Study suggests blood test could guide precision treatment in bladder cancer
A blood test that can detect tiny amounts of circulating cancer DNA may be able to identify risk of cancer recurrence and guide precision treatment in bladder cancer following surgery, according to a clinical study published in Nature
2021-06-21
(Press-News.org) A blood test that can detect tiny amounts of circulating cancer DNA may be able to identify risk of cancer recurrence and guide precision treatment in bladder cancer following surgery, according to a clinical study led by Professor Tom Powles from Queen Mary University of London and Barts Health NHS Trust. The findings from the study, published in Nature, may change our understanding of cancer care following surgery.
The study found that patients with urothelial cancer who had a particular cancer DNA marker in their blood following surgery to remove their tumour had a higher likelihood of cancer relapse. These patients could benefit from subsequent treatment with an immunotherapy called atezolizumab.
Globally, there were approximately 573,000 cases of and 212,000 deaths from bladder cancer in 2020. Surgery is often among the first treatments for advanced bladder cancer that has grown into the muscle layer of the bladder wall (muscle-invasive). However, relapse rates after surgery are high as some cancer cells can be left behind when the tumour is removed. These remaining cancer cells, known as molecular residual disease (MRD), increase the chances of a patient's cancer reoccurring as the cells can spread and establish tumours elsewhere in the body.
This study, funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd./Genentech, Inc, and Barts Cancer Institute/Queen Mary University of London evaluated treatment outcomes in a subgroup of patients (comprising 581 individuals) who were enrolled onto a randomised phase III trial (IMvigor010) and a phase II study (ABACUS) which investigated whether the drug atezolizumab could reduce cancer recurrence in high-risk muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma.
To identify patients with increased likelihood of MRD following surgery, a blood test was used to detect the presence or absence of circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) - tumour-derived fragments of genetic material that can escape into the bloodstream and are considered to be indicative of MRD. The team found that patients with ctDNA-positive blood tests after surgery were at higher risk of cancer recurrence than those who were ctDNA-negative.
Treatment with atezolizumab did not significantly improve disease-free survival (DFS; the length of time after treatment during which no sign of cancer is found) nor overall survival (OS) in the whole IMvigor010 study population; however, in the ctDNA-positive subgroup of patients evaluated in this study, treatment with atezolizumab compared with observation alone significantly improved DFS (5.9 vs 4.4 months) and OS (25.8 vs 15.8 months). The outcomes in patients who were ctDNA-negative did not appear to differ whether they received atezolizumab or not.
Lead researcher, Tom Powles, Professor of Genitourinary Oncology at Queen Mary's Barts Cancer Institute and Director of Barts Cancer Centre at Barts Health NHS Trust, said:
"These novel findings demonstrate ctDNA as a marker for residual disease and response to atezolizumab. We also found ctDNA measurement to be more accurate than traditional radiology at identifying disease relapse. These findings may change our understanding of post-surgical cancer care and, if validated in this setting as well as across tumour types, they may also change clinical practice."
It is difficult to determine which patients harbour MRD and which are cured after surgery. As a result, many patients who are cured by surgery are unnecessarily exposed to toxicities from additional treatments, and other patients with residual disease may not receive potentially beneficial treatment until disease progression is detectable by imaging. The findings from this study suggest that detection of ctDNA shortly after surgery may overcome these clinical limitations by enabling early identification of patients harbouring MRD.
Initiating personalised treatment based on the identification of MRD rather than treating unselected patients or waiting for relapse would be a significant change in cancer treatment. Further studies will now be required to validate and expand the clinical utility of this method, and to determine whether ctDNA measurement could aid in directing post-surgical treatment to those who need it.
INFORMATION:
Research paper: Powles, T., Assaf, Z.J., Davarpanah, N. et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature (2021). Available here: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03642-9
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-06-21
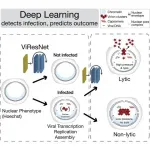
In humans, adenoviruses can infect the cells of the respiratory tract, while herpes viruses can infect those of the skin and nervous system. In most cases, this does not lead to the production of new virus particles, as the viruses are suppressed by the immune system. However, adenoviruses and herpes viruses can cause persistent infections that the immune system is unable to completely suppress and that produce viral particles for years. These same viruses can also cause sudden, violent infections where affected cells release large amounts of viruses, such that the infection spreads rapidly. This can lead to serious acute diseases of the lungs or nervous system.
Automatic detection of virus-infected cells
The research group of Urs ...
2021-06-21
The authors of new research say supporting children and young people's mental health is as important as supporting their academic progress, and that particular attention should be paid to the fact that some young people have struggled more than others.
Findings from their study, published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, focused on the connections between loneliness, social contact, parental relationships, and the mental health of adolescents aged 11-16 during the first full UK lockdown from March to May 2020.
Their analysis drew on self-reported data from 894 young people who each completed a survey throughout to gauge their experiences of lockdown and its effects on their emotions, relationships, and feelings.
The team from the universities of Bath, Bristol, ...
2021-06-21
Hypoxia, or the inadequate oxygenation of a tissue, is a condition occurring frequently in all solid tumours such as melanoma skin cancer. Melanoma cells are not only able to survive oxygen deprivation, but also to use it to their own advantage by hijacking the anti-tumour immune response and developing resistance mechanisms to conventional anti-cancer therapies. A key gene responsible for cancer cell adaptation to hypoxia is HIF-1α (Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 alpha). Led by Dr Bassam Janji, head of the Tumor Immunotherapy and Microenvironment (TIME) research group at the Luxembourg Institute ...
2021-06-21
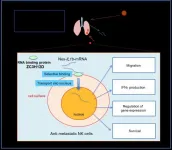
A research group led by Professor Sachie Hiratsuka, Institute for Biomedical Research, Shinshu University, has found that a specific sequence of messenger RNA (mRNA), which exists outside cells, binds to receptors on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells and is taken up into the nucleus. The group found that NK cells with mRNA uptake are able to enhance their migration activity and interferon gamma production. Furthermore, NK cells incorporating the mRNA showed an inhibitory effect on cancer metastasis in animal experiments.
In recent years, the results of cancer treatment have been improving with the increase of medical ...
2021-06-21
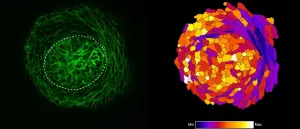
Helsinki University research group used live tissue imaging for the first time to visualise the emergence of the mammary gland.
Despite long-standing interest, the cellular mechanisms driving the initiation of mammary gland development have remained elusive for decades, mostly due to technical limitations in studying dynamic cell behaviors in live tissues. Recent advances in microscopic methods and availability of various mouse models allowed the research group of Marja Mikkola from HiLIFE Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki to address this question. This is the first time when live tissue imaging has been used to visualise the emergence of the mammary gland.
Mammary gland is the class-defining organ of mammals, yet we know surprisingly little how its ...
2021-06-21
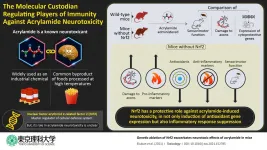
Acrylamide is a toxic chemical compound that affects the nervous system. Not only is it widely used in industries such as paper production, plastics, and wastewater management, but it is also a byproduct of commonly used food processing methods, which makes human exposure to acrylamide inevitable. Therefore, many studies have focused on understanding the toxic effects of acrylamide and our body's response to them. Generally, in response to toxicity, the body's cells release protective factors and antioxidants to remedy the damage. This response is activated by various cellular machinery. One such activator is a protein called "nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2" (Nrf2), ...
2021-06-21
Special diets, exercise programs, supplements and vitamins, there is everywhere something supposed to help us live longer. Whether it actually works has not always been shown, but the average life expectancy of people has increased over the last 150 years. A study by an international team of researchers, including Claudia Fichtel and Peter Kappeler, scientists in the Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology Unit at the German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research in Göttingen, indicates that we probably cannot slow down aging. The comparative studies with humans and non-human primates, indicates that it is not the rate at which humans age that slows ...
2021-06-21
Washington, DC, June 21, 2021 - Depression in youth, between the ages of 10 and 24 years, is both a leading cause of stress and a possible risk factor for future diseases and impairment. Now, a study in the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (JAACAP), published by Elsevier, confirms that depression in childhood or adolescence is associated with higher levels of adult anxiety and substance use disorders, worse health and social functioning, less financial and educational achievement, and increased criminality.
The findings are based on the Great Smoky Mountains Study, an ongoing longitudinal ...
2021-06-21
TEL AVIV, Israel and RALEIGH, NC, June 21, 2021, RedHill Biopharma Ltd. (Nasdaq: RDHL) ("RedHill" or the "Company"), a specialty biopharmaceutical company, today announced presentation of the positive Phase 2 safety and efficacy data for oral opaganib (Yeliva®, ABC294640) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 pneumonia at the World Microbe Forum (WMF) 2021 (poster #: 5574).
Results and post hoc analyses of data from the 40-patient U.S. Phase 2 study were presented in a poster entitled, "Opaganib, an Oral Sphingosine Kinase-2 (SK2) Inhibitor in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Phase 2A Study, in ...
2021-06-21
In 2013, François ENGLERT and Peter HIGGS won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the theoretical discovery of a mechanism that contributes to our understanding of the origin of mass of subatomic particles, which was confirmed through the discovery of the predicted fundamental particle by the A Toroidal LHC Apparatus (ATLAS) and the Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiments at The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)'s Large Hadron Collider in 2012. The Higgs mode or the Anderson-Higgs mechanism (named after another Nobel Laureate Philip W ANDERSON), has widespread influence ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study suggests blood test could guide precision treatment in bladder cancer
A blood test that can detect tiny amounts of circulating cancer DNA may be able to identify risk of cancer recurrence and guide precision treatment in bladder cancer following surgery, according to a clinical study published in Nature