to have survived in different present-day humans of non-African descent, but spread out so that any individual genome is only composed of up to two percent Neanderthal material. Some human populations also carry genetic material from Denisovans - a mysterious group of archaic humans that may have lived in Eastern Eurasia and Oceania ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Anthropogenic forcing increases drought risks in Southeast Asia