(Press-News.org) Nanodecoys made from human lung spheroid cells (LSCs) can bind to and neutralize SARS-CoV-2, promoting viral clearance and reducing lung injury in a macaque model of COVID-19. By mimicking the receptor that the virus binds to rather than targeting the virus itself, nanodecoy therapy could remain effective against emerging variants of the virus.
SARS-CoV-2 enters a cell when its spike protein binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on the cell's surface. LSCs - a natural mixture of lung epithelial stem cells and mesenchymal cells - also express ACE2, making them a perfect vehicle for tricking the virus.
"If you think of the spike protein as a key and the cell's ACE2 receptor as a lock, then what we are doing with the nanodecoys is overwhelming the virus with fake locks so that it cannot find the ones that let it enter lung cells," says Ke Cheng, corresponding author of the research. "The fake locks bind and trap the virus, preventing it from infecting cells and replicating, and the body's immune system takes care of the rest."
Cheng is the Randall B. Terry Jr. Distinguished Professor in Regenerative Medicine at North Carolina State University and a professor in the NC State/UNC-Chapel Hill Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering.
Cheng and colleagues from NC State and UNC-CH converted individual LSCs into nanovesicles, or tiny cell membrane bubbles with ACE2 receptors and other lung cell-specific proteins on the surface.
They confirmed that the spike protein did bind to the ACE2 receptors on the decoys in vitro, then used a fabricated SARS-Co-V-2 mimic virus for in vivo testing in a mouse model. The decoys were delivered via inhalation therapy. In mice, the nanodecoys remained in the lungs for 72 hours after one dose and accelerated clearance of the mimic virus.
Finally, a contract research organization conducted a pilot study in a macaque model and found that inhalation therapy with the nanodecoys accelerated viral clearance, and reduced inflammation and fibrosis in the lungs. Although no toxicity was noted in either the mouse or macaque study, further study will be necessary to translate this therapy for human testing and determine exactly how the nanodecoys are cleared by the body.
"These nanodecoys are essentially cell 'ghosts,' and one LSC can generate around 11,000 of them," Cheng says. "Deploying millions of these decoys exponentially increases the surface area of fake binding sites for trapping the virus, and their small size basically turns them into little bite-sized snacks for macrophages, so they are cleared very efficiently."
The researchers point out three other benefits of the LSC nanodecoys. First, they can be delivered non-invasively to the lungs via inhalation therapy. Second, since the nanodecoys are acellular - there's nothing living inside - they can be easily preserved and remain stable longer, enabling off-the-shelf use. Finally, LSCs are already in use in other clinical trials, so there is an increased likelihood of being able to use them in the near future.
"By focusing on the body's defenses rather than a virus that will keep mutating we have the potential to create a therapy that will be useful long-term," Cheng says. "As long as the virus needs to enter the lung cell, we can keep tricking it."
The research appears in Nature Nanotechnology and was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the American Heart Association. Dr. Jason Lobo, pulmonologist at UNC-CH, is co-author of the paper.
INFORMATION:
Note to editors: An abstract follows.
"Cell-Mimicking Nanodecoys Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 and Mitigate Lung Injury in a Nonhuman Primate Model of COVID-19"
DOI: 10.1038/s41565-021-00923-2
Authors: Zhenhua Li, Zhenzhen Wang, Phuong-Uyen C. Dinh, Dashuai Zhu, Kristen D. Popowski, Halle Lutz, Shiqi Hu, Ke Cheng, North Carolina State University; Leonard J. Lobo, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill; Mark G. Lewis, Anthony Cook, Hanne Andersen, Jack Greenhouse, Laurent Pessaint, Bioqual, Inc.
Published: Online June 17, 2021 in Nature Nanotechnology
Abstract:
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has grown into a global pandemic, and no specific antiviral treatments have been approved to date. The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) plays a fundamental role in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis as it allows viral entry into host cells. Here we show that ACE2 nanodecoys derived from human lung spheroid cells (LSCs) can bind and neutralize SARS-CoV-2 and protect the host lung cells from infection. In mice, the nanodecoys were delivered via inhalation therapy and resided in the lungs for over 72 hours post-delivery. Furthermore, inhalation of nanodecoys accelerated clearance of SARS-CoV-2 mimics from the lungs, with no observed toxicity. In cynomolgus macaques challenged with live SARS-CoV-2, four doses of nanodecoys delivered by inhalation promoted viral clearance and reduced lung injury. Our results suggest that LSC-nanodecoys can serve as a potential therapeutic agent for treating COVID-19.
Current approaches for planning relocation for potentially millions of people affected by climate change and related risks are "woefully inadequate" and risk worsening societal inequities, experts wrote in a policy perspective on June 17 in Science. Policymakers and scientists need to rethink how they work together to develop, communicate and carry out relocation plans.
"Relocation involves moving people away from risk and into totally new settings," said the team of experts led by Richard Moss. Moss is a Gerhard R. Andlinger Visiting Fellow at Princeton's Andlinger Center ...
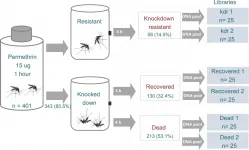
The Yellow fever mosquito (scientific name, Aedes aegypti) spreads multiple untreatable viruses in humans and is primarily controlled using a pesticide called permethrin. However, many mosquitoes are evolving resistance to the pesticide. A new study by Karla Saavedra-Rodriguez of Colorado State University and colleagues, published in the journal PLOS Genetics, identifies mutations linked to different permethrin resistance strategies, which threaten our ability to control disease outbreaks.
When treated mosquitoes encounter permethrin in the wild, they will do one of the following: immediately die, be knocked out but recover, or be unaffected. Saavedra-Rodriguez and her colleagues decided to investigate the genetic variations that lead to these ...
A new treatment approach focused on fixing cell damage, rather than fighting the virus directly, is effective against SARS-CoV-2 in lab models.
Combination of two drugs reduces spread of SARS-CoV-2 infection in cells by up to 99.5%.
If found safe for human use, this anti-viral treatment would make
COVID-19 symptoms milder and speed up recovery times.
When a person is infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, it invades their cells and uses them to replicate - which puts the cells under stress. Current approaches to dealing with infection target the virus itself with antiviral drugs. But ...
Patents with all-female inventor teams are more likely than all-male teams to address problems that specifically or disproportionately affect women, according to a new study. The findings, derived from an analysis of more than 440,000 U.S. biomedical patents filed from 1976 to 2010, suggest that who benefits most from innovation largely depends on who gets to invent. While the gender gap in research and innovation is well known, its broader impact on what gets invented - and for whom - isn't well understood. To address this question, Rembrand Koning and colleagues used machine learning text analysis to evaluate all U.S. biomedical patents filed from 1976 to 2010. They found that patents ...
Daunting and uncertain is the future for people who must decide whether, where, when, and how to vacate their homes as the climate changes. Communities who will absorb this influx of uprooted people also face challenges. In a special issue of Science, "Fallback Strategies: Planning for Climate-Induced Relocation," experts examine ways in which interdisciplinary basic and applied research can - and must - engage with and support communities and governments navigating this landscape. As this work is done, "we must consider not only what science can do, but how science ...
Using LIGO's suspended mirrors, researchers have demonstrated the ability to cool a large-scale object - the 10-kilogram optomechanical oscillator the suspended mirrors form - to nearly the motional quantum ground state. Upgrading LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) with such a modification would not only increase the device's sensitivity and range in detecting gravitational waves but could also provide new insights into large-scale quantum phenomena. For most mechanical objects to be coaxed into a quantum state, they need to be cooled to exceedingly low temperatures to overcome the thermal vibrations, or phonons, that mask the signature of quantum motion. This brings the ...
Marine-terminating glaciers may be less vulnerable to rapid and irreversible collapse than previously suggested, according to a new study, which finds that ice cliff collapse is limited by upstream thinning of the ice sheet and how quickly calved icebergs and sea-ice float away. The glaciers of Greenland and Antarctica slowly flow to the sea, terminating in massive vertical ice cliffs. Occasionally, these partially submerged margins can collapse under their own weight and trigger rapid disintegration of ice sheets. It's thought that this process, called marine ice cliff instability (MICI), could lead to the catastrophic retreat of some of the planet's largest ice sheets, substantially contributing to global sea level rise. However, current ...
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- To the human eye, most stationary objects appear to be just that -- still, and completely at rest. Yet if we were handed a quantum lens, allowing us to see objects at the scale of individual atoms, what was an apple sitting idly on our desk would appear as a teeming collection of vibrating particles, very much in motion.
In the last few decades, physicists have found ways to super-cool objects so that their atoms are at a near standstill, or in their "motional ground state." To date, physicists have wrestled small objects such as clouds of millions of atoms, or nanogram-scale objects, into such pure quantum states.
Now for the first time, scientists at MIT and elsewhere have cooled a large, human-scale object to close to its motional ground state. The object ...
Research conducted by Qiang et al has discovered a link between a protein in red blood cells and age-related decline in cognitive performance. Published in the open access journal PLOS Biology on 17th June 2021, the study shows that depleting mouse blood of the protein ADORA2B leads to faster declines in memory, delays in auditory processing, and increased inflammation in the brain.
As life expectancies around the world increase, so are the number of people who will experience age-related cognitive decline. Because the amount of oxygen in the blood also declines with age, the team hypothesized that ...
CLEVELAND--Case Western Reserve University researchers studying prions--misfolded proteins that cause lethal incurable diseases--have identified for the first time surface features of human prions responsible for their replication in the brain.
The ultimate goal of the research is to help design a strategy to stop prion disease in humans--and, ultimately, to translate new approaches to work on Alzheimer's and other neurodegenerative diseases.
Scientists have yet to discover the exact cause of Alzheimer's disease, but largely agree that protein issues play a role in its emergence and progression. Alzheimer's disease afflicts more than 6 million people in the U.S., and the Alzheimer's Association ...