INFORMATION:
* - Also involved in this work were scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Germany), the Centre Suisse de recherches scientifiques Taï Chimpanzee Project (Ivory Coast Harvard University (USA), the University of Stirling (UK), Florida International University (USA), the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF; Central African Republic), the Robert Koch Institute (Germany) and l'Université Félix Houphouët (Ivory Coast).
** - Working at l'Institut des sciences cognitives Marc Jeannerod (CNRS/Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1)
Orphaned chimpanzees do not suffer from chronic stress
2021-06-18
(Press-News.org) The loss of a loved one can be a defining moment, even in the animal world. In chimpanzees, for example, individuals whose mothers die when they are young are smaller than their counterparts, reproduce less and are also more likely to die at a young age. But why? To find out, an international research team* led by a CNRS researcher** studied the short- and long-term effects of maternal loss on the stress levels of orphaned chimpanzees over a 19-year period. By comparing the levels of a stress hormone marker, cortisol, between young and adult orphans and non-orphans, the scientists found that young orphans were highly stressed; however, those who had lost their mothers for more than two years or who were adults at the time of the study were no more stressed than other chimpanzees whose mothers were still alive. This means that they do not suffer from chronic stress, unlike in humans, where children whose mothers die when they are very young are subject to chronic stress throughout their lives. According to the research team, chimpanzees often adopt young orphans, which could be one of several explanations why the stress of maternal loss does not persist. Since stress alone cannot explain the differences between orphans and non-orphans, the researchers now want to look at chimpanzee mothers to see whether they contribute to these differences, for example whether mothers offer protection to offspring that is not available to orphans. The results of this work were published in eLife on 16 June 2021.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Start-stop system of hunting immune cells
2021-06-18
The body is well protected against invading pathogens by barriers such as the skin. But if you injure yourself and break your skin, pathogens can easily enter your body through the wound and cause severe infections. If this occurs, the innate immune system takes over the first rapid defense with an effective arsenal of cellular weapons infiltrating the wounded tissue in large numbers. As one of the first cell types on the spot, neutrophil granulocytes are recruited within few hours from the bloodstream to the infection site to eliminate potential microbial invaders.
Swarming against infections
"Neutrophils are very efficient in hunting and ...
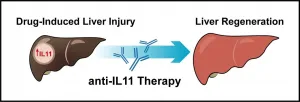
Blocking IL-11 signalling can help liver regenerate after injury from paracetamol toxicity
2021-06-18
Singapore, 18 Jun 2021 - Scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School and National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS), in collaboration with colleagues in Singapore and the UK, have shown that the human form of the signalling protein interleukin 11 (IL-11) has a damaging effect on human liver cells--overturning a prior hypothesis that it could help livers damaged by paracetamol poisoning. The finding, published last week in Science Translational Medicine, suggests that blocking IL-11 signalling could have a restorative effect.
Paracetamol, also called acetaminophen, is a widely available over-the-counter painkiller, and an overdose can lead to serious liver damage and even death. It is the most common pharmaceutical ...
Cognitive care using medicinal plant peptides
2021-06-18
Most of us have heard of Alzheimer's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder marked by brain cell death and the shrinking of the brain. It is the most common cause of dementia and cognitive impairment, which typically have a devastating effect on a person's quality of life. There is still no cure for Alzheimer's.
One way of tackling the progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is to prevent the underlying adverse changes in the brain. A team of researchers from the National Centre for Biological Sciences (NCBS) has recently published a study in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, dedicated to neuroprotection against these toxic changes. They used tiny free-living soil worms --called Caenorhabditis elegans--and the often-ornamental ...
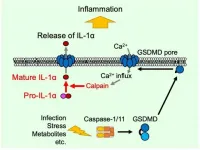
A key player in cell death moonlights as a mediator of inflammation
2021-06-18
Kanazawa, Japan - Interluekin-1α (IL-1α) is an important part of the immune response, but until now it has been unclear how this molecule is processed from its precursor, pro-IL-1α, and exits the cell during inflammasome activation. Now, researchers from Japan have found that gasdermin D, a protein that was already known to mediate pyroptosis, a form of regulated cell death, plays a crucial role in the maturation and release of IL-1α.
In a study published in March in Cell Reports, researchers from Kanazawa University report that, when the ...
Separating natural and man-made pollutants in the air
2021-06-18
COVID-19 has changed the world in unimaginable ways. Some have even been positive, with new vaccines developed in record time. Even the extraordinary lockdowns, which have had severe effects on movement and commerce, have had beneficial effects on the environment and therefore, ironically, on health. Studies from all around the world, including China, Europe and India, have found major drops in the level of air pollution. However, to fully understand the impact of anthropogenic causes, it is important to separate them from natural events in the atmosphere like wind flow.
To demonstrate this point, a new study by researchers at the Research Institute for Humanity and Nature, Japan, uses satellite data and mathematical modeling to explain just ...
Researchers review data on reputed toxins thought to cause neurodegeneration
2021-06-18
Identifying the causes of human neurodegenerative diseases is a global research priority, warranting frequent reviews of the accumulating knowledge. In doing just that, biologists from the Plant Physiology Laboratory at the University of Guam and neuroscientists from the Experimental Medicine Program at The University of British Columbia have published an update on the reputed environmental toxins that have been suspected of being involved in mammal neurodegeneration. Their summary was published in April in the book Spectrums of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, which is available online ...
Moderate and vigorous physical activity attenuate arterial stiffening already in children
2021-06-18
According to a recent Finnish study, higher levels of moderate and vigorous physical activity can curb arterial stiffening already in childhood. However, sedentary time or aerobic fitness were not linked to arterial health. The results, based on the ongoing Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children (PANIC) Study conducted at the University of Eastern Finland, were published in the Journal of Sports Sciences. The study was made in collaboration among researchers from the University of Jyväskylä, University of Eastern Finland, the Norwegian School of Sport sciences, and the University of Cambridge.
Arterial stiffening predisposes to heart diseases, ...
Earlier flood forecasting could help avoid disaster in Japan
2021-06-18
Tokyo, Japan - In Japan, thousands of homes and businesses and hundreds of lives have been lost to typhoons. But now, researchers have revealed that a new flood forecasting system could provide earlier flood warnings, giving people more time to prepare or evacuate, and potentially saving lives.
In a study published this month in Scientific Reports, researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science have shown that a recently developed flood forecasting system provides much earlier advance warnings of extreme flooding events than current systems. ...
Dragonflies: Species losses and gains in Germany
2021-06-18
Germany is a hotspot for dragonflies and damselflies (Odonata) species in Europe, owing to the range of habitats and climates that it provides. While many recent and mostly small-scale studies suggest long-term declines of insect populations in different parts of Europe, studies of freshwater insects - including dragonflies and damselflies - suggest that some species have increased in occurrence. Researchers of iDiv, FSU and UFZ have now provided a nationwide analysis of the occurrence and distribution of dragonflies and damselflies in Germany between 1980 and 2016. For this, they analysed over 1 million occurrence records on 77 species from different regional ...
Cells optimised to produce substance that holds potential to improve 'healthy ageing'
2021-06-18
The population on Earth is increasingly growing and people are expected to live longer in the future. Thus, better and more reliable therapies to treat human diseases such as Alzheimer's and cardiovascular diseases are crucial. To cope with the challenge of ensuring healthy ageing, a group of international scientists investigated the potential of biosynthesising several polyamines and polyamines analogues with already known functionalities in treating and preventing age-related diseases.
One of the most interesting molecules to study was spermidine, which is a natural product already present in people's blood and an inducer of autophagy that is an essential cellular process for clearing damaged proteins, e.g., misfolded proteins ...